Monoclonal antibody manufacturing is at a crossroads. Biomanufacturers could continue exploring new technologies and fine-tuning proven systems such as mammalian cell expression systems in stirred-tank bioreactor fed-batch cultures. But some experts say an opportunity is arising to turn the industry on its head by taking lessons from other branches of bioprocessing, such as the industrial enzyme sector. Drug makers are criticized often these days for the high prices of their products. The lay media, governments, payers, and patients themselves all…
MAb
eBook: The Commercial Expression Systems Market — What Has Changed in the Past Decade
A decade ago, BioPlan Associates prepared the findings of its 2008 directory of expression system technologies that were being promoted or considered likely to be suitable for commercial licensing for biopharmaceutical manufacturing (1). Due in part to the relatively slow advances in this critical area of bioprocessing, this study remains perhaps the only directory of biopharmaceutical-relevant expression systems available for licensing. Here I discuss aspects of related bioprocessing technologies that have and have not changed in the past decade. Expression…
eBook: Of Microbrews and Medicines — Understanding Their Similarities and Differences in Bioprocessing Can Help Improve Yields and Quality While Reducing Cost
Meeting a biopharmaceutical scientist or engineer who proclaims a love for brewing is not surprising. Perhaps it’s because of the challenge of mixing raw ingredients together and waiting patiently for the final product, maybe it’s the hands-on nature of the equipment or the data analytics entertainment, or it just might be the simple joy of creating something. Whatever attracts a scientist or engineer to making medicines and/or craft brews, a surprising number of principles hold true for both bioprocesses despite…
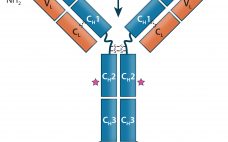
Therapeutic IgG-Like Bispecific Antibodies: Modular Versatility and Manufacturing Challenges, Part 1
Antibody-based immunotherapy has advanced significantly since 1986, when the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first mouse monoclonal antibody (MAb) for clinical use: Orthoclone OKT-3 (muromonab-CD3). In the intervening years, researchers have applied the tools of genetic engineering to clone immunoglobulin G (IgG) genes into a number of expression vectors. In the 1990s, the bioprocess industry was able to produce fully human antibodies in cultured cells. As of June 2017, the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA)…
Polysorbates, Biotherapeutics, and Anaphylaxis: A Review
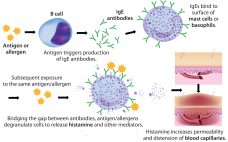
Rapidly increasing use of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) in the treatment of neoplastic, autoimmune, and inflammatory diseases has led to a dramatic increase in hypersensitivity reactions worldwide, complicating the use of MAbs as first-line therapies and limiting patient survival and quality of life (1). The origins of anaphylaxis are not well understood, though its mechanism is fairly straightforward (Figure 1). It is usually attributed to some undefined intrinsic property or properties of a biotherapeutic — despite the fact that biotherapeutic formulations…
Difficult-to-Express Proteins: Resolving Bioprocessing Challenges with a Scalable Perfusion Bioreactor
Recent advances in protein engineering have identified new classes of complex biotherapeutics that challenge existing manufacturing platforms. These products have unique cell culture requirements that make them difficult to manufacture cost effectively. Industry standard bioprocessing platforms include large-scale (1,000–5,000 L) batch and fed-batch stirred-tank bioreactors. Historically, the powerhouse molecule of the biologics industry has been human IgG, which necessitates those large-scale platforms. Difficult-to-express proteins and other new modalities (including precision medicine and orphan drugs) have increased pressure on manufacturers to…
The Industry’s Hesitation to Adopt Continuous Bioprocessing: Recommendations for Deciding What, Where, and When to Implement
The US Food and Drug Administration has stated its appreciation of continuous bioprocessing (CBP), and some studies have shown that it can save manufacturers time and money. However, the bioprocessing industry is still reluctant to implement continuous bioprocessing right away. It will be interesting to see which companies will be among the first-movers to harness the competitive benefits. Although few biologics today are made using CBP-enabled equipment (e.g., advanced bioreactors), the industry is changing. For biologics already in production, it…
Conditional/Inducible Gene-Expression Mouse Models Using Advanced Gene Editing
Transgenic mouse models have been an essential part of biomedical research for many decades. They have provided valuable insights in developmental biology, gene regulation, and our understanding of the genetic basis of human disease. And they play a critical role in drug discovery and development. Traditional methods to generate these mouse models entailed a milieu of disadvantages: e.g., low efficiency, high incidence of undesirable recombination outcomes, randomly and multiply inserted genes of interest, ectopic expression, gene silencing, and insertional mutations…
Buffers in Biologics Manufacturing
Biotechnology has enabled commercialization of protein-based drugs including insulin, growth factors, blood factors, and antibodies. Production and purification of such biologic products require different buffers for pH control and stabilization of reactions in different steps during biomanufacture. These processes include cell culture production (the “upstream” phase), purification (the “downstream” phase), and a final phase in which excipients are introduced to the drug substance to create a drug product (“formulation and storage”). In upstream processes, buffers are primarily used for their…
Special Report: A Strategy for Cost-Effective Capture Using Agarose-Based Protein A Resins
It is well recognized that the cost of Protein A resins is substantial. If a developmental monoclonal antibody (MAb) makes it to marketing approval and manufacturing, the high cost of purification using a Protein A resin is amortized over a large number of purification cycles, and the contribution to cost of goods is reduced to acceptable levels. However, a high percentage of clinical projects will fail, and the Protein A resin will be used only for a small number of…