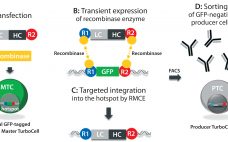
Most recombinant monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) are produced by mammalian cells. Because biopharmaceuticals derived from mammalian tissue culture carry the risk of adventitious virus contamination, regulatory agencies expect risk-mitigation strategies to include validation of purification unit operations for their ability to clear viruses (1). Guidelines from the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) describe how to prove viral clearance in downstream purification processes using an orthogonal approach (2). Viral log10 reduction values (LRVs) are…
Author Archives: Anja Trapp
Antibody–Drug Conjugates: Fast-Track Development from Gene to Product
In the fight against cancer, antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) represent an increasingly important therapeutic approach. These biopharmaceuticals are designed to maximize the therapeutic index of cytotoxic small-molecule drugs through their selective delivery to tumor cells while leaving normal, healthy cells untouched. Structurally, an ADC is a monoclonal antibody (MAb) conjugated by a chemical linker to a potent cytotoxic drug. Conceptually, the MAb serves as the delivery component, targeting a specific tumor antigen that ideally is not expressed (or is expressed at…