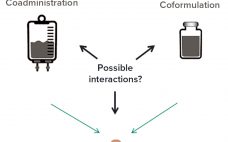
Coformulation of two or more proteins in a single formulation is an emerging approach to delivering multiple biotherapeutics that previously have been administered in sequence. This approach brings multiple benefits to all stakeholders. Foremost for patients, the primary benefits are combined therapeutic effects and improved convenience (e.g., fewer administration events). Healthcare providers see logistical benefits and decreased risk of medical errors. Additionally, coformulations also simplify manufacturing logistics, reduce costs of packaging and distribution, and provide new opportunities for product portfolio…
Manufacturing
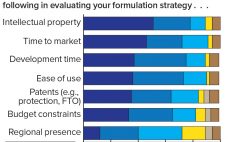
Early Stage Development of Advanced Formulations in the Drug Development Process Provides Competitive Advantages: Survey Predicts That Drug Product Formulation Recognition and Budgets Will Increase Significantly
New antibody formats and aggregate-prone, subcutaneously administered protein therapeutics present biopharmaceutical companies with major challenges regarding protein stability and aggregation. At the same time, protein stability often is not given enough attention in early stages of development. Protein aggregation reduces drug activity so that increasing doses are needed to achieve the same desired effect. Even worse, protein aggregates can induce immunogenecity that endangers patients and compromises product approval. A market study presented for the first time at the Bio-Europe 2018…
Recommended Practices for Assuring Integrity of Single-Use Systems
The increasing uptake of single-use technologies (SUTs) in critical current good manufacturing practice (CGMP) processes and applications has made their integrity a critical quality attribute (CQA) for both suppliers and end users of such systems. Current regulations focus on final packaging, however, without taking into account the unique aspects of assemblies used in bioproduction. Ongoing initiatives include revision of PDA TR 27 (1) and creation of A STM workstreams (2, 3) to propose good practices for the integrity of single-use…
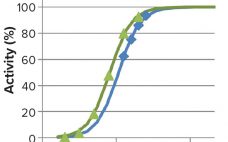
Apparent Matrix Effects in an Iduronate 2-Sulfatase Specific Activity Assay
The recombinant fusion protein SHP631 consists of a chimeric monoclonal antibody binding to human insulin receptor and iduronate-2-sulfatase (I2S). This product is being developed as an enzyme replacement therapy to treat cognitive symptoms of Hunter’s syndrome. Because the current therapy (idursulfase, brand name Elaprase from Shire) cannot cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB), SHP631 is being developed to do so, enabling the presence of I2S in the brain. The enzymatic activity of this molecule is measured using the substrate 4-methyl umbelliferyl-α-L-idopyranosiduronic…
Smart Modular Package Units for Single-Use Processing: Addressing Cost, Speed, and Flexibility Challenges in Biologics Manufacturing
How to reduce costs, while still increasing speed, and flexibility in biologics manufacturing currently represent major issues for the biopharma industry. In this article, Burkhard Joksch, Product Manager Bioprocess Automation and Stuart Tindal, Product Manager FlexAct® Platform at Sartorius Stedim Biotech GmbH, detail the evolution of automation for single-use technology towards modular packaging units. They also including case studies of how these units can be used in real life cGMP processes, as well as explain the manufacturing and industry benefits…
Continuous Chromatography: Experts Weigh in on the Possibilities and the Reality
Discussions of continuous processing in the biopharmaceutical industry are an important part of current efforts toward intensifying bioproduction and bioprocessing. Biomanufacturers are looking at all components of their development and manufacturing processes for ways to reduce the size of their facilities, lower costs, and increase speed and flexibility of operations. Increasing options for and availability of single-use technologies have been major enablers of myriad attempts to improve efficiencies. Although the general consensus may still be that single-use components are more…
Worldwide Biopharmaceutical CMO Capacity Analysis
Contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) are a core part of the biopharmaceutical industry, with commercial manufacturing making up about a third of marketed products. Here we examine worldwide CMO biopharmaceutical manufacturing (bioprocessing) capacity, concentrating on “mainstream” CMOs — defined as those providing primarily mammalian cell culture or microbial fermentation services for manufacture at any scale of proteins and antibodies. This analysis follows our recent article examining worldwide bioprocessing capacity status and trends (1). Survey Methodology The 2018 15th Annual Report and…
Partnerships in Immunotherapy for the Future of Cancer Treatment
Immunotherapy seeks to harness the power of our human immune system to fight disease. In this rapidly evolving field, collaboration among different stakeholders is essential to bringing new treatments to market. Patient advocacy groups, researchers, hospitals, manufacturers, and government entities all are working together to translate promising new research into life-saving products. Types of immunotherapy include monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) and antibody derivatives, checkpoint inhibitors (immune-modulating proteins), cancer vaccines, T-cell therapies, and cytokines — so the approach involves a range of…
Development of Large-Scale Bulk Freezing Systems
The biopharmaceutical industry is under pressure to generate value for shareholders and find innovative therapies while driving down development and manufacturing costs. As the industry considers more flexible and scalable production solutions for patients, new therapies will continue to be developed faster than ever before. These products will need to rely on robust and reliable manufacturing solutions. To deliver on that challenge, streamlining manufacturing processes will be necessary so that many lots of drug substances can be manufactured, stored, and/or…
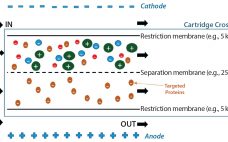
Tangential-Flow Electrophoresis: Investigation of Factors Involved in an Effective Separation of Human Serum Albumin from Human Plasma
Human plasma is a complex mixture of biomolecules such as serum albumin, immunoglobulins, coagulation factors, and others (1). These important protein biomolecules often are present at low levels or lacking in affected patients with certain life-threatening conditions. To extract those valuable proteins, a number of purification methods have been developed over time. Plasma fractionation can be traced back to the middle of the 20th century, when Edwin Cohn of Harvard University developed the first industrial process to purify proteins from…