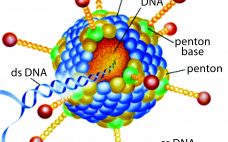
In December 2013, a two-year-old child in Guinea became the first person to be killed by Ebola in the most recent outbreak. In March of the following year, that outbreak was declared in West Africa. By mid-2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) had declared it to be a public health emergency of international concern and urged pharmaceutical companies to accelerate their development of candidate vaccines. At the peak of the outbreak in 2014, more than 1,200 new cases of Ebola…
Analytical
Rational Design of Liquid Protein Formulations: Application of Biophysical Stability Predictors and Descriptors to Reformulate Biotherapeutics
Successful development of liquid biopharmaceutical formulations requires careful assessment of the biophysical properties of the protein in solution, primarily focused on achieving optimal conformational and colloidal stability of the drug-substance molecule (1–11). It also involves extensive stability studies under stressed conditions. Using state-of-the-art biophysical tools for characterization of developed products, those studies are based on key biophysical descriptors and extended particulate characterization methods (subvisible particles in micro- and nano-size range) to deliver a stable product for market with a shelf…
Statistical Assessments of Bioassay Validation Acceptance Criteria
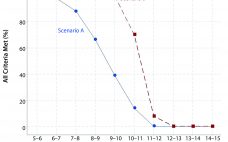
Analytical linearity as well as assessments of precision and accuracy determine the range for a bioassay (1). USP <1033> recommends comparing confidence intervals (CIs) against target validation acceptance criteria in a bioassay validation exercise, but there are no clear guidelines for determining the criteria (2). Here I address several aspects of a bioassay validation, namely • Linearity (coefficient of determination (R2), slope, and intercept parameters) • Accuracy (%relative bias, %RB) • Precision (percent coefficient of variation, %CV) CIs for the…
eBook: Production Cell-Line Development and Control of Product Consistency During Cultivation — Myths, Risks, and Best Practices
Health authorities are requesting substantial details from sponsors regarding practices used to generate production cell lines for recombinant DNA–(rDNA) derived biopharmaceuticals. Authorities also are asking for information about the clonality of master cell banks (MCBs) and control strategies to minimize genetic heterogeneity. Such requests are prompted by recent reports indicating “nonclonality” for certain production cell lines. To address these and related issues, the CASSS CMC Strategy Forum on “Production Cell Line Development and Control of Product Consistency During Cell Cultivation:…
The Relationship Between R2 and Precision in Bioassay Validation
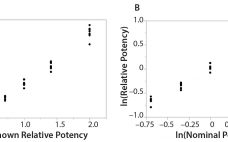
Analytical linearity along with assessments of precision and accuracy determine the range for bioassays (1). Practitioners can include coefficient of determination (R2) criteria from a linearity study in the bioassay validation protocol. Herein I illustrate the relationship of R2 to study design and analytical method variation. Overview of the Simple Linear Regression Model Dilutional linearity assesses the “ability (within a given range) of a bioassay to obtain measured relative potencies that are directly proportional to the true relative potency of the…
eBook: Development of a Representative Scale-Down UF/DF Model: Overcoming Equipment Limitations and Associated Process Challenges
Scale-down models (SDM) are physical, small-scale models of commercial-scale unit operations or processes that are used throughout the biopharmaceutical industry for validation studies, commercial deviation investigations, and postapproval process improvements. To support these studies, regulatory guidelines state that SDMs should be representative of the commercial process. For some downstream unit operations such as column chromatography, developing a representative SDM is straightforward because a linear scale-down approach can be used. However, developing a representative SDM for other downstream unit operations such…
Therapeutic IgG-Like Bispecific Antibodies: Modular Versatility and Manufacturing Challenges, Part 2
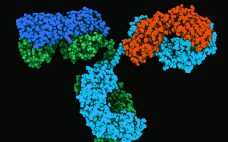
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) are bivalent and monospecific, with two antigen-binding arms that both recognize the same epitope. Bispecific and multispecific antibodies, collectively referred to herein as bispecific antibodies (bsAbs), can have two or more antigen-binding sites, which are capable of recognizing and binding two or more unique epitopes. Based on their structure, bsAbs can be divided into two broad subgroups: IgG-like bsAbs and non–IgG-like bsAbs. We have chosen to focus on the former in this review. Part one provides a…
Implementation of the BPOG Extractables Testing Protocols: Working with Multiple Single-Use Components
Single-use technologies offer significant advantages over traditional stainless-steel solutions for biopharmaceutical manufacturing. Reductions in setup times, cleaning and cleaning-validation costs, elimination of cross-contamination risks, and smaller footprints are just some of the benefits they provide. Although adoption of single-use systems (SUS) for commercial manufacturing is expanding, concerns persist that extractable and leachable (E&L) compounds from plastic SUS components potentially can leach into final drug products and compromise efficacy and safety. Those concerns are magnified amid the growing number of SUS…
Integrated PAT Automated Feedback Control of Critical Process Parameters Using Modern In Situ Analytics
Simply put, the best way to control a critical process parameter (CPP) is to measure that specific parameter, integrate the live signal into your control system, and apply a smart feedback algorithm for an automated control loop. The challenge in doing this for bioprocesses has been due, in part, to the complex, highly dynamic, and variable nature of the process along with the lack of robust, scalable, and multiformat (single-use or multiuse) technologies that can monitor (in real time) such…
CO2, O2, and Biomass Monitoring in Escherichia coli Shake Flask Culture: Following Glucose–Glycerin Diauxie Online
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an important parameter in microbial cultures because it can inhibit or stimulate growth under certain conditions. In our experiment, we monitored Escherichia coli diauxie growth phases online and focused on dissolved CO2 (dCO2) and oxygen readings. We assessed diauxic growth in medium containing glycerin and glucose online with the SFR vario system (from PreSens), which optically measures oxygen, pH, and biomass in an Erlenmeyer flask. The shake flask contained an oxygen sensor spot and an optical…