Design of experiments (DoE) is one of the most valuable techniques for organized and efficient planning, execution, and statistical evaluation of experiments. Although a DoE investigation can be completed using several runs in one bioreactor, small-scale bioreactor systems designed for parallel operation (such as the ambr15 or ambr250 systems) provide the optimal basis to economically realize a series of experiments. Because of the multitude of interdependent parameters involved in applications such as cell line development, culture media screening, and the…
Analytical
Targeting G Protein–Coupled Receptors with Biologics for Therapeutic Use, Part 2
In part 1, we summarized the advances made in new approaches developed to address the challenges of antigen generation for targeting G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs). We reviewed the antibody and biologics pipeline with progress highlighted by some interesting case studies on new targets (1). Here, we conclude by reviewing progress attained with other biologics. Peptides Targeting G Protein–Coupled Receptors More than 50 peptide-based therapeutic products are commercially available, but very few of them have been derived from recombinant display technology.…
Paired ADCC Reporter Bioassays Enable Differentiation of Antibody Fc Effector Activities via V158 and F158 Variant FcyRIIIa Receptors
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) contributes to clinical efficacy of a broad range of therapeutic antibodies. FcÎłRIIIa polymorphism of individual cancer patients are correlated with clinical efficacy of some of these antibody drugs. Classic ADCC cytotoxicity assays rely on primary effector cells, which are highly heterogeneous and variable. To quantitatively measure antibody activity and evaluate the impact of FcÎłRIIIa polymorphism, we developed a pair of reporter-based ADCC assays using two engineered effector cell lines in Jurkat that stably express an NFAT-RE driven…
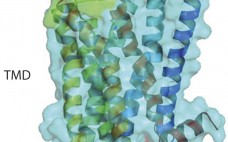
Targeting G Protein–Coupled Receptors with Biologics for Therapeutic Use, Part 1
G -protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) represent a target superfamily linked to many disorders across all therapeutic areas. Although this target class has been historically treated by small molecules and peptides, antibodies can offer a number of advantages over such molecules by virtue of their specificity, dosing frequency, and restricted penetration. They also can provide other functional effects specifically mediated by the Fc region (ADCC and CDC) as well as different modalities such as those offered by bispecific and antibody drug…
Site-Specific Characterization of Glycosylation on Protein Drugs
A large proportion of biotherapeutic products are glycoproteins. These include erythropoietin and other cytokines, antibodies, glycosyltransferases, and glycosidases, which together generate billions of dollars in sales worldwide. Such drugs are inherently complex. As new treatments emerge and biosimilars are evaluated, the need to better understand their molecular structures is more acute than ever. Therapeutic glycoproteins are typically produced as recombinant products in cell culture systems. Glycosylation is of major importance during development of these drugs because their glycan chains markedly…
Analytics for Modern Bioprocess Development
Twelve years ago, about the same time the US Food and Drug Administration was putting the finishing touches on its quality by design (QbD) and process analytical technology (PAT) guidelines, I wrote an article about breakthrough pharmaceutical educational programs. That article included the perspectives from a few members in academia of the future essential skills for pharmaceutical students. At the time, bioinformatics and computerized industrial process modeling were relatively new disciplines, but their importance in future manufacturing was clear. Several…
Essentials in Quality By Design
Quality by design (QbD) is a systematic approach to drug development. It begins with predefined objectives and emphasizes product and process understanding and process control, all based on sound science, data-based decision making, and quality risk management (QRM). As introduced by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), QbD brings modern drug development methodologies to chemistry, manufacturing, and control (CMC) teams working on biologics, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines. The innovations associated with QbD are not so much the development concepts (which…
Reference Standards for Therapeutic Proteins: Current Regulatory and Scientific Best Practices
Sponsors developing and manufacturing protein therapeutic products use a variety of analytical tests (e.g., cell-based potency and chromatographic assays) to assess quality attributes of their active ingredients and drug products. Those tests are used to assess product quality in a number of activities, including characterization, comparability, lot release, and confirmation product quality and stability. Reference standards play a critical role in calibrating and confirming the suitability of such tests and in helping analysts to draw scientifically sound conclusions from data…
Cell Therapy Bioprocessing Technologies and Indicators of Technological Convergence
The cell therapy industry is undergoing a natural evolution from scientific curiosity into a commercially and clinically attractive opportunity (1). This evolution is by no means complete, and growing evidence suggests that its progression is driving significant developments in cell therapy bioprocessing — notably, convergence. Table 1: 194; () Progressively, bioprocessing technologies primarily used in production of noncell-based products are being evaluated for cell therapy bioprocessing applications (2). Consequently, this process of convergence is leading to an increasing proportion of…
Activatable Immunoconjugates for Target Cancer-Cell–Specific Diagnosis and Therapy
In cancer treatment, early diagnosis and targeted therapies are assumed to yield the highest cure rates. However, most current methods are limited by their low sensitivity to early disease and a lack of specificity for targeted cell killing. Newly developed, activatable immunoconjugates assist in the accurate detection of cancer through in vivo imaging with high target-to-background contrast (1,2). They also provide for the possibility of highly specific, light-mediated treatment with minimal effects on healthy cells surrounding tumors (3). In fact,…