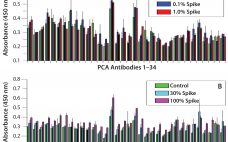
For protein therapeutics and other biologics, the importance of the molecule’s structure to its efficacy and safety is well established (1–5). In particular, their tertiary and quaternary structures play very important roles in product quality and have been monitored extensively in comparability studies (6–12). However, because of both the large molecular size and rotational property of amino acid α carbons, a protein can assume an enormous number of different conformations (13). For antibody-based biologics such as monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), fusion…
Analytical
Particulate Contamination in Single-Use Systems: Challenges of Detection, Measurement, and Continuous Improvement
Patients receiving particulate contamination through parenteral delivery of biopharmaceuticals presents a significant potential health risk. However, the severity of that risk often is unclear. It depends on the route of administration, dosage volume administered, particle properties and amount received, and the ultimate fate of particles within a patient’s body (1). The appearance of particulate contamination also can be a visible indicator of product quality. Consequently, when such contamination is discovered within biopharmaceutical manufacturing operations, often it triggers costly investigations and…
Recent Advances in Endotoxin Removal: An Upgrade to a Traditional Method and a New Adsorption Chemistry
Endotoxin contamination has been the bane of the bioprocessing industry since its inception. Endotoxins are everywhere: They are toxic and/or interfere with every type of therapeutic, diagnostic, and research product; they are indestructible within the limits of product tolerance; and they are difficult to remove (1–4). Beyond that, they interact with various biological species in ways that prevent accurate measurement (5, 6). Managing these issues has been a focus of the industry for at least half a century, yet it…
Viral Vector Particle Integrity and Purity Analyses in Early Process Development
Gene therapy is the transfer of genetic material to a patient’s cells to achieve a therapeutic effect. Therapeutic DNA typically is delivered using a viral vector system, and adenoviruses have been used for this purpose for over 20 years (1–3). Within the past 10 years or so, lentiviruses have shown promise in clinical trials (1–3), and adenoassociated viruses (AAVs) have been used in the first approved gene therapies in the Western world (4). The number of gene therapy applications based…
Development of a Host-Cell Protein Platform Assay for a Chinese Hamster Ovary Cell Line
The Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line is the most prevalent biopharmaceutical expression system and has been proven safe for commercial production of protein therapeutics (1). However, even after multiple purification steps, biopharmaceuticals contain residual host-cell protein (HCP) impurities that pose a potential safety risk to patients (2). Health authorities demand close monitoring of HCP impurities and require sensitive analytical methods with high coverage: the ability to detect a broad range of HCP impurities (3, 4). Polyclonal sandwich immunoassays are…
Moving DSC Downstream: Exploiting Differential Scanning Calorimetry As a Process Development Tool
The primary goal of biopharmaceutical process development is to determine what steps and conditions will maximize and optimize yields of purified product in the most reproducible, robust, and cost-efficient way. Characterized by high batch-to-batch comparability minimizing economic losses associated with batch failures, success relies on a thorough understanding of a given biological drug. Determining how its activity and stability are affected by processing and how to mitigate and control associated risks is advocated by a quality by design (QbD) approach.…
Development Approaches to Adenoassociated Virus Production
After many years of development, gene therapy is beginning to deliver on its promises in the clinic, in some cases with spectacular outputs. Those clinical successes also have led to an influx of funding and engagement from large pharmaceutical companies, thereby bringing the required financial support and expertise for late-stage clinical developments and product commercialization. Although many initial studies were confined to small patient groups and focused on a range of rare monogenetic diseases, new approaches to gene editing have…
BPI Lab: Essential Technologies for Development, Characterization, and QA/QC
There’s a secret hiding in plain sight: many analytical methods and technologies initially designed for pre-clinical development have equally important applications in commercial development. BioProcess International and BioTechniques, sister publications and leading journals that combined, cover the entire biopharmaceutical process, from discovery to development and manufacturing, partnered to create this special eBook, highlighting and detailing fourteen analytical technologies that provide laboratory technicians and scientists with vital information to help project managers and engineers make educated decisions that ultimately affect every…
Opportunities and Challenges in Biosimilar Development
A biosimilar biotherapeutic product is similar (but not identical) in terms of quality, safety, and efficacy to an already licensed reference product. Unlike generic small molecules, it is difficult to standardize such inherently complex products based on complicated manufacturing processes. Table 1 describes the main differences between biosimilar and generic drug molecules. The global biosimilar market is growing rapidly as patents on blockbuster biologic drugs expire (Table 2) and other healthcare sectors focus on reduction of costs. Biologics are among…
Implementing Quality By Design in Analytical Development: A Case Study on the Development of an Anion-Exchange HPLC Method
The concept of quality by design (QbD) initially was outlined in ICH Q8 guidance for drug-product development and later in Q11 for drug-substance development (1, 2). Since then, the QbD concept was further expanded to the development of analytical methods. FDA issued a 2015 guidance on analytical procedures and method validation for drugs and biologics (3). Although the agency did not explicitly state the requirement for implementation of QbD in analytical method development, the concept is embedded in its section…