There has been a rapid rise in the number of positive clinical outputs from clinical studies based on gene and cell therapies. This is in addition to the licensing of products such as GlaxoSmithKline’s Strimvelis ex-vivo stem-cell therapy for treatment of severe combined immunodeficiency caused by adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA-SCID) in 2016 (1) — has led to an increase in demand for therapeutic vector manufacturing capabilities. Viral vectors are being used for an increasing range of conditions, including monogenetic conditions.…
Upstream Processing
Continuous Processes: Disposables Enable the Integration of Upstream and Downstream Processing
Despite decades of advancement in characterization analytics, biotherapeutics still are largely defined by the manufacturing processes used to make them. This linking of process to clinical results (and thus to commercial success) has made the biopharmaceutical industry somewhat risk-averse when it comes to the adoption of new technologies. That desire to “derisk” biomanufacturing through better process understanding — as well as the need to adapt to uncertainties in patient population size through process flexibility — in turn drives the need…
Difficult-to-Express Proteins: Resolving Bioprocessing Challenges with a Scalable Perfusion Bioreactor
Recent advances in protein engineering have identified new classes of complex biotherapeutics that challenge existing manufacturing platforms. These products have unique cell culture requirements that make them difficult to manufacture cost effectively. Industry standard bioprocessing platforms include large-scale (1,000–5,000 L) batch and fed-batch stirred-tank bioreactors. Historically, the powerhouse molecule of the biologics industry has been human IgG, which necessitates those large-scale platforms. Difficult-to-express proteins and other new modalities (including precision medicine and orphan drugs) have increased pressure on manufacturers to…
The Industry’s Hesitation to Adopt Continuous Bioprocessing: Recommendations for Deciding What, Where, and When to Implement
The US Food and Drug Administration has stated its appreciation of continuous bioprocessing (CBP), and some studies have shown that it can save manufacturers time and money. However, the bioprocessing industry is still reluctant to implement continuous bioprocessing right away. It will be interesting to see which companies will be among the first-movers to harness the competitive benefits. Although few biologics today are made using CBP-enabled equipment (e.g., advanced bioreactors), the industry is changing. For biologics already in production, it…
BioPhorum Operations Group Technology Roadmapping, Part 3: Enabling Technologies and Capabilities
Although great strides have been made over the past 20 years to increase the productivity and robustness of manufacturing processes for biopharmaceuticals, the cost and complexity of their development and manufacturing remain high, especially in comparison with those of small-molecule pharmaceuticals. Process improvements are required to increase patient access while maintaining the viability of an R&D-driven biopharmaceutical industry. Facility productivity, cost of goods (CoG), and capital investment all have significant margins for improvement. Such goals can be achieved not only…
Aggregation from Shear Stress and Surface Interaction: Molecule-Specific or Universal Phenomenon?
Exposure to solid–liquid and air–water interfaces during production, freezing and thawing, shipment and storage of protein therapeutics may be a contributing factor in their degradation (e.g., aggregation, fragmentation) (1, 2). Surface exposure, particularly during manufacturing processes, often is accompanied by various degrees and durations of shear stresses originating from fluid flow and acting on proteins at interfaces. The magnitude and duration of shear rates depends on velocity gradients within each solution and varies significantly among manufacturing steps. On the low…
How to Set Up a Perfusion Process for Higher Productivity and Quality
Biotherapeutic proteins usually are produced by either fed-batch or perfusion processes. Perfusion manufacturing can provide much higher levels of productivity than fed-batch systems can, thereby reducing production costs. A 2013 study showed that perfusion is more cost effective than fed-batch processes for most combinations of titers and production volumes (1). Moreover, because a perfusion process is much closer to steady state than is a fed-batch process, it often produces a more consistent product — especially for molecules that are sensitive…
Comparing Culture Methods in Monoclonal Antibody Production: Batch, Fed-Batch, and Perfusion
Recombinant protein manufacturing with Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells represents over 70% of the entire biopharmaceutical industry (1). In fact, human monoclonal antibodies (hMAbs) produced by CHO cells have played a major role in both the diagnostic and therapeutic markets for decades. One of the first human–mouse chimeric MAbs to obtain FDA approval was Roche’s rituximab treatment for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and rheumatoid arthritis. Since that approval in 1997, scores of chimeric, humanized, and human MAbs have gained…
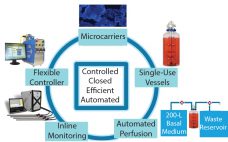
Platform Solutions for Cell Therapy Manufacturing
Advances in cell therapy have resulted in significant progress toward treating some widespread and difficult diseases, many of which represent unmet medical needs. For example, phase 3 clinical trials are already under way for therapies based on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), including therapies for graft-versus-host disease, acute myocardial ischemia, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (1–3). Successful cell therapy treatments for such afflictions will be not only significant medical breakthroughs, but also in very high demand. However, their commercialization is…
Buffers in Biologics Manufacturing
Biotechnology has enabled commercialization of protein-based drugs including insulin, growth factors, blood factors, and antibodies. Production and purification of such biologic products require different buffers for pH control and stabilization of reactions in different steps during biomanufacture. These processes include cell culture production (the “upstream” phase), purification (the “downstream” phase), and a final phase in which excipients are introduced to the drug substance to create a drug product (“formulation and storage”). In upstream processes, buffers are primarily used for their…