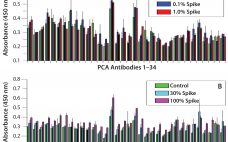
For protein therapeutics and other biologics, the importance of the molecule’s structure to its efficacy and safety is well established (1–5). In particular, their tertiary and quaternary structures play very important roles in product quality and have been monitored extensively in comparability studies (6–12). However, because of both the large molecular size and rotational property of amino acid α carbons, a protein can assume an enormous number of different conformations (13). For antibody-based biologics such as monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), fusion…
Monday October 27, 2025