Happy New Year! This is our first combined January–February issue, but it should give you plenty of reading material to compensate for the absence of a January issue. There are some new approaches at work for us this year that bring new opportunities for both end-user and supplier authors, as well as offering us additional options for more timely publication of high-priority information. As you look at our table of contents, the most obvious change is the change to sponsored…
Friday, February 16, 2018 Daily Archives
Spotlight for January-February
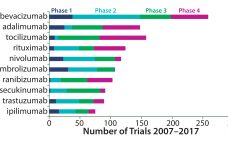
Tracking Antibodies in the Clinic In tracking clinical trial activity around the world, GlobalData has identified 5,273 clinical trials of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) that started between 1 January 2007 and 31 December 2016. The top three drugs in numbers of trials were bevacizumab, adalimumab, and tocilizumab. Rounding out the top 10 were rituximab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, ranibizumab, secukinumab, trastuzumab, and ipilimumab. Healthcare analyst Marco Borria said, “All the top 10 drugs are marketed, and the majority of trials initiated for them…
Market Research and Life Sciences: From Laboratory to Market
Start-ups in life sciences are constantly reshaping and redefining markets. As such, these companies must understand their unique markets because potential partners and investors seek out companies with such understanding. In my experience, it is not unusual for entrepreneurs to believe that they already know their market. They might have been active in their market for a long time, or they might have operated in similar industries and are making parallel assumptions. But markets are fluid environments, and they change…
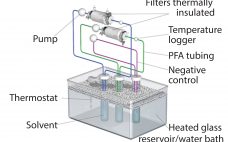
Implementation of the BPOG Extractables Testing Protocols: Comparing USP and BPOG Extractables Data for Autoclaved Polyethersulfone Filters
Benefits of single-use technologies over traditional stainless-steel solutions in biopharmaceutical manufacturing include reductions in set-up times, cleaning/cleaning validation costs, elimination of cross-contamination risks, and smaller operating footprints. But despite increasing adoption of such systems, concerns remain about extractable and leachable (E&L) compounds from plastic single-use systems (SUS) components with the potential to compromise the efficacy and safety of final drug products. Such concerns are magnified by the growing number of SUS suppliers and the complex supply chain for SUS and…
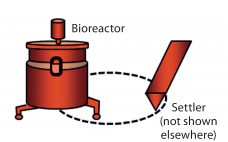
Reducing Variability in Cell-Specific Productivity in Perfusion Culture: A Case Study
Variation in bioproduction is recognized in the industry and often attributed to one or more of four sources: raw materials (including consumables), operational inputs (measurements, methods, personnel, equipment), environmental factors, and biological variation inherent to living cells (1). Variability can occur even among replicate units regardless of production mode (e.g., fed-batch or perfusion), and it can manifest as variability in productivity, cell metabolism, and/or product quality (2–4). In commercial biomanufacturing, meeting all product quality attributes is a requirement for regulatory…
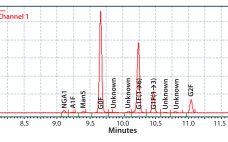
Enhanced Galactosylation of Monoclonal Antibodies: Using Medium Supplements and Precursors of UDP-Galactose, Part 1
The biopharmaceutical industry needs better understanding of how monoclonal antibody (MAb) glycosylation is influenced by components in cultivation media — and it needs methods to exert some control over the structure of MAb glycans. That structure can affect MAb function. Thus, a high-throughput (HTP) assay is needed for characterizing MAb glycosylation so that developers can observe the effects of cultivation conditions on MAb glycosylation rapidly, with a goal of producing MAbs that have a desired glycan structure. The method also…
Therapeutic IgG-Like Bispecific Antibodies: Modular Versatility and Manufacturing Challenges, Part 2
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) are bivalent and monospecific, with two antigen-binding arms that both recognize the same epitope. Bispecific and multispecific antibodies, collectively referred to herein as bispecific antibodies (bsAbs), can have two or more antigen-binding sites, which are capable of recognizing and binding two or more unique epitopes. Based on their structure, bsAbs can be divided into two broad subgroups: IgG-like bsAbs and non–IgG-like bsAbs. We have chosen to focus on the former in this review. Part one provides a…