The biopharmaceutical industry is in the midst of an exciting transformation as biologics experience massive growth — even outpacing the small-molecule segment (1). Biologics are predicted to comprise over a quarter of the pharmaceutical market in 2020 (2). At the same time, a plethora of new biologically derived therapy concepts — e.g., cell and gene therapies — are in development. Some biologics classes have become mainstream — e.g., monoclonal antibodies — with biosimilars entering the market and contract manufacturing organizations…
Analytical
Detection and Clearance of Viruses in the Biopharmaceutical Industry
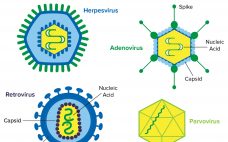
Viral contamination is a common threat to all animal- and human-derived biopharmaceuticals. This type of contamination can affect any part of a bioproduction process, so biomanufacturers need to perform viral testing studies and incorporate viral clearance methods into their processes. Viral contaminants can come from cell lines (e.g., endogenous retroviruses) or from adventitious (e.g., mycoplasma) introduction during drug manufacturing. Virus testing of master cell banks (MCBs), working cell banks (WCBs), end-of-production cell banks, and bulk unprocessed harvest material is called…
Analytical Testing Strategies for CAR T-Cell Products
Assay lifecycle development for traditional biopharmaceuticals such as vaccines and monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) has a clearly defined pathway, from preclinical method selection, development, and optimization through the milestones in preclinical phase trials, and finally to postlicensure method evaluations, comparability, and improvements. The analytical development roadmap for nontraditional biologics such as chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies and gene therapies are not as clearly defined and can present many challenges along the way. Understanding the “what, how, and when” of analytical…
Measure Twice, Treat Once: Navigating the Regulatory Landscape of Assay Development to Ensure High-Quality CGT Products
Cell and gene therapies (CGTs) are a novel and fast-growing class of transformative therapies designed to address gaps in traditional treatment strategies of some of the most severe diseases. By definition, gene therapy “seeks to modify or manipulate expression of a gene to alter the biological properties of living cells for therapeutic use” (1). That can be either an in vivo delivery of a gene or delivery of a gene to a patient’s cells that are manipulated outside of the…
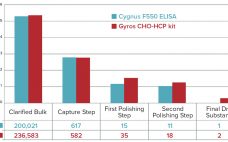
Host-Cell Protein Analysis to Support Downstream Process Development: A High-Throughput Platform with Automated Sample Preparation
In the past few years, increasing numbers of biotherapeutics have been approved for market (1). Among all the regulatory concerns for commercial biotherapeutics, host-cell proteins (HCPs) are a major class of process-related impurities that remains a critical quality attribute (CQA) for bioprocess development because of associated risks to product quality, safety, and efficacy. HCP identification, clearance, assay setup, and process control are critical points for health authorities, and many guidelines aim for better control of HCP content in final biologic…
Cell Viability in Bioprocesses: Making a Case for Reevaluation
Trypan blue dye exclusion first was proposed as a means of measuring mammalian cell damages over a century ago in 1917 (1). Despite extensive documentation of its limitations (2), it remains the “gold standard” method of measuring cell viability in common use today. But can this method truly measure viability? And how do we define cell viability, for that matter? Those fundamental questions are linked to whether we refer to cells as “alive” or “dead” in the context of bioprocessing…
Demonstrating Intactness of Biopharmaceutical Products: Intact Molecular-Weight Analysis and Terminal Sequencing of Proteins
Regulations require that biomanufacturers assess the intactness of protein and glycoprotein products as well as confirm the terminal sequences to look for existing variations. ICH Q6B guideline section 6.1.1 c states: Terminal amino acid analysis is performed to identify the nature and homogeneity of the amino- and carboxy-terminal amino acids. If the desired product is found to be heterogeneous with respect to the terminal amino acids, the relative amounts of the variant forms should be determined using an appropriate analytical…
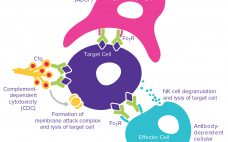
Mitigate Risk with Effector Function Characterization for Antibody Therapeutics
The complexities of biomanufacturing combined with heterogeneity introduced by cellular expression systems present significant challenges to assessing the quality of biologics such as monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). Information related to the critical quality attributes (CQAs) of MAb drug candidates is unknown during early phase drug development. It must be established empirically by physical, structural, and functional analyses as early as possible to accelerate development and mitigate risk through greater understanding of product characteristics. High-resolution analytical techniques are required to answer questions…
eBook: Bioassays for Biopharmaceuticals: Finding Best Practices in a Quality Systems World
Bioassays are complex and challenging experiments to run reliably with accurate and dependable results. Consistent performance requires a controlled environment and qualified reagents; skilled analysts who understand cell physiology, regulatory requirements, and the latest techniques; and assay protocols that are intelligently developed, characterized, and validated. Here, BPI’s senior technical editor discusses bioassay best practices with representatives of the Biopharmaceutical Emerging Best Practices Association (BEBPA) organization. Topics span quality by design, assay validation, cell banking, potency testing and host-cell protein monitoring,…
Viral Nanofilter Integrity: Using Variable-Pathlength UV-Vis Spectroscopy for the Gold Nanoparticle Test
Viral filtration (VF) using nanofilters removes endogenous and/or adventitious viruses from biologic drug-substance manufacturing processes (1). The gold particle test (GPT) is performed as part of postuse integrity testing — to complement postuse leakage testing — for cellulose filters such as Planova 20N filters from Asahi Kasei Corporation. First, a proprietary gold-colloid solution matched to the filter type (e.g., 20N) is filtered through the test article. That filter’s pore-size distribution can be assessed using spectrophotometric absorbance readings of the integrity-test…