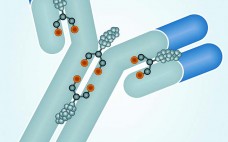
Antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) for treatment of cancer combine the tumor-targeting properties of antibodies with the cell-killing properties of cytotoxic drugs. By targeting a drug to a tumor, it is possible to reduce systemic toxicity and thereby enable administration of drugs that are otherwise too toxic to be effective therapies. Although the concept of an ADC is simple, in reality developing an effective treatment is somewhat more challenging. Whether an ADC has sufficient efficacy at a tolerable dose depends on four…
Sunday September 14, 2025