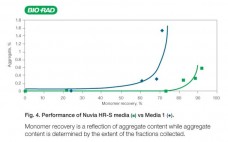
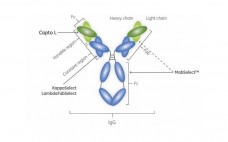
Nuvia HR-S media is a new strong cation exchanger that has been optimized for particle size and chemistry that provides exceptional resolution and high recovery. Nuvia HR-S media demonstrates fast mass transfer kinetics, excellent flow characteristics, and robust chemical stability against common caustic cleaning protocols. Its excellent scalability gives process developers the confidence that results obtained on the bench will be reproducible for large-scale downstream manufacturing. Nuvia HR-S media is the preferred solution for intermediate and final polish applications where…
BPI White Papers
TOYOPEARL AF-rProtein A HC-650F Host Cell Protein Removal
The following paper compares the host cell protein (HCP) removal capabilities of TOYOPEARL AF-rProtein A HC-650F, TOYOPEARL AF-rProtein A-650F, and another commercially available high capacity protein A resin.
An environmental life cycle assessment comparison of single-use and conventional bioprocessing technology
Single-use technologies offer an attractive option for biopharmaceutical manufacturing, but their environmental impact needs be considered. This paper documents the findings of a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) study comparing single-use and conventional bioprocessing technology for the production of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). The study examines the life cycle environmental impacts at 100 L, 500 L, and 2000 L. The results presented focus on the 2000 L production scale. This assessment was reviewed by a third-party review panel. The results demonstrate that…
Six Essential Workflow Steps for Paperless, Automated, End-to-End Environmental Monitoring
The consequences of microbiological contamination range from FDA warning letters through product quarantines and recalls all the way to plant shutdowns. This makes quality control, specifically microbiological and environmental monitoring (EM) a mission-critical priority for pharmaceutical and biotechnology drug manufacturing operations.
Are you currently struggling with integrating a home-grown, paper-based or semi-automated EM system to your LIMS only to find out that it’s error-prone and resource hungry? Are your current LIMS or IT systems over extended when it comes to customizing automated, paperless, mobile data capture and workflow management for EM? Are you searching for a proven, best-practices approach to automate EM and LIMS workflows and reporting in a cGMP environment without hindering new product development and production?
This whitepaper provides an overview of the essential workflow steps for implementing a paperless, automated, end-to-end environmental monitoring solution to increase productivity, reduce compliance risk and generate a healthy return on investment.
Anticipating Success: Meeting the Inherent Challenges of Complex Drug Substances
Realizing the full potential of a novel injectable drug compound is no small task. In the months and years that lead from the exciting discovery phase to the rigorous demands of a commercial launch, unexpected scientific and technical challenges can slow development to a halt, often at key stages. A careful, systematic approach to identifying where and why these roadblocks can occur is fundamental to staying on course. Just as important is a robust, repeatable process design focused on retaining…
Designing Quality into the Product: Early Developability Assessment in Biopharmaceutical Development
The ultimate objective in the development of any new therapeutic candidate is the validation of its mechanism of action and therapeutic efficacy in a clinical setting. Three important areas of product development critical to determining the success of a new drug candidate are: manufacturing, safety, and delivery of the product to patients. Early attrition observed during preclinical stages can often extend development timelines or require additional process optimization, therefore costing the developer more time and money. It is desirable to…
Validation of the New Single-Use Freeze-Pakâ„¢STS Storage and Transport Solution Containers
Production of biotherapeutics whether for clinical development or large scale manufacturing campaigns intended to be converted to final drug product often involves frozen storage. Frozen storage provides manufacturing process flexibility while enabling long-term product stability. Products are frozen and stored using a variety of technologies including stainless steel vessels, bottles, carboys and single-use bags. Use of bags has become popular due to their low investment cost and process flexibility attributes. Single-use bags intended for freezing and storage are often made with films using EVA and/or LDPE with product routinely blast frozen and stored to -30°C in a cold storage warehouse. During freezing and transport, the bags will typically experience temperatures well below -30°C ranging from -50 to -80°C. Under these conditions, the bags have to endure a wide variety of stresses (film brittleness, volume expansion, etc.) impacting integrity. With applications (like working cell banks for example) requiring lower temperatures for maintenance of long-term product stability, frozen storage films and containers designed for these conditions are needed. The new single-use Freeze-Pak™STS (FP-STS) frozen storage and transport solution containers from Charter Medical, Ltd. are manufactured using a unique polyolefin monolayer film designed for freezing applications The FP-STS bags (including tubing and connectors) have been validated for storage to -80°C, while the Freeze-Pak™ film remains flexible to temperatures as low as -196°C. The new Freeze-Pak™ STS bags deliver the flexibility and durability required for frozen storage and transport.
E. coli Cultivation in a 12L and 120L CELL-tainerâ„¢ Single-Use Bioreactor
Single-use bioreactors are usually applied in the biopharmaceutical industry for mammalian cell culture processes. For microbial processes, concepts like the CELL-tainer® technology allow comparable gas-liquid mass transfer rates like in stirred tank reactors. In the CELL-tainer, the rocking motion of the bag is generated with a combination of a vertical and horizontal movement. Due to a 2-D rocking motion, the turbulence in the liquid is intensified. Thus, volumetric oxygen transfer rates (kLa) of over 400 h-1 could be achieved. Recently, the successful scale-up of an Escherichia coli nutrient-limited fed-batch cultivation from the 15 L to the 150 L scale in the CELL-tainer single-use bioreactor has been conducted. A final biomass concentration of 45 gL-1 within 24 hrs was obtained in cultivations proving the general suitability of this reactor concept for the application of bacterial processes. The combination of intelligent software sensor control strategies and currently improving (single-use) sensors will lead to a reduction of current drawbacks and improve control of bacterial fed-batch processes. The availability of single-use bioreactors for microbial cultivations widens their potential, not only in biopharmaceutical processing, but also as a pre-culture bioreactor for large scale processes and as a suitable tool in bioprocess development.
Selecting a Transfection Reagent for Large Scale Protein Production in Suspension 293 Cell Types
Decrease time to produce usable protein by maximizing target protein yields through transient transfection. The TransIT-PRO® Transfection Kit uses animal origin free components designed for high and reproducible nucleic acid delivery into suspension CHO and 293 derived cells. Since it is compatible with varied media formulations, the same media can be used for both transient and stable expression. The TransIT-PRO outperforms linear PEI in protein yield, while providing a cost-effective alternative to FreeStyle™ MAX and 293Fectin™ Transfection Reagents.
A Platform Approach for the Purification of Domain Antibodies (Dabs)
A three-step purification process for a Dab successfully developed and verified. The step yield ranged between 86% and 99%, giving a total process yield of approximately 81%. The ECP in the start sample was more than 200 000 ppm whereas the final sample contained only 5.5 ppm. The endotoxin content in the feed was approximately 2 million endotoxin units/mg of protein and the final sample was below the limit of quantification. Protein L leakage was undetectable in all samples. This…