There is an established, global pipeline of existing and upcoming monoclonal antibody (MAb) drugs that treat a wide variety of clinical indications. In MAb manufacturing, protein A chromatography is a proven downstream purification process, but there remains a need to reduce total costs while improving purity and yield. The Avantor J.T.Baker BAKERBOND PROchievA recombinant protein A chromatography resin advances the production of MAbs by providing different choices to biopharmaceutical supply chains. Offered both as a bulk resin and as prepackaged…
Downstream Processing
eBook: Process-Related Impurities — Emerging Strategies for Detection, Identification, and Management of Host-Cell Proteins
Host-cell proteins (HCPs) represent a major class of process-related impurities (PRIs) that are generated during biopharmaceutical manufacture. Although the vast majority of such proteins are removed from a drug substance during downstream purification, residual HCPs can remain in a finished drug product. Even in minimal concentrations, copurifying HCPs can pose safety risks and compromise protein-product yield, efficacy, and stability. Thus, regulatory agencies consider the presence of HCPs to be a critical quality attribute (CQA). Sufficient clearance of these impurities helps…
Ligand-Based Exosome Affinity Purification: A Scalable Solution to Extracellular Vesicle Downstream Bottlenecks
Novel therapeutics based on extracellular vesicles (EVs) recently passed a critical development milestone. During 2020, some of the first experimental EV products developed by biopharmaceutical companies entered human clinical trials (1–3). EVs are nanometer-sized, lipid-wrapped spheres released by almost every cell type in the human body. EVs are loaded with a cargo of proteins, lipids, and RNA, and they are tagged with surface markers that favor uptake by target cells. Thus, EVs are a key mode of cell-to-cell communication (4).…
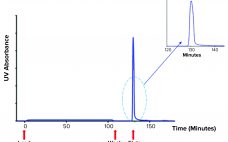
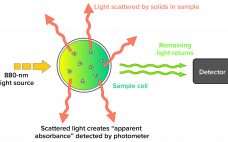
Validation of a Next-Generation Single-Use Turbidity System
Turbidity describes the relative clarity of a liquid as the result of suspended solids. Instruments that measure turbidity typically use a beam of light to detect particles by measuring the difference between the amount of light emitted from the light source and the amount that is received by a detector. Such measurements are affected by the size, shape, and number of particles in a sample of liquid because those solids scatter the incoming light, which provides an apparent absorbance that…
Eliminating the Analytical Bottleneck in Production and Purification of mRNA
COVID-19 has focused a spotlight on the ability of mRNA technology to accelerate vaccine development and approval (1). That same technology can hasten development and approval of other therapeutic classes, including cancer immunotherapy, protein replacement, and gene therapy. Fulfilling those opportunities imposes significant challenges on process developers and manufacturers to improve existing processes. Scale-up to produce millions of doses (tens of kilograms) compounds those challenges. Furthermore, every step of the journey requires high-performance analytical methods, to ensure patient safety and…
Ask the Expert: Selecting the Right Buffer Management Strategy
Although buffers are among the simplest materials used in bioprocessing, they are critical to biopharmaceutical manufacturing success. Buffer preparation, storage, and handling can require significant investments in time, labor, equipment, and facility space. Jenny Dunker, MSc, and Alexander Troken, PhD (global product managers for customized bioprocess solutions and for process liquids and buffers, respectively, at Cytiva), delivered an “Ask the Expert” presentation on 30 March 2021 to explore strategies for intensifying buffer management. Available Options Biopharmaceutical manufacturers often prepare buffers…
Predicting Viral Clearance in Downstream Process Development
As viruses can arise during the manufacture of biopharmaceuticals, regulatory agencies require viral clearance validation studies for each biopharmaceutical prior to approval. These studies are typically conducted in biosafety level (BSL)-2 facilities and require large capital and human resources. The use of an accurate, economical, and quantifiable noninfectious viral surrogate would enable downstream purification scientists to study viral clearance throughout process development. This report explores the use of a BSL-1 compatible, noninfectious MVM particles to predict viral clearance results over…
eBook: Chromatography Resins — Addressing Challenges in Biologic Purification Workflows
Although chromatography remains the backbone of downstream workflows, selecting appropriate technologies to optimize processes can be challenging. Numerous resin options are available, and the fact that most biologics are large, complex, and inherently unstable further complicates development of a robust workflow. Because chromatography processes can alter a biologic in ways that could impair its intended therapeutic function, investment in process development is critical. Techniques such as design of experiments (DoE) can be used to identify the best approach during process…
Virus Assay Variation Is the Main Source of Variation in Viral Clearance Studies: Retrospective Analysis of a Large Data Set
Biopharmaceuticals produced from mammalian cell cultures are susceptible to viral contamination. That risk is mitigated by applying complementary approaches. Those include extensive testing of cell banks, selecting low-risk raw materials, testing cultivations for viruses, and documenting the capacity of a purification process to inactivate and remove viral contaminants. The latter commonly is referred to as viral clearance and usually expressed as a log reduction value (LRV). Novo Nordisk has performed several viral clearance studies for different processes and process steps.…
Viral Clearance in a Downstream AAV Process: Case Study Using a Model Virus Panel and a Noninfectious Surrogate
Over the past decade, adenoassociated virus (AAV) vectors have become established as leading gene-delivery vehicles. In 2017, the pipeline for gene therapies included 351 drugs in clinical trials and 316 in preclinical development (1–4). As those candidates advance, significant efforts are being made in process development and manufacturing for viral vectors, with the overall goal of reducing process impurities while maintaining the highest possible process yield. To address that goal, industry suppliers have developed innovative AAV-specific separation technologies. Thermo Fisher…