The rapidly developing global cell therapy market poses numerous industry challenges for drug development, process scalability, commercialization, and patient safety. The processes of procuring donated human tissue for clinical applications are fraught with many technical, ethical, and legal issues. Allogeneic cell therapies involving primary cell types such as bone marrow mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (BM-MSCs), hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs), and T and natural killer (NK) cells for immunotherapy applications are especially challenging because of the vigorous process of screening…
Cell/Gene Therapies
Driving Cell Therapy Innovation: Applying Key Lessons from the Evolution and Commercialization of Protein-Based Therapies
After many trials and errors — and milestones — regenerative medicine has become a mainstream part of the biopharmaceutical industry, supported by at least 670 companies and clinics of all sizes. But many experiences in the protein-based industry segment can be leveraged to further improve successful commercialization of advanced therapies. At the 2017 Biotech Week Boston conference, BioProcess International editor in chief Anne Montgomery hosted a panel of industry cell therapy experts to discuss key lessons that can be gleaned…
Cell Expansion with Dissolvable Microcarriers
In recent years we have seen an exponential increase in the number of companies testing and validating new regenerative medicine products. Many of these products are reaching late-phase trials with the potential to receive final approval and marketing authorization from regulatory agencies such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA). In the past several years, we have seen successful launches of regenerative medicine products, including Holoclar (Holostem Advanced Therapies), Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel, Novartis), Yescarta…
eBook: Bioinks for Bioprinting — Three-Dimensional Printing in Research and Medicine
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is one method of digital biomanufacturing for both basic biological research and translational, clinical applications. The medical field has used it to create such constructions as 3D surgical models for preoperative planning, to assist surgeons in their procedure preparations, which improves postsurgical outcomes. Examples here include generation of cleft-palate models (1), orthopedic applications (2), and cardiovascular surgical planning (3). Other forms of 3D printing for biological applications — such as 3D bioprinting — go beyond such surgical…
Process Development of Microbial Plasmid DNA: Fast-Tracking with Modular Single-Use Minibioreactors
There has been a rapid rise in the number of positive clinical outputs from clinical studies based on gene and cell therapies. This is in addition to the licensing of products such as GlaxoSmithKline’s Strimvelis ex-vivo stem-cell therapy for treatment of severe combined immunodeficiency caused by adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA-SCID) in 2016 (1) — has led to an increase in demand for therapeutic vector manufacturing capabilities. Viral vectors are being used for an increasing range of conditions, including monogenetic conditions.…
The Cell and Gene Therapy Industry: Looking at 2016 and Beyond
Politically 2016 was surprising and dramatic here in the United Kingdom and elsewhere. Although it was not surprising for cell and gene therapies per se, the growth that we have seen in this industry has been pretty dramatic around the world as well. The industry has seen investors of all types maintaining their interest in cell and gene therapy, with a number of new deals made: e.g., Bluebird bio and Medigene signed a strategic R&D collaboration and licensing agreement, and…
Introduction: Process Issues in Cell, Gene, and Tissue Therapies
It’s hard to believe that just six years ago, BioProcess International published its first cell therapy supplement, which included just one article on “cell therapy bioprocessing” (1). At the time, most such processing was conducted in special clinical laboratories and academic institutions. As BPI continued to cover this relatively new segment of the biopharmaceutical industry, we heard more about “the product is the process” and “scale out instead of scaling up.” After many trials, errors, and milestones, regenerative medicine has…
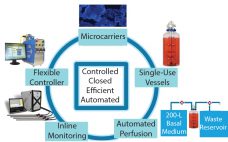
Expansion Platform Components
I first met Chris Mach at the Biotech Week Boston conference in October. We discussed the challenges that biomanufacturers are facing in cell expansion, especially in three specific areas in scale-up systems. View the full article below – Login Required
Platform Solutions for Cell Therapy Manufacturing
Advances in cell therapy have resulted in significant progress toward treating some widespread and difficult diseases, many of which represent unmet medical needs. For example, phase 3 clinical trials are already under way for therapies based on mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), including therapies for graft-versus-host disease, acute myocardial ischemia, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (1–3). Successful cell therapy treatments for such afflictions will be not only significant medical breakthroughs, but also in very high demand. However, their commercialization is…
Scalable Purification of Viral Vectors for Gene Therapy: An Appraisal of Downstream Processing Approaches
Gene therapy is the transfer of genetic material to a patient’s cells to achieve a therapeutic effect. Therapeutic DNA is largely delivered using viral vector systems based on adenoviruses (Ad), adenoassociated viruses (AAV), and lentiviruses (LV). With the application of such viral vectors as clinical therapeutics growing, scalable commercial processes (particularly for purification) are being investigated and optimized to best ensure that critical quality attributes (CQAs) are retained. Herein we review viral vector purification techniques and the effect of different…