Bioassay development is a complex process that must be undertaken with great rigor and attention to detail. Potency testing experts use a range of methods including cell-based and binding assays. Consistency and reliability of results over time are paramount. Well-developed and -characterized methods are the end result of much phase-appropriate development work that goes on in parallel with bioprocess and biotherapeutic product development. This eBook begins with BPI senior technical editor Cheryl Scott’s report from the Biopharmaceutical Emerging Best Practices…
Analytical
eBook: Potency Bioassays — Development, Trending,
Smart, Real-Time Quality Insights Boost Life Sciences Manufacturing
The COVID-19 pandemic has shone a light on restrictive business processes, information silos, and poor supply-chain visibility in many sectors. In biopharmaceutical manufacturing, for example, difficulties associated with product-quality management have been exposed and starkly felt. However, public healthcare measures over the past 18 months have put physical distance between team members, thereby hampering the usual form-filling, manual sign-offs and spreadsheet-based recordkeeping associated with monitoring traditional manufacturing processes. In some cases, a lack of formal face-to-face discussions in the workplace…
Mycotoxin Risk Determination: Measuring the Potential for Patient Exposure with Antithrombin Alfa Sourced from Transgenic Goat Milk
Antithrombin alfa is a recombinant human antithrombin developed as an anticoagulant treatment for people with hereditary antithrombin deficiency who are undergoing surgical or childbirth procedures (1). Marketed under the ATryn brand name by LFB SA (Les Ulis, France), antithrombin alfa was approved for use in adults by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in February 2009 (2). Antithrombin alfa is expressed in the milk of transgenic goats and purified through a multistep downstream process encompassing both filtration and chromatography.…
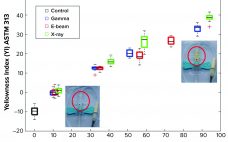
Supplementing Gamma Sterilization with X-Ray and E-Beam Technologies: An International Industry and Academia Collaboration
Ionizing-technology–based industries are growing rapidly around the world. The expansion is driven mostly by the technology’s myriad applications, including polymer crosslinking, medical device sterilization, food pasteurization, and phytosanitary treatment. Ionization also is used in the manufacture of some healthcare products such as medical devices and biopharmaceuticals. Industrial sterilization methods render single-use products and manufacturing components safe and ready for their intended use. ISO11137-1 describes the validation and routine control of a sterilization process for medical devices and mentions the three…
eBook: Sensors — Process Analytics for Modern Biopharmaceutical Workflows
To achieve quality by design in biopharmaceutical production, manufacturers need tools that can ensure the stability of critical process parameters (CPPs) and other performance indicators related to product critical quality attributes (CQAs). Over the past couple of decades, sophisticated process analytical technologies (PATs) have emerged to address such needs. Offerings are now abounding for single-purpose sensors that measure temperature, pressure, pH, glucose, protein concentration, or dissolved oxygen. New in-line formats are enabling such instruments to provide data in real time,…
Posttranslational Modifications and Their Control in CHO Culture
The Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line was first established by Theodore Puck in the 1950s and was used mainly for cytogenetics studies (1). Since the 1990s, CHO cells have increased in popularity as expression host cells because they can be adapted easily into suspension culture and genetically modified. The CHO cell line also has a human-like glycosylation profile (2–4). Therapeutic proteins undergo different posttranslational modifications (PTMs) during manufacturing. Some modifications can lead to undesired effects such as decreased stability,…
Analyzing Single-Use Polymers for Cell Culture Processes: Comparison of Cell Growth and Viability Test Procedures
The acceptance and implementation of single-use systems (SUS) or “disposables” has increased strongly in bioprocess development and biopharmaceutical manufacturing over the past two decades. Typically, suppliers provide SUS presterilized and ready to use. Using SUS eliminates time-consuming and expensive cleaning procedures (which often require corrosive chemicals and a large amounts of water) and removes the need to perform cleaning validation between batches. The application of SUS reduces the risk of product cross-contamination and increases product and patient safety (1–5). Polypropylene…
eBook: Diagnostics — Developing Rapid and Accessible Testing Solutions
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought myriad economic disruptions, social complications, and public-health calamities to the world. They have understandably overshadowed the silver lining of boosting biomedical science and technology in the realms of infectious disease, oncology, and more. But alongside the much-publicized commercial debut of novel vaccine technologies have come promising advances in medical diagnostics. In this eBook, BPI’s senior technical editor brings together perspectives from industry, academia, and expert organizations to highlight some of the latest diagnostic methods and…
Automated Process Control Based on In Situ Measured Glucose Concentration
A process analytical technology (PAT) strategy involves defining critical process parameters (CPPs) of a biomanufacturing process that influence critical quality attributes (CQAs) and controlling those CPPs within defined limits. Doing that enables consistent product quality and helps companies reduce waste and costs. Glucose is an important CPP in bioprocessing and cell therapy. Glucose often is fed as a bolus addition based on daily off-line measurements, but that can lead to high glucose fluctuations and to excessive glucose feeding, which can…
Finding the Right Partner for Outsourced Cell-Line Development
The successful commercialization of a biopharmaceutical product begins with a robust and productive cell line. Inefficient cell-line development (CLD) can lead to costly delays and roadblocks. For that reason, small, new, and virtual companies — and even established and mid-size companies — often seek the support of outsourcing partners to develop their cell lines. Outsourcing CLD activities can ease many pressures associated with manufacturing new biotherapeutics. The benefits of outsourcing CLD and associated processes include access to specialized expertise and…