Since the 2009 enactment of the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act (BPCIA) (1), the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has licensed six biosimilar products under PHS 351(k) and approved one product under FD&C 505 (b)(2). It also provided complete response letters (CRLs) to four biologics license application (BLA) filings (Table 1) (2). By comparison, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has approved 31 biosimilar products (3) and refused or withdrawn about five. There is no doubt that US market…
Manufacturing
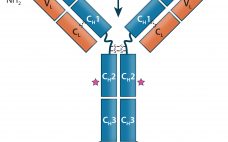
Therapeutic IgG-Like Bispecific Antibodies: Modular Versatility and Manufacturing Challenges, Part 1
Antibody-based immunotherapy has advanced significantly since 1986, when the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first mouse monoclonal antibody (MAb) for clinical use: Orthoclone OKT-3 (muromonab-CD3). In the intervening years, researchers have applied the tools of genetic engineering to clone immunoglobulin G (IgG) genes into a number of expression vectors. In the 1990s, the bioprocess industry was able to produce fully human antibodies in cultured cells. As of June 2017, the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA)…
Advanced Control Strategies at Biotech Week Boston
Attendees at this year‚Äôs Biotech Week Boston (24‚Äď28 September) had the opportunity to participate in several preconference symposia on the first day, including one on advanced control strategies for bioprocessing and biomanufacturing. Chaired by William Whitford (GE Healthcare), the session included presentations from Dan Kopec (Sartorius Stedim Data Analytics), Markus Gershater (Synthace), Jonathan Bones (National Institute for Bioprocessing), Robert Thomas (Loughborough University), Chris McCready (Sartorius Stedim Data Analytics), and Victor Konakovsky (Newcastle University). BPI has collaborated with conference organizer KNect365…
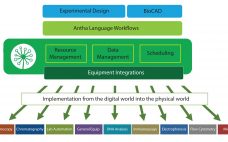
Accelerating Process Development Through Flexible Automated Workflows
Synthace began as a bioprocess optimization company in 2011, spun out of University College, London. The company worked on multifactorial approaches with 15‚Äď30 factors simultaneously instead of seven or eight. The work investigated genetic strain engineering factors alongside process parameters, defining deep interactions between the way strains were designed and the way they were treated in bioprocesses. Those complex experiments gave unique insight into the complexities of biological processes, but they were exceptionally taxing to plan and carryout manually. Automation…
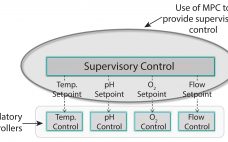
Model Predictive Control for Bioprocess Forecasting and Optimization
Automation hierarchy in bioprocess manufacturing consists of a regulatory layer, process analytics technology (PAT), and (potentially) a top-level model-predictive or supervisory layer. The regulatory layer is responsible for keeping typical process measurements such as temperature, pressure, flows, and pH on target. In some cases, spectral instrumentation in combination with multivariate analysis (MVA) can be configured to measure parameters such as glucose concentration. A cascade control structure can be set up when the nutrient flow setpoint is adjusted to maintain the…
Antibody‚ÄďDrug Conjugates: Fast-Track Development from Gene to Product
In the fight against cancer, antibody‚Äďdrug conjugates (ADCs) represent an increasingly important therapeutic approach. These biopharmaceuticals are designed to maximize the therapeutic index of cytotoxic small-molecule drugs through their selective delivery to tumor cells while leaving normal, healthy cells untouched. Structurally, an ADC is a monoclonal antibody (MAb) conjugated by a chemical linker to a potent cytotoxic drug. Conceptually, the MAb serves as the delivery component, targeting a specific tumor antigen that ideally is not expressed (or is expressed at…
The 2017 World Biological Forum: Successes and Future Trends in Continuous Biomanufacturing
Continuous biomanufacturing was a central topic at the fourth annual World Biological Forum in Oxford, UK, on 26‚Äď28 June 2017. A well-rounded lineup of presenters appeared at this forum held in Oxford University‚Äôs Lady Margaret Hall, an eclectic location that well captured the historic charm of the university. Delegates were well supported throughout the meeting with generous meals, refreshments, and assistance provided by helpful staff. Papers were presented in Talbot Hall in the center of the college. The stately main…
Introduction: Emerging Therapies Come of Age
According to a 2017 industry report, 74% of biopharmaceuticals currently in development (phase 1‚Äď3) are possible first-in-class medicines (those that use a unique mechanism of action), thus representing a potential new pharmacological class of treatment (1). They include regenerative medicines, conjugated monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), and DNA and RNA therapeutics. Some emerging therapies ‚ÄĒ such as antibody‚Äďdrug conjugates (ADCs) and biobetters ‚ÄĒ have been more at the forefront of discussions than others, but all are poised to bring exciting changes to…
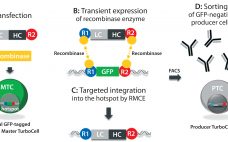
Process Needs of Antibody Fragments and Bispecifics: A Discussion with Jonathan Royce of GE Healthcare
Although the number of bispecific antibodies approved so far (two) and antibody fragments either approved or with an investigational new drug (IND) filed (‚ąľ20, both antigen-binding and variable) are far below the number of approved and candidate monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), research in both fragments and bispecifics continues to look promising. And as Jonathan Royce, business leader for chromatography resins at GE Healthcare, discusses here, both offer specific therapeutic advantages over MAbs. But manufacturers should be aware that their diverse structures…
Controlling Glycosylation in Fusion Protein Manufacturing to Generate Potent Biobetters
The pipelines of pharmaceutical companies are full of biological drugs. Many of them are innovative therapeutic proteins, but a growing number represent biosimilars and biobetters (Figure 1) (1). Biobetters typically are defined as being ‚Äúbased on innovative biologics but with improved properties‚ÄĚ (2). Their development benefits from known therapeutic approaches and mechanisms of action resulting in low risk, fast paths to the clinic and thus lower costs. Superiority is achieved through extended half-life (t1/2), improved efficacy, and reduced immunogenicity or…