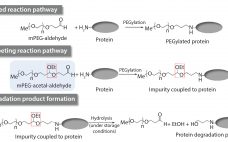
Impurities related to raw materials used for bioproduction can be inadvertently introduced into a manufacturing process, causing potential failure to meet in-process controls or release specifications. Unexpected impurities also can reduce yield and affect the quality, safety, and effectiveness of a final product (1). Raw-material impurities can originate from starting components or reagents used in manufacture. They can be generated in situ during synthesis or as degradation products. Impurities also can result from improper handling, packaging, and storage. Identification and…
Upstream Validation
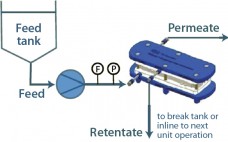
Using Technology to Overcome Bioprocessing Complexity: Advanced Concentration and Analytical Technologies Accelerate Development and Manufacture of mAbs, Vaccines, and Biosimilars
Unlike chemically synthesized drugs, whose structure is known and reproducible, biological drugs are derived from living cells and are sensitive, complex mixtures requiring cutting-edge biological technologies for their production. The growing importance of biosimilars in recent years is reflected in a corresponding rise in market value. The value of the global biologic therapeutic drug market reached approximately US$230 billion in 2014 and, according to BCC Research, will increase to nearly $390 billion by the end of 2019. This corresponds to…
CMC Strategy Forum Special Focus Series: Part 2 Product-Related Impurities, An Overview
Introduction by Cheryl Scott The CMC Strategy Forums focus on relevant chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) issues throughout the life cycle of a therapeutic and thereby foster collaborative technical and regulatory interaction. Forum chairs share information with regulatory agencies to help them merge good scientific and regulatory practices. Outcomes of forum meetings are published in BioProcess International and on the CASSS website. This process is meant to help ensure that biopharmaceutical products manufactured with advancing technologies in a regulated environment…
Monitoring Live Biomass in Disposable Bioreactors
Often simply referred to as capacitance, radio-frequency (RF) impedance has been used for over two decades to measure online biomass. It is generally regarded as the most robust and reliable method to monitor live-cell concentrations in mammalian cell culture (1). Many biopharmaceutical companies have now made the transition from conventional glass or stainless steel multiuse (MU) vessels to single-use (SU) bioreactors. Disposables are rapidly becoming the preferred platform for new processes requiring current good manufacturing practice (CGMP) compliance. At the…
Using Optical Sensors for Bioprocess Monitoring: A Measurement Technique for Bioprocessors
Over the past decade, the application of chemical optical sensors for bioprocess monitoring has gradually taken roots. Constant further development of this measurement technology and the possibility to manufacture such sensors in various designs (even for single-use applications) have led to new state-of-the-art devices for the biotechnology sector. Chemical optical sensors enable in situ, real-time monitoring of important culture parameters without sampling and therefore without disturbing a culture. Implementing this technology can decrease workloads and deepen knowledge about bioprocesses. In…
High-Throughput Methods Evaluation: Impurities Determination During Upstream and Downstream In-Process Development
Getting biologic drugs through development and into clinical proof-of-concept studies quickly and efficiently is critical for success in the biopharmaceutical industry. Implementing high-throughput approaches to both upstream and downstream process development is increasingly helping companies stay competitive. Innovative and highthroughput analytical technologies are needed to support rapid process development. The study reported herein focuses on innovative immunoassay platforms for impurity-removal monitoring of both host-cell proteins (HCPs) and leached protein A. HCPs come from host cells during cell culture production. Their…
Using Glycosidases to Remove, Trim, or Modify Glycans on Therapeutic Proteins
One of the most common posttranslational modifications of eukaryotic proteins is glycosylation. Glycosylation of proteins can affect many biological activities. For therapeutic glycoproteins, it can modify biological activity, targeting, trafficking, serum half life, clearance, and recognition by receptors (1, 2). For such reasons, biomanufacturers must monitor and characterize the glycosylation patterns of their recombinant therapeutic proteins (3, 4). Therapeutic proteins have two main types of glycosylation: N-linked glycans and O-linked glycans (5). Attachment of an N-glycan starts in the endoplasmic…
Development of a Novel Host-Cell Protein Assay: Supporting the Physcomitrella patens Expression System
Host-cell proteins (HCPs) constitute an inevitable impurity of biopharmaceutical products originating from recombinant-cell culture. HCPs are a heterogeneous mix of different proteins, their specific characteristics depending on the kind of organism used as an expression platform, on the “destination” of the expressed recombinant product (extra- or intracellular), and on the corresponding purification approach (1–3). Contamination of a final drug substance with residual HCPs could lead to immunogenic reactions in some patients who receive the drug product (DP). So a reliable…
Experiences with a Benchtop-Scale Glass Bioreactor: Engineering Data and Cultivation Results
Animal cell lines (the dominant expression systems in biopharmaceutical production processes) are mostly cultivated in stirred bioreactors (1). Although such bioreactors are widely accepted and applicable over a wide range of scales, engineering data for these systems are still lacking. Nevertheless, studies have shown that the correct choice of key parameters (e.g., power input, tip speed, mixing time, and oxygen mass transfer) can influence the growth of animal cell cultures (2). Therefore, detailed characterization is essential. It enables reliable scaling…
Foundation Elements for Cell Therapy Smart Scaling
Cell therapy is the injection of cellular material into patients. The injected cell-therapy product (CTP) usually consists of intact living cells. In recent years, cell therapies have evolved and matured, moving from academia to industry. That maturation is reflected in the number of open clinical trials that include the term cell therapy in their descriptions: To date, there are more than 8,700 open trials listed on the US National Institutes of Health’s online database (clinicaltrials.gov), most of which are in…