The BioPhorum Operation Group’s (BPOG’s) Container Closure Integrity Testing (CCIT) workstream would like to congratulate the United States Pharmacopeia’s committee for its latest revision to USP chapter <1207> Package Integrity Evaluation: Sterile Products. Generally, we believe it provides a comprehensive overview of the available methods for container–closure testing and outlines many important elements for consideration in establishing a successful CCIT strategy. We first responded to the USP <1207> draft when it was released for comment in 2014. And from our…
Analytical
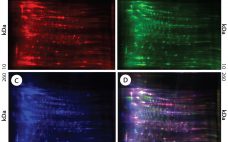
HCP Antigens and Antibodies from Different CHO Cell Lines
Cell lines derived from Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells are widely used in therapeutic protein production because they can perform human-compatible posttranslational modifications, they are easy to use for manufacturing, and they do not propagate most human pathogenic viruses (1, 2). Expressed therapeutic proteins are secreted into CHO culture supernatant along with impurities originating from the host cells themselves. Such host cell proteins (HCPs) are important contaminants for monitoring because they directly affect drug quality, safety, and efficacy. HCPs are…
Special Report on Process- and Product-Related Impurities (A CMC Strategy Forum Special Focus Series): Extractables, Leachables, Particles, and Aggregates
The CMC Strategy Forums focus on relevant chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) issues throughout the life cycle of a therapeutic and thereby foster collaborative technical and regulatory interaction. Forum chairs share information with regulatory agencies to help them merge good scientific and regulatory practices. Outcomes of forum meetings are published in BioProcess International and on the CASSS website (www.casss.org). This process is meant to help ensure that biopharmaceutical products manufactured with advancing technologies in a regulated environment will continue to…
Mass Spectrometric Conjugate Characterization: Process Qualification of Recombinant Protein–Hapten Conjugation
Conjugated protein biotherapeutics such as PEGylated proteins (with polyethylene glycol), antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs), and protein–haptens often present unique analytical challenges related to characterizing the conjugation aspect of their manufacturing processes. Analytical characterization of this class of proteins requires knowledge of the sites of conjugation, the degree of conjugation, and the drug-to-protein ratio. Here we present case studies in development of reliable methods based on mass spectrometry (MS) to characterize a protein–hapten drug substance during late-phase process validation. This protein is…
Providing Lipids Boosts Protein Productivity: Testing a Feed Supplement with Multiple Cell Clones and Media Formulations
As the biologics (and now biosimilar) markets continue to grow, pressure increases on biomanufacturers to reduce cost of goods sold (CoGS). One way they can reduce cost is by increasing protein productivity in terms of protein titer per volume of culture. Media optimization is a key strategy for increasing protein productivity. In the past few decades, average titers across the industry have increased greatly — from <0.5 g/L in the 1980s to >3 g/L today, and it is not uncommon…
Advanced Protein Engineering Enhances Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing and Analytics
Production of proteins for pharmaceutical use is a complex, multistep process that requires technologies for purifying such molecules from highly complex biological mixtures. It also calls for reliable, cost-effective, high-throughput analytical techniques to determine protein quality and functionality to ensure the safety and efficacy of end-products. Mistakes in product development and manufacturing not only are immensely costly, but they can also put patients at risk. Many well-established processes and analytical tools are available for use in manufacturing antibody drugs (e.g.,…
Reveal Information That Gives Insights: New Approaches to Sub-Visible Particle Characterization
This webcast features: Josefina Nilsson, Head of EM Services, and, Gustaf Kylberg, Product Manager – MiniTEM, Vironova Sub-visible particle characterization is essential when comparing sample quality after different purification steps or for the understanding of product stability. Analysis performed with MiniTEM provides both morphology and accurate quantitative data that can help speed up process and formulation development. In this webinar you will learn: How MiniTEM automatically images, detects and classifies a large number of particles resulting in statistically significant and…
Viral Risk Evaluation of Raw Materials Used in Biopharmaceutical Production
Ensuring a continuous supply of safe medicines to patients is a key objective for both health authorities and the pharmaceutical industry. A critical component to that end is maintaining a reliable supply of qualified raw materials (RMs). Manufacturers must ensure not only the suitability of RMs for their intended use in a manufacturing process, but also their highest attainable safety with regards to viruses and other adventitious agents. The need to apply a risk-based RM control strategy is in line…
Quality By Design for Monoclonal Antibodies, Part 2: Process Design Space and Control Strategies
Process design space and control strategy are two fundamental elements of quality by design (QbD) that must be established as part of biopharmaceutical development and regulatory filings. Like all of QbD, they are interconnected and iterative. Both are based on knowledge gained during product and process development — but both need to be in place (in a potentially very limited form) when a company begins to manufacture drug substance for clinical trials. Part 1 of this discussion appears on pages…
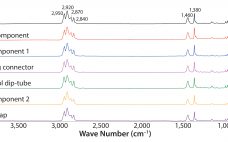
Investigation of Foreign-Particle Contamination: Practical Application of FT-IR, Raman, and SEM-EDS Technologies
The presence of visible foreign particulate matter is considered a critical defect in parenteral products and one of the main reasons they can be recalled (1). Foreign particles present during any stage of manufacturing are considered to be contaminants and can impose a risk to the control of the manufacturing processes (2). For those reasons, particle contamination arising in any manufacturing step initiates a nonconformance or out-of-specification observation. That requires an investigation to identify root cause so as to mitigate…