Endotoxin ‚ÄĒ also known as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) ‚ÄĒ is a large molecule made up of a lipid and a polysaccharide portion found in the outer membrane of each Gram-negative bacterial cell. Examination of endotoxins is necessary for microbial and animal cell-culture operations that produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and vaccines. If a cell culture is contaminated with endotoxins, it could affect cell growth and function (thus potentially affecting product quality). Biopharmaceutical companies need to understand the endotoxin levels within their…
Process Monitoring and Controls
eBook: Raw Material Control Strategy — Leveraging Knowledge of Material Attributes and Data Analytics as Key Elements
Ensuring pharmaceutical quality begins with in-depth understanding of process/platform capabilities, which is informed by knowledge gained through product and process development, subject-matter expertise, and lessons learned from experience. And all outside factors that can affect manufacturing outcomes must be taken into consideration. Extra vigilance is necessary for understanding potential sources of variation and maintaining robust control strategies to ensure process consistency ‚ÄĒ and ultimately product quality for patients. Biomanufacturing unit operations require multiple raw materials that must be documented as…
Dissolved Oxygen Control Tuning for Cell Culture Applications
Proper tuning of dissolved oxygen (DO) controller proportional integral (PI) values is essential for optimal cell culture performance in a bioreactor. When DO-PI values are optimized, gas flows are smoothed, and foaming and cell stress are reduced. Traditionally, this tuning has been performed by using nitrogen gas to purge oxygen from a test solution, thus simulating oxygen demand. That method has several drawbacks, however. First, nitrogen gassing cannot simulate the high demands of high-density fermentation. Second, nitrogen competes with other…
Novel Integrated Raman Spectroscopy Technology for Minibioreactors: Accelerating Raman Model Building for Cell Culture Monitoring and Control
Raman spectroscopy is used widely in biomanufacturing as a process analytical technology (PAT) for monitoring analytes such as glucose and lactate (1). Predictive Raman models also can be used to control glucose concentration in cell cultures (2). The technique is becoming more popular for pilot- and manufacturing-scale bioreactors, but it only recently has been studied with minibioreactors for measuring analytes and producing predictive Raman models for feedback control (3) thanks to advances in integrated technology for automating sampling, analysis, and…
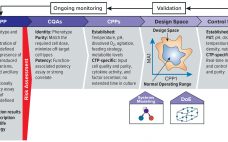
Quality By Design for Advanced Therapies: An Informed Route to Enhanced Late-Stage Clinical Success and Empowered Process Flexibility
As advanced therapies, including regenerative medicines, progress toward commercialization and market approval, early warnings from key opinion leaders (1, 2) regarding the importance of better understanding quality target product profiles (QTPPs) and critical quality attributes (CQAs) of such products have resounded ever louder (see the ‚ÄúTerminology‚ÄĚ box for definitions). Costly late-stage delays, redirections, and even abandonment of clinical programs can be linked to quality issues associated with inadequate understanding of process and product. Therefore, a review of the benefits of…
Bioprocessing 4.0 Accelerates Biological Research and Development Using Computer-Aided Biology
Computer-aided biology describes a growing ecosystem of tools that augment human capabilities in the laboratory. In this report we give two case study examples of how computer-aided biology has transformed industrial gene therapy bioprocessing. Read on to discover how Synthace‚Äôs Antha cloud-based software platform has enabled industrial collaborators Oxford Biomedica and the Cell and Gene Therapy Catapult to harness the power of Bioprocessing 4.0 by: incorporating new process analytical technologies (PAT), such as Raman Spectroscopy, into their unit operations automating…
A Future-Proof Solution for Bioprocess Applications: The New Eppendorf Flexible Bioreactor Control System Evolves with the Changing Needs of Modern Biotechnology
In the biopharmaceutical industry‚Äôs quality-by-design (QbD) era, optimizing tools for process monitoring and control has become a major focus of development and manufacturing. This increased attention brings challenges into upstream and production processes, cell-line development, process optimization, and scale-up. Suppliers of equipment and technologies also focus on helping their customers improve development timelines. With that increased attention to speed, they are offering tools such as the Eppendorf SciVario twin bioreactor control system to streamline development and maximize flexibility. BPI spoke…
Trends in Data Analytics As Organizations Undergo a Digital Transformation
The biopharmaceutical industry is in the midst of an exciting transformation as biologics experience massive growth ‚ÄĒ even outpacing the small-molecule segment (1). Biologics are predicted to comprise over a quarter of the pharmaceutical market in 2020 (2). At the same time, a plethora of new biologically derived therapy concepts ‚ÄĒ e.g., cell and gene therapies ‚ÄĒ are in development. Some biologics classes have become mainstream ‚ÄĒ e.g., monoclonal antibodies ‚ÄĒ with biosimilars entering the market and contract manufacturing organizations…
eBook: Automation ‚ÄĒ The Value of Plug-and-Play Automation in Single-Use Technology
The biopharmaceutical industry‚Äôs movement away from large-scale, fixed-tank facilities to flexible facilities featuring single-use technologies (SUTs) has demonstrated the value of modular equipment and agile process design. SUTs have proven to be clear advantages to end users because those technologies enable quick facility build and changeover times. But linking SUT equipment with equally flexible automative technology has been difficult. Herein a group of automation experts from the BioPhorum Operations Group (BPOG) elaborate “plug-and-play” principles and introduce a supervisory control system…
Determining Control Chart Limits for Continued Process Verification with Autocorrelated Data
Control charts are used to assist in process monitoring activities. They use an estimate of central tendency (the overall mean) and variation (the standard deviation). Sample standard deviations (S) tend to underestimate process standard deviations (ŌÉ) when they are calculated using limited sample sizes of independent results (1). For this reason, the unbiasing constant c4 is used as a divisor when calculating Shewhart control-chart limits. If data used for control charting are positively autocorrelated, that tends to underestimate ŌÉ further…