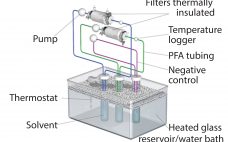
Identifying the greatest defect size, both for liquid leaks and microbial ingress, is a fundamental step toward protecting the integrity of single-use systems (SUS) under real process conditions. Integrity testing of such systems may become a prerequisite in the future because they are used in the most critical process steps, with detection limits correlating to liquid leaks and microbial ingress. Such testing guarantees the sterility of drug substances and drug products packaged in single-use systems and, therefore, enhance patient safety.…
Manufacturing
eBook: Innovations in CRISPR Technology — A Perspective on Research and Bioprocess Applications
One of the fastest growing areas in genome engineering is research using the powerful editing tool of clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR). When paired with the Cas9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9), an RNA-guided DNA endonuclease enzyme from Streptococcus pyogenes, the site-specific prokaryotic immune system can be used to cut and manipulate DNA strands in cells of patients with genetic diseases to treat, or in some cases, prevent such diseases. Within the past couple of years, CRISPR has been shown…
Driving Cell Therapy Innovation: Applying Key Lessons from the Evolution and Commercialization of Protein-Based Therapies
After many trials and errors — and milestones — regenerative medicine has become a mainstream part of the biopharmaceutical industry, supported by at least 670 companies and clinics of all sizes. But many experiences in the protein-based industry segment can be leveraged to further improve successful commercialization of advanced therapies. At the 2017 Biotech Week Boston conference, BioProcess International editor in chief Anne Montgomery hosted a panel of industry cell therapy experts to discuss key lessons that can be gleaned…
eBook: Viral Vaccine Production — Cultivation of Vero Cells in Packed-Bed Bioreactors
Vero cells are anchorage-dependent cells that are used widely as a platform for viral vaccine production (1). In stirred-tank bioreactors, they are grown ordinarily on microcarriers. Fibra-Cel disks are an alternative attachment matrix because they provide a three-dimensional environment that protects cells from damaging shear forces. However, such disks have not been tested for the cultivation of Vero cells. We tested whether benchtop single-use and glass bioreactors with a packed bed made of Fibra-Cel disks would be suitable for cultivation…
eBook: Alternative Delivery of Biologics — Underdogs Pursue Roads Less Traveled
A number of failures in development of noninjectable delivery methods for therapeutic proteins have caused numerous development programs to crash and burn along with investors’ hopes, dreams, and cash. Most everyone reading BioProcess International is familiar with the issues and challenges: Needles hurt and involve risks to both caregivers and patients. Injections often require administration by trained personnel in specialized settings. But alternative delivery methods are fraught with greater challenges related to dosing, bioavailability (particularly for oral dosing), and inherent…
Implementation of the BPOG Extractables Testing Protocols: Comparing USP and BPOG Extractables Data for Autoclaved Polyethersulfone Filters
Benefits of single-use technologies over traditional stainless-steel solutions in biopharmaceutical manufacturing include reductions in set-up times, cleaning/cleaning validation costs, elimination of cross-contamination risks, and smaller operating footprints. But despite increasing adoption of such systems, concerns remain about extractable and leachable (E&L) compounds from plastic single-use systems (SUS) components with the potential to compromise the efficacy and safety of final drug products. Such concerns are magnified by the growing number of SUS suppliers and the complex supply chain for SUS and…
Extend the Life of Your Facility: Flexibility Allows for Biopharmaceutical Process Innovation
For an industry built on constant change, there’s a surprising disconnect between the continuous drive for innovation and the inflexible facilities that house biopharmaceutical operations. Some of today’s facilities are built for today’s use with little thought about tomorrow’s. The typical approach for a new process or drug coming to market is to start with a brand-new building and permanently embedded equipment designed around that specific process. That approach is expensive and unsustainable. New bioproduction facilities can cost US$500 million…
Conference Report: The Drug Product Track at 2017’s BioProcess International Conference and Exhibition in Boston, MA
At the Hynes Convention Center in Boston, MA, during Knect365’s “Biotech Week Boston” in late September of 2017, one track of the BioProcess International Conference focused on drug products, fill–finish, and formulations. Presenters represented a number of major biopharmaceutical companies — AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Genentech (Roche), GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson, Lonza, Pfizer, and Sanofi — as well as suppliers Bosch, Merck (MilliporeSigma), ReForm, and Single-Use Support. They focused on predictive modeling, quality by design (QbD) and process analytics,…
A Vaccine Case Study: Qualifying Redundant Disconnection Technologies As Container-Closure Systems for Long-Term Storage and Shipping
The expanding complexity of biopharmaceutical manufacturing puts increasing pressure on single-use systems to meet the demands of the modern industry’s global footprint. Individual sites within a given organization often are specialized to a fixed number of “modular” process steps (1). Such product segregation increases plant efficiency and output while making the best of staff competencies. But it also can create an additional need for transportation of intermediate or bulk drug substance (BDS) over long distances. Freezing generally is used to…
eBook: Bioinks for Bioprinting — Three-Dimensional Printing in Research and Medicine
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is one method of digital biomanufacturing for both basic biological research and translational, clinical applications. The medical field has used it to create such constructions as 3D surgical models for preoperative planning, to assist surgeons in their procedure preparations, which improves postsurgical outcomes. Examples here include generation of cleft-palate models (1), orthopedic applications (2), and cardiovascular surgical planning (3). Other forms of 3D printing for biological applications — such as 3D bioprinting — go beyond such surgical…