Antithrombin alfa is a recombinant human antithrombin developed as an anticoagulant treatment for people with hereditary antithrombin deficiency who are undergoing surgical or childbirth procedures (1). Marketed under the ATryn brand name by LFB SA (Les Ulis, France), antithrombin alfa was approved for use in adults by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in February 2009 (2). Antithrombin alfa is expressed in the milk of transgenic goats and purified through a multistep downstream process encompassing both filtration and chromatography.…
Chromatography
Removing Aggregates and Fragments of Recombinant IgG1: Evaluating a Process Change to Implement Appropriate Chromatographic Media
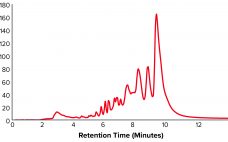
High–molecular-weight (HMW) and low–molecular-weight (LMW) product variants are critical quality attributes (CQAs) for monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) because they can cause severe immunogenic responses in human recipients. Aggregation is a common problem that can compromise the quality, efficacy, and safety of therapeutic proteins. It can occur at different stages in a biomanufacturing process: during cell-culture–based production, downstream process purification, drug-substance formulation, and storage of bulk drug substances or formulated drug products. Hence, the removal and control of MAb aggregates and fragments…
Improving the Performance of Tried-and-True Chromatography Technology
Efficient and effective downstream processing of biopharmaceuticals reduces manufacturing costs and time. Chromatography is the primary purification method for traditional recombinant proteins, monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), plasmid DNA, and viral vectors. Although interest in membrane separation technologies is growing, traditional resin-based solutions continue to be preferred when high-resolution purification is required. Ion-exchange chromatography (IEC)(e.g., cation and anion-exchange chemistries) and hydrophobic-interaction chromatography (HIC) are established bioseparation technologies. Cation-exchange resins are used widely for MAb polishing and aggregate clearance steps. Anion-exchange (AEX) resins…
Chromatography in mRNA Production Workflow
Rapid response to global pandemics requires the manufacture of billions of vaccine doses within months. This short timeline must allow for design and testing of active ingredients, development of production and purification processes, clinical evaluations, regulatory filings, and manufacturing. Existing purification methods often have been adopted from laboratory-scale techniques to allow rapid implementation, and those have provided adequate product quality. But future mRNA development will require optimized production and purification processes. Chromatography has been a workhorse of biomanufacturing for decades,…
Rethinking Chromatography
Dynamic trends in the biotherapeutic industry are shifting manufacturers towards new modalities and intensified production strategies. This development is supported by ongoing scientific and technical advances in both upstream and downstream processing steps. Downstream processing of new modalities requires chromatography technologies that can handle large, fragile molecules (such as mRNA and viral particles). To maximize speed and productivity, platforms supporting continuous processing will become essential. In this feature, Sartorius discusses current and future concerns for process chromatography operations. They then…
Development of a Universal Preparative Anion-Exchange Method to Purify Oligonucleotides
Oligonucleotide-based therapeutics have been studied over recent decades, and their promise as a new drug modality is now being realized. The growing interest in oligonucleotides is driven by their high potential for treating different medical conditions, the growing number of oligonucleotide drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an increased focus on personalized medicines, the development of therapies for rare diseases, and the wide adoption of nucleotide-based COVID-19 vaccines. Oligonucleotides are short, linear sequences of DNA or…
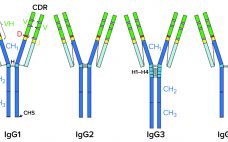
New Antibody Formats on the Block:
More Complex Modalities Demand Innovation in Manufacturing and Purification
Some of the latest, most promising therapeutic developments in the biologics industry use antibody fragments — either separate functional subunits of antibodies or recombinant molecules that are composed of immunoglobulin domains. The most popular fragments are antigen-binding fragments (Fabs), variable single-chain fragments (scFvs), diabodies, and nanobodies. Such molecules raise several advantages over their parent molecules for upstream production but pose several challenges for downstream purification. To facilitate antibody-fragment capture, Tosoh Bioscience has developed Toyopearl AF-rProtein L-650F resin. Its ligand uses…
Achieve Best-in-Class Purification with the Avantor J.T.Baker BAKERBOND PROchievA Resin
There is an established, global pipeline of existing and upcoming monoclonal antibody (MAb) drugs that treat a wide variety of clinical indications. In MAb manufacturing, protein A chromatography is a proven downstream purification process, but there remains a need to reduce total costs while improving purity and yield. The Avantor J.T.Baker BAKERBOND PROchievA recombinant protein A chromatography resin advances the production of MAbs by providing different choices to biopharmaceutical supply chains. Offered both as a bulk resin and as prepackaged…
Ligand-Based Exosome Affinity Purification: A Scalable Solution to Extracellular Vesicle Downstream Bottlenecks
Novel therapeutics based on extracellular vesicles (EVs) recently passed a critical development milestone. During 2020, some of the first experimental EV products developed by biopharmaceutical companies entered human clinical trials (1–3). EVs are nanometer-sized, lipid-wrapped spheres released by almost every cell type in the human body. EVs are loaded with a cargo of proteins, lipids, and RNA, and they are tagged with surface markers that favor uptake by target cells. Thus, EVs are a key mode of cell-to-cell communication (4).…
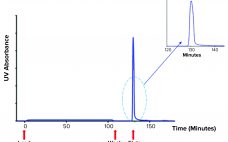
Eliminating the Analytical Bottleneck in Production and Purification of mRNA
COVID-19 has focused a spotlight on the ability of mRNA technology to accelerate vaccine development and approval (1). That same technology can hasten development and approval of other therapeutic classes, including cancer immunotherapy, protein replacement, and gene therapy. Fulfilling those opportunities imposes significant challenges on process developers and manufacturers to improve existing processes. Scale-up to produce millions of doses (tens of kilograms) compounds those challenges. Furthermore, every step of the journey requires high-performance analytical methods, to ensure patient safety and…