Antibody production platform processes have been widely adopted in biomanufacturing, but many unit operations are not suitable for integration and automation. Here we describe the work of integrating unit operations by transforming a column operation to a more robust cassette format. We have selected a biomolecule-friendly buffer (phosphate) to eliminate, or delay, the performance of a circulating tangential flow ultrafiltration/diafiltration (UF/DF) operation, so the harvest-to-purified-bulk process can be integrated, resulting in a single, direct-flow operation, that reduces the batch process…
Downstream Processing
Making Downstream Processing Continuous and Robust: A Virtual Roundtable
Current biomanufacturing is driven to pursue continuous processing for cost reduction and increased productivity, especially for monoclonal antibody (MAb) production and manufacturing. Although many technologies are now available and have been implemented in biodevelopment, implementation for large-scale production is still in its infancy. In a lively roundtable discussion at the BPI West conference in Santa Clara, CA (11 March 2019), participants touched on a number of important issues still to be resolved and technologies that are still in need of…
Modeling Virus Clearance: Use of a Noninfectious Surrogate of Mouse Minute Virus As a Tool for Evaluating an Anion-Exchange Chromatography Method
Viral safety is a critical focus during biopharmaceutical manufacturing (1–5). Although well-characterized mammalian cells such as the Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) line have been used for decades, both endogenous expression of retroviral-like particles and exogenous contamination events from viruses warrant continued vigilance (6, 7). International regulatory agencies require biomanufacturers to validate the “viral clearance” efficacy of their downstream manufacturing process steps before resulting products can be awarded clinical trial or commercial approval (8–10). Currently, viral clearance testing is based on…
eBook: Making Filtration Work
Steady improvements in batch-fed cell culture have led to bottlenecks in downstream processing. Filter suppliers are working to improve available tools for purifying therapeutic proteins, to wring every possible efficiency out of those tools, and to make them operate together harmoniously. The combination of high titers and high-value products places a premium on preventing yield loss. Bioprocessors want to optimize filtration primarily for cost reasons. In this eBook, author Angelo DePalma discusses financial aspects, clarification/harvest and virus filtration options, and…
Developing an End-to-End Scale-Down Model for a Commercial-Scale Downstream Process: Enhancing Technology Transfer Efficiency
Large and complex protein molecules used as therapeutic agents are manufactured in a series of process steps that start with thawing of cell-bank vials and finish with filling and packaging (Figure 1). The cost and complexity of commercial-scale biomanufacturing processes make them prohibitive to troubleshoot or experiment at full commercial scale. Biopharmaceutical companies routinely use scale-down models (SDMs) of licensed commercial-scale processes to evaluate raw material changes, process improvements, and deviations (1) (Figure 2). Here, we outline some considerations in…
Continuous Chromatography: Experts Weigh in on the Possibilities and the Reality
Discussions of continuous processing in the biopharmaceutical industry are an important part of current efforts toward intensifying bioproduction and bioprocessing. Biomanufacturers are looking at all components of their development and manufacturing processes for ways to reduce the size of their facilities, lower costs, and increase speed and flexibility of operations. Increasing options for and availability of single-use technologies have been major enablers of myriad attempts to improve efficiencies. Although the general consensus may still be that single-use components are more…
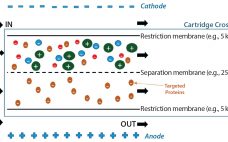
Tangential-Flow Electrophoresis: Investigation of Factors Involved in an Effective Separation of Human Serum Albumin from Human Plasma
Human plasma is a complex mixture of biomolecules such as serum albumin, immunoglobulins, coagulation factors, and others (1). These important protein biomolecules often are present at low levels or lacking in affected patients with certain life-threatening conditions. To extract those valuable proteins, a number of purification methods have been developed over time. Plasma fractionation can be traced back to the middle of the 20th century, when Edwin Cohn of Harvard University developed the first industrial process to purify proteins from…
Development and Application of a Simple and One-Point Multiparameter Technique: Monitoring Commercial-Scale Chromatography Process Performance
In commercial-scale biopharmaceutical manufacturing, downstream chromatography steps are still a bottleneck and contribute to significant operational costs (1, 2). Some of those costs are inherent (e.g., resins, large buffer quantities, and cleaning) whereas others are avoidable (e.g., product loss due to rejected lots or deviations that result in production downtime). Maintaining efficient and robust chromatography process performance is therefore critical for minimizing operating costs. To do so, we introduce a simple and one-point multiparameter technique (SOP-MPT) for monitoring chromatographic process…
The Complete e-Book of Biosafety Testing
Expect the expected. But plan for the unexpected. If your Biosafety Development takes a nose dive, Eurofins Lancaster Laboratories’ team of regulatory experts and experienced scientists will help you land safely on two feet. Download The Complete e-Book of Biosafety Testing to learn more about our expertise in biologics raw materials, cell bank preparation, adventitious virus testing, viral clearance studies, next-generation sequencing, genetic stability testing, and more. This e-Book contains the following chapters: Mitigating Risk and Reducing Regulatory Scrutiny of…
Manufactured by Jetting: The Future in Protein A Affinity Matrix Design
Protein A affinity chromatography continues to be the preferred method for commercial purification of antibodies because of its high selectivity and robust resin performance over repeated purification cycles. Reports estimate that US$125 billion of yearly sales will be generated from monoclonal antibody (MAb) products by 2020 (1). Most of those will be purified by largescale protein A affinity chromatography. With the continued growth and commercial importance of MAb production, availability of high-quality resin material and options for secondary sourcing are…