Most recombinant monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) are produced by mammalian cells. Because biopharmaceuticals derived from mammalian tissue culture carry the risk of adventitious virus contamination, regulatory agencies expect risk-mitigation strategies to include validation of purification unit operations for their ability to clear viruses (1). Guidelines from the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) describe how to prove viral clearance in downstream purification processes using an orthogonal approach (2). Viral log10 reduction values (LRVs) are…
Downstream Processing
eBook: Development of a Representative Scale-Down UF/DF Model: Overcoming Equipment Limitations and Associated Process Challenges
Scale-down models (SDM) are physical, small-scale models of commercial-scale unit operations or processes that are used throughout the biopharmaceutical industry for validation studies, commercial deviation investigations, and postapproval process improvements. To support these studies, regulatory guidelines state that SDMs should be representative of the commercial process. For some downstream unit operations such as column chromatography, developing a representative SDM is straightforward because a linear scale-down approach can be used. However, developing a representative SDM for other downstream unit operations such…
New Dimensions in Single-Use Filtration
Whether viral vectors are clarified or the bioburden after cell harvest needs to be reduced to recover antibodies, such applications in biopharmaceutical production require large filtration areas. Single-use technologies are indispensable in many such bioprocesses. Although some single-use filter assemblies have reached their limits, Sartorius Stedim Biotech has made developments to revolutionize these production steps. Scale-Up Limitations in Single-Use technology Conventional stainless steel process systems have been established for decades in the pharmaceutical industry. They are the basis of safe…
Establishing Effective High-Throughput Contaminant Removal with Membrane Chromatography
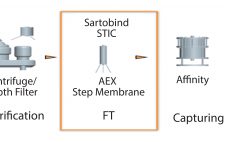
Bharat Serums and Vaccines Limited (BSV) in India conducted a study based on effective removal of host cell proteins (HCPs) from a recombinant hormone with a wide isoform profile in the acidic range imparting drug-product activity. Because the hormone and HCPs have a similar range of active species, the purification process with conventional chromatography resins had difficultly removing those HCPs from the active isoforms of the hormone. To solve that issue, a membrane chromatography technique was implemented. Our initial choice…
Streamlined Column-Packing Design for a New Commercial Launch Facility
To meet network demand for a commercial launch facility, Genentech (Roche) designed a new downstream train and built it within an existing building shell at the company’s Oceanside, CA, site. This downstream train included new technologies to allow for rapid technology transfer of different new products in the company’s drug pipeline. One technology that was pursued was the Axichrom column platform from GE Healthcare and associated column packing equipment to streamline column packing design. Here we focus on how a…
Addressing the Challenge of Complex Buffer Management: An In-Line Conditioning Collaboration
Read this article from scientists at Cytiva (GE Healthcare at the time of publication) to learn more about buffer preparation strategies now. Preparation and storage of buffers is a challenge for biopharmaceutical companies developing protein-based pharmaceuticals. The need for volumes of buffer to purify increasing upstream titers have become a major bottleneck in biopharmaceutical downstream processing. Italian biopharmaceutical company Kedrion Biopharma collects and fractionates blood plasma to produce plasma-derived therapeutic products for treating and preventing serious diseases, disorders, and conditions…
µPAC™ Microchip Chromatography: Better By Design
The boundaries of technology can be pushed significantly when insights from different fields reinforce each other. Based on in silico simulations demonstrating the importance of order on the efficiency of chromatographic separations, PharmaFluidics has combined expertise from the analytical chromatography and semiconductor chip manufacturing industries to create a new type of nanoscale liquid chromatography (LC) column. Conventional LC columns contain randomly packed beads as a stationary phase. By contrast, PharmaFluidics uses a lithographic etching process to create a perfectly ordered…
Recent Advances in Endotoxin Removal: An Upgrade to a Traditional Method and a New Adsorption Chemistry
Endotoxin contamination has been the bane of the bioprocessing industry since its inception. Endotoxins are everywhere: They are toxic and/or interfere with every type of therapeutic, diagnostic, and research product; they are indestructible within the limits of product tolerance; and they are difficult to remove (1–4). Beyond that, they interact with various biological species in ways that prevent accurate measurement (5, 6). Managing these issues has been a focus of the industry for at least half a century, yet it…
Moving DSC Downstream: Exploiting Differential Scanning Calorimetry As a Process Development Tool
The primary goal of biopharmaceutical process development is to determine what steps and conditions will maximize and optimize yields of purified product in the most reproducible, robust, and cost-efficient way. Characterized by high batch-to-batch comparability minimizing economic losses associated with batch failures, success relies on a thorough understanding of a given biological drug. Determining how its activity and stability are affected by processing and how to mitigate and control associated risks is advocated by a quality by design (QbD) approach.…
Continuous Processes: Disposables Enable the Integration of Upstream and Downstream Processing
Despite decades of advancement in characterization analytics, biotherapeutics still are largely defined by the manufacturing processes used to make them. This linking of process to clinical results (and thus to commercial success) has made the biopharmaceutical industry somewhat risk-averse when it comes to the adoption of new technologies. That desire to “derisk” biomanufacturing through better process understanding — as well as the need to adapt to uncertainties in patient population size through process flexibility — in turn drives the need…