Getting biologic drugs through development and into clinical proof-of-concept studies quickly and efficiently is critical for success in the biopharmaceutical industry. Implementing high-throughput approaches to both upstream and downstream process development is increasingly helping companies stay competitive. Innovative and highthroughput analytical technologies are needed to support rapid process development. The study reported herein focuses on innovative immunoassay platforms for impurity-removal monitoring of both host-cell proteins (HCPs) and leached protein A. HCPs come from host cells during cell culture production. Their…
Upstream Processing
The Case for a Standardized Assay to Test Suitability of Single-Use Systems in Cell Culture Applications
Increased commercial use of single-use systems (SUS) for large-scale biopharmaceutical production creates the need for consensus on industry best practices and standards for materials in SUS components. End users and suppliers are beginning to develop a shared vision of industry needs in such areas (1, 2). For example, highly visible efforts to harmonize extractables testing include contributions from groups such as the BioPhorum Operations Group (BPOG), Bio-Process Systems Alliance (BPSA), Parenteral Drug Association (PDA), ASTM, and ISPE. In addition to…
Development, Qualification, and Application of a Bioreactor Scale-Down Process: Modeling Large-Scale Microcarrier Perfusion Cell Culture
Qualified scale-down models of large-scale cell culture processes are essential to conducting studies for applications such as investigating manufacturing deviations, enhancing process understanding, and improving process robustness. For example, scale-down models can be used for raw material investigations as well as evaluation and qualification of new good manufacturing practice (GMP) cell banks for manufacturing implementation. Process characterization studies are performed also with qualified scale-down models to improve process consistency (1, 2). Often it is impractical to conduct investigational studies at…
Heading for a CHO Revolution: The Need for Cell Line Engineering to Improve Manufacturing Cell Lines
The first recombinant protein licensed for use by the United States Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) was human insulin in 1982 (1). That approval was followed in 1987 by the development of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), the first complex glycosylated protein generated in mammalian cells to be licensed for therapeutic use. Since then, this area of biology has rapidly expanded in clinics: The FDA approved an average of 15 new biological entities every year between 2006 and 2011 (2).…
Accelerating Biologic and Biosimilar Drug Development: Ready-to-Use, Cell-Based Assays for Potency and Lot-Release Testing
With the drug industry’s expanding emphasis on biologics, the need for robust cell-based assays has grown at all stages of development. Requirements for efficacy, quality, and potency testing often demand a complex set of bioassays and/or cell-based assays for new therapeutics or biosimilars. Developers of the latter have found this need for cell-based assays to be particularly challenging. Commercially available, ready-to-use cell-based assays provide a robust functional response from specific therapeutic targets. They can significantly shorten assay development time while…
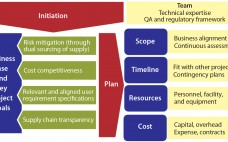
A Risk-Based Approach to Supplier and Raw Materials Management
Ensuring a continuous supply of safe medicines is a key objective for the pharmaceutical industry and health authorities alike. A critical component to that end is maintaining a reliable supply of qualified raw materials (RMs) used in drug production. However, changes in suppliers, their processes, their providers, and consequently the materials they supply can occur (for a number of reasons) at any time during the life cycle of drug production. A product-supply organization therefore must be prepared to address such…
Experiences with a Benchtop-Scale Glass Bioreactor: Engineering Data and Cultivation Results
Animal cell lines (the dominant expression systems in biopharmaceutical production processes) are mostly cultivated in stirred bioreactors (1). Although such bioreactors are widely accepted and applicable over a wide range of scales, engineering data for these systems are still lacking. Nevertheless, studies have shown that the correct choice of key parameters (e.g., power input, tip speed, mixing time, and oxygen mass transfer) can influence the growth of animal cell cultures (2). Therefore, detailed characterization is essential. It enables reliable scaling…
Comparison of Concentration Measurement Technologies in Bioprocess Solutions
Biopharmaceutical manufacturing involves complex process steps. Exacting production conditions are typically required to maximize the yield, purity, and quality of biological products. In recent years, process analytical technology (PAT) has been increasingly used to monitor key process and performance parameters in real time. That has enabled better control of production conditions. An important parameter required to achieve consistent results in many bioprocessing steps is solute concentration in process fluids. The Critical Need for Concentration Measurement Many biopharmaceutical manufacturing process steps require measuring…
Ask the Expert: Cell Culture Media Supplementation
with Dr. James Brooks (BD Biosciences) Improvements in cell culture media and supplementation have enabled significant advancements in bioproduction titers. But optimization to meet the specific needs of individual production cell lines is key to achieving desired production and protein quality, especially for biosimilars. Not only is it desirable to achieve cost-effective levels of production, but quality characteristics also are essential — and for biosimilars must closely resemble those of the originator molecules. Fully chemically defined (CD) media formulations are…
Bioreactor Design for Adherent Cell Culture: The Bolt-On Bioreactor Project, Part 4 — Process Economics
The Bolt-on Bioreactor (BoB) project is an independent initiative developing and commercializing a bioreactor for efficient, automated culture of adherent cells for biopharmaceutical applications (1). After conducting thorough research on available culture systems for adherent cells, the BoB team believes that a successful alternative to existing devices must solve four major challenges: volumetric productivity (2), process automation (3), containment and sterility (4), and process economics. This month concludes a four-part series addressing each of those challenges while describing design features…