Recombinant monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) maintain their ranking as the best-selling class of biologic drugs. The introduction of high titer bioprocessing for the majority of these MAb products has focused efforts towards maintaining desired quality attributes and reducing time to market. Furthermore, patents covering several blockbuster MAbs and the expression technologies, which facilitate their high-level expression, are due to expire over the next decade. A wave of second generation or “follow-on” biopharmaceuticals/bioprocesses will therefore be vying for market share and regulatory approval. Consequently, should biopharmaceutical manufacturing companies rely on traditional “platform” methods of cell line development (CLD), which are well known but yield extensive variation and unpredictable stability of expression, or invest in emerging technologies, which offer the potential of greater reproducibility and speed? Enabling technologies in this area include host cell engineering, engineered expression vectors, and rapid transient gene expression. Given the well-known mantra “the product is the process”, implementation of these disruptive technologies will require a thorough understanding of how changes at the CLD-phase affect key production process characteristics such as high cell-specific productivity, correct product processing and rapid cell proliferation. Traditionally, CLD optimisation is carried out using a lengthy trial-and-error approach where cells are treated as a “black box” and characteristics are iteratively improved. Further advancement in CLD is therefore likely to benefit from the tools of systems biology. These tools will ensure that future CLD manipulations will be informed by an understanding of the genetic, regulatory, and metabolic networks that determine key process characteristics during a production process.
Sponsored Content
Regulation of cell apoptosis by insulin and IGF-I
An increase in the number of cells growing in cell culture is the result of two opposing effects: an increase in the number of cells that traverse the cell cycle and divide into two daughter cells (mitosis), or a decrease in the number of cells that die according to different modalities, the most prominent one being apoptosis (1), or both. Insulin and IGF-I are both capable of facilitating cell progression through the cell cycle, and of inhibiting apoptotic mechanisms. In…
Monoclonal Antibody Purification with a High Capacity Protein A Resin
“Protein A resins constitute a substantial cost in state-of-the-art mAb purification processes. Factors such as operating cycles, capacity, and mAb titer can have an impact on total costs associated with mAb purification. The purification of a monoclonal antibody from crude feed stock using TOYOPEARL® AF-rProtein A HC-650F, a high capacity protein A resin from Tosoh Bioscience, show that this particular high capacity protein A resin delivers highly pure antibodies at yields approaching 90%.”
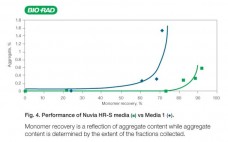
Introducing Nuvia HR-S Chromatography Media
Nuvia HR-S media is a new strong cation exchanger that has been optimized for particle size and chemistry that provides exceptional resolution and high recovery. Nuvia HR-S media demonstrates fast mass transfer kinetics, excellent flow characteristics, and robust chemical stability against common caustic cleaning protocols. Its excellent scalability gives process developers the confidence that results obtained on the bench will be reproducible for large-scale downstream manufacturing. Nuvia HR-S media is the preferred solution for intermediate and final polish applications where…
TOYOPEARL AF-rProtein A HC-650F Host Cell Protein Removal
The following paper compares the host cell protein (HCP) removal capabilities of TOYOPEARL AF-rProtein A HC-650F, TOYOPEARL AF-rProtein A-650F, and another commercially available high capacity protein A resin.
An environmental life cycle assessment comparison of single-use and conventional bioprocessing technology
Single-use technologies offer an attractive option for biopharmaceutical manufacturing, but their environmental impact needs be considered. This paper documents the findings of a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) study comparing single-use and conventional bioprocessing technology for the production of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). The study examines the life cycle environmental impacts at 100 L, 500 L, and 2000 L. The results presented focus on the 2000 L production scale. This assessment was reviewed by a third-party review panel. The results demonstrate that…
Six Essential Workflow Steps for Paperless, Automated, End-to-End Environmental Monitoring
The consequences of microbiological contamination range from FDA warning letters through product quarantines and recalls all the way to plant shutdowns. This makes quality control, specifically microbiological and environmental monitoring (EM) a mission-critical priority for pharmaceutical and biotechnology drug manufacturing operations.
Are you currently struggling with integrating a home-grown, paper-based or semi-automated EM system to your LIMS only to find out that it’s error-prone and resource hungry? Are your current LIMS or IT systems over extended when it comes to customizing automated, paperless, mobile data capture and workflow management for EM? Are you searching for a proven, best-practices approach to automate EM and LIMS workflows and reporting in a cGMP environment without hindering new product development and production?
This whitepaper provides an overview of the essential workflow steps for implementing a paperless, automated, end-to-end environmental monitoring solution to increase productivity, reduce compliance risk and generate a healthy return on investment.
Scalable Method for Packing Chromatography Columns
Currently the bio-pharmaceutical industry is heading towards cost cutting, time saving and single use manufacturing approach. This has opened up a whole new market for disposable technologies. Pre-packed disposable chromatography columns are a best fit for preclinical and clinical stage Monoclonal Antibody (mAb) production and vaccine manufacturing processes which require quick turnaround times and aggressive validation respectively. This work describes development of pre-packed and ready to use chromatography columns to meet this need in the industry. A robust packing method…
Rapid Antigen Production in Pseudomonas fluorescens Utilizing a High-throughput, Parallel Processing Approach
Pseudomonas fluorescens, a Gram-negative bacterium, has been specifically developed as a protein production platform to enable rapid identification of strains capable of expressing high titers of soluble and active protein. PfÄ“nex Expression Technology (TM) employs a toolbox of engineered P. fluorescens host strains, including protease deficient mutants and chaperone/ foldase overexpressors combined with a set of expression vectors encoding a variety of transcription and translation regulators, as well as a collection of periplasmic secretion signals. High-throughput automated transformation, growth, and…
Expansion of T-cells using the Xuri Cell Expansion System W25 and WAVE Bioreactor 2/10 System
Immunotherapeutics include drugs and biologics that render therapeutic benefit by harnessing the power of the immune system. The promise of immune-mediated therapies is to target specificity with a consequent reduction in off-therapeutic effects. Immunotherapeutic products can be classified broadly into (1) active immunotherapy (therapeutic vaccines), (2) adoptive cellular immunotherapy (transfer of immune cells, genetically modified T-cells or precursor cells) or (3) passive immunotherapy (antibody or receptor ligand administration). Recent scientific advances have led to clinical trials of both active and…