As anyone who has focused on host-cell proteins as process contaminants can tell you, trying to purify a specific type of molecule from a large mixture of many similar molecules is like trying to find a few particular needles in a huge pile of varied needles. The same could be said for purifying viral vectors from cell culture fluids. When viruses are the products, unwanted viruses are contaminants that must be separated away — or better yet, prevented from being…
Downstream Processing
Viral Safety of Viral Vectors:
MAb Viral Clearance Studies:
A Substantiated Platform Approach for the IND Stage
Virus removal/inactivation is a major concern in the safety of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) and other recombinant-protein drugs. Some methods (such as nanofiltration and low-pH inactivation) have been demonstrated repeatedly by the industry to be reliable for most viruses, with >4 log10 removal. Based on my company’s virus-removal experiences with its MAb downstream-process platform, we propose a “bracketing method” — testing only samples that lie at the extremes of a design space — to prove proactively that small differences in operating…
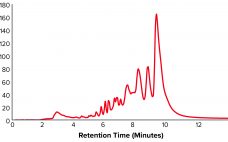
Risk Determination of Potential Mycotoxin Exposure to Patients: Testing Recombinant Human Factor VII from Transgenic Rabbits
Sevenfact eptacog beta is a new recombinant human factor VIIa (rFVIIa) developed by LFB SA in Les Ulis, France, as a bypassing agent (BPA) for treatment and control of bleeding in people with hemophilia A and B and inhibitors (1, 2). The product was approved for use in adults and adolescents by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 2020 (3). It is expressed in the milk of transgenic rabbits and purified through a multistep process using both…
Comparing Single-Use Multicycle Cake Filtration with Depth Filtration: Eliminating the Downstream Bottleneck
Over the past few decades, single-use (SU) technology has increased bioproduction efficiency significantly, especially with the introduction of disposable bioreactors in upstream processing. To keep pace with major developments and increases in upstream capacity, downstream processes also must increase capacity and efficiency. However, cell harvesting and downstream processing continue to present bottlenecks in manufacturing (1). Typical clarification processes are composed of primary and secondary clarification steps, such as centrifugation followed by depth filtration, respectively (1). Two sets of SU depth…
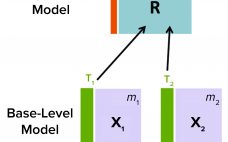
Advanced Data-Driven Modeling for Biopharmaceutical Purification Processes
Purification is an essential process in biopharmaceutical manufacturing that separates a therapeutic protein in its active form from impurities. A typical purification process consists of several chromatography unit operations, and each unit operation comprises multiple phases. During the operation of each step, continuous (time-series data per parameter for each batch) and batch data (one data point per parameter for each batch) are generated by in-line sensors installed in chromatography skids on the production floor and with at-line/off-line in-process samples, respectively.…
Development of a Universal Preparative Anion-Exchange Method to Purify Oligonucleotides
Oligonucleotide-based therapeutics have been studied over recent decades, and their promise as a new drug modality is now being realized. The growing interest in oligonucleotides is driven by their high potential for treating different medical conditions, the growing number of oligonucleotide drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an increased focus on personalized medicines, the development of therapies for rare diseases, and the wide adoption of nucleotide-based COVID-19 vaccines. Oligonucleotides are short, linear sequences of DNA or…
The Effect of Benzonase Endonuclease Addition to Purification of Sabin Poliovirus Type 3
During production of vaccines and viral vectors, the size and quantity of extracellular nucleic acids must be reduced using endonuclease enzymes. Merck/MilliporeSigma’s proprietary Benzonase endonuclease is a genetically engineered nuclease derived from the Gram-negative bacteria Serratia marcescens. It attacks and degrades all forms of DNA and RNA. It is manufactured under good manufacturing practice (GMP) conditions and has a drug master file (MDF) in place with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which can be cited in regulatory filings.…
New Antibody Formats on the Block:
More Complex Modalities Demand Innovation in Manufacturing and Purification
Some of the latest, most promising therapeutic developments in the biologics industry use antibody fragments — either separate functional subunits of antibodies or recombinant molecules that are composed of immunoglobulin domains. The most popular fragments are antigen-binding fragments (Fabs), variable single-chain fragments (scFvs), diabodies, and nanobodies. Such molecules raise several advantages over their parent molecules for upstream production but pose several challenges for downstream purification. To facilitate antibody-fragment capture, Tosoh Bioscience has developed Toyopearl AF-rProtein L-650F resin. Its ligand uses…
PendoTECH Sensors and Industry 4.0: Integrating a PendoTECH Single-Use Sensor System with a Digital Highway
Biopharmaceutical manufacturing is evolving with the progression of Industry 4.0. Industry 4.0 refers to the ongoing “fourth industrial revolution,” which is transforming modern manufacturing and production practices through the use of “smart” technology. This is appealing especially to the biopharmaceutical industry, where production can be a long, meticulous, complex process, and optimizing manufacturing procedures is critical for success. As a leading supplier of single-use technology for the biopharmaceutical industry, PendoTECH recently has explored how its products can be integrated easily…
The iCapTag Protein Purification Platform: Bridging Research and Manufacturing
Purification of recombinant proteins remains a critical challenge for applications ranging from basic biological research to the development and production of lifesaving biopharmaceuticals. At laboratory scales, the rapid purification of large numbers of new and uncharacterized protein targets effectively compels the use of affinity tags, which enable reliable purification using simple, established protocols with minimal optimization. Tags cannot be used for therapeutic applications, however, because of their potential for immunogenicity. Thus, for proteins other than monoclonal antibodies (which typically use…