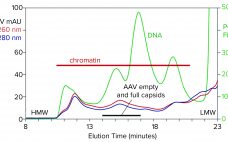
Although formulation and drug-product activities are critical to developing gene therapies, much remains to be learned about their degradation mechanisms, and firm criteria still need to be established for buffer and excipient selection. Sarathi Vijay Boddapati (associate director of formulation and drug development at Catalent Cell and Gene Therapy) joined BPI on 25 March 2021 to present what his company continues to learn about formulating gene therapies by adapting methods used for other biologics. Boddapati’s Presentation Adenoassociated virus (AAV) remains…
Cell/Gene Therapies
Preparing for Process Improvements: Discussions of the Cell Therapy Industry’s Supply Chain, Automation, and Control Needs
As editors, we are fortunate to have the opportunity to listen to biopharmaceutical developers and innovators discuss the intricacies of their work. Typically, we find that the best discussions come from asking two fundamental questions: What need did you observe in the industry that drove your work, and what technologies would help you do your job better? Over the past five years or so, the answers have shifted. Cell and gene therapy (CGT) innovators are focusing on increasingly complex diseases…
The Difficulties of Manufacturing Cell and Gene Therapies At Scale
From large-scale manufacturing of one-size-fits-all blockbusters to small-scale processing of personalized therapies, the biopharmaceutical industry has undergone a revolution over the past decade. Among the standout milestones is the development of advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs). More than 1,000 of these research-intensive therapies are progressing through clinical trials toward potential commercial manufacturing. Cell and gene therapies (autologous and allogeneic) are targeted for many incurable diseases and conditions, including autoimmune disorders and cancers. Despite the excitement about ATMP potential, developers and…
Manufacture and Regulation of Cell, Gene, and Tissue Therapies: Part 2 — Regulatory Guidances
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), and Japan’s Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) all offer support and guidance for developers of advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs). Some agencies have issued guidelines to help companies through different stages of product development — from research and development to marketing authorization and postauthorization activities. Such guidelines are updated regularly as more knowledge becomes available from the development and…
Viral Clearance in a Downstream AAV Process: Case Study Using a Model Virus Panel and a Noninfectious Surrogate
Over the past decade, adenoassociated virus (AAV) vectors have become established as leading gene-delivery vehicles. In 2017, the pipeline for gene therapies included 351 drugs in clinical trials and 316 in preclinical development (1–4). As those candidates advance, significant efforts are being made in process development and manufacturing for viral vectors, with the overall goal of reducing process impurities while maintaining the highest possible process yield. To address that goal, industry suppliers have developed innovative AAV-specific separation technologies. Thermo Fisher…
Rapid Development of Viral Vector Production Processes: Iterative Parameter Optimization
With recent developments and successes in cell and gene therapy, the biopharmaceutical industry is facing increased demand for safe and efficient delivery systems (1). Viral vectors, including adenoviruses (AV), adenoassociated viruses (AAV), and lentiviruses (LV), are among the most common delivery agents because they infect mammalian cells efficiently. Suspension cultures have become a popular choice for robust and scalable viral manufacturing systems. Using stable cell lines that integrate all or part of the viral production elements adds further benefits by…
Improving Cell Manufacturing Outcomes Using In-Line Biomarker Monitoring
Cell-based advanced therapies are changing modern medicine dramatically. Immunotherapies such as chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies are treating different forms of cancer. Gene therapies are reversing the course of inherited diseases, and tissue-engineered medical products are restoring, maintaining, and replacing damaged organs (1–4). The development of new advanced therapies is booming. As of January 2020, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has reported more than 900 investigational new drug (IND) applications for cell and gene therapy products. However,…
Optimization of Processes and Advanced Platforms for Viral Vector Processing
Viral vectors are synonymous with gene therapies, so their development, production, and processing are of upmost importance to all gene therapy researchers and manufacturers. Every year, I look forward to attending the Cell and Gene Bioprocessing and Commercialization conference in Boston and talking to leaders in industry and academia about their current approaches to advancing gene therapies. Like most other meetings this year, the conference was entirely online and had to provide a shortened agenda. Nonetheless, there was no shortage…
Manufacture and Regulation of Cell, Gene, and Tissue Therapies, Part 1: Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Control Challenges
Cell, gene, and tissue (CGT) therapies and other advanced-therapy medicinal products (ATMPs) have made tremendous progress over the past decade. They are different from other biologics and small molecules because of their inherent complexity and variability. Although many unknowns remain about the development of these products, their clinical success has enabled the CGT therapy and ATMP fields to advance rapidly. We are seeing an increase in the number of marketing authorization applications (MAAs) filed in the European Union and new…
Streamlining Industrial Purification of Adeno-Associated Virus
With its first licensed therapeutic now marketed worldwide (1), adeno-associated virus (AAV) has become a preferred vector for gene therapy. However, unlocking its full potential still poses challenges, many of which are associated with purification. The first involves the transition from upstream to downstream processes. AAV-bearing lysates are laden with debris that foul filtration media and limit or prevent concentration. Another challenge involves reduction of soluble host-cell DNA, which is complicated by its strong association with nucleoproteins. A third involves…