In the biopharmaceutical industry, continuous manufacturing is often cited as a method for increasing the productivity of bioprocesses (1). Compared with batch processing, it has the potential to enable production of more product within a smaller facility footprint — while improving product quality, particularly for sensitive and unstable molecules. Investigation into continuous methods is taking place for both upstream and downstream operations. For the full benefit of continuous processing to be realized, an argument has been made that cell culture,…
Upstream Development
Providing Lipids Boosts Protein Productivity: Testing a Feed Supplement with Multiple Cell Clones and Media Formulations
As the biologics (and now biosimilar) markets continue to grow, pressure increases on biomanufacturers to reduce cost of goods sold (CoGS). One way they can reduce cost is by increasing protein productivity in terms of protein titer per volume of culture. Media optimization is a key strategy for increasing protein productivity. In the past few decades, average titers across the industry have increased greatly — from <0.5 g/L in the 1980s to >3 g/L today, and it is not uncommon…
Advanced Protein Engineering Enhances Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing and Analytics
Production of proteins for pharmaceutical use is a complex, multistep process that requires technologies for purifying such molecules from highly complex biological mixtures. It also calls for reliable, cost-effective, high-throughput analytical techniques to determine protein quality and functionality to ensure the safety and efficacy of end-products. Mistakes in product development and manufacturing not only are immensely costly, but they can also put patients at risk. Many well-established processes and analytical tools are available for use in manufacturing antibody drugs (e.g.,…
Emerging Technology Trends in Biologics Development: A Contract Development and Manufacturing Perspective
For a contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO), process development and manufacturing of recombinant proteins must be linked because of tight timelines driven by client expectations. Those are in turn driven by a need for rapid progression to clinical testing. Early in process development, the choice of raw materials needs to reflect existing supply chain and manufacturing infrastructure, but remain suitable for scaling up to meet future needs. One approach is to establish platform processes for a class of molecules…
Quality By Design for Monoclonal Antibodies, Part 2: Process Design Space and Control Strategies
Process design space and control strategy are two fundamental elements of quality by design (QbD) that must be established as part of biopharmaceutical development and regulatory filings. Like all of QbD, they are interconnected and iterative. Both are based on knowledge gained during product and process development — but both need to be in place (in a potentially very limited form) when a company begins to manufacture drug substance for clinical trials. Part 1 of this discussion appears on pages…
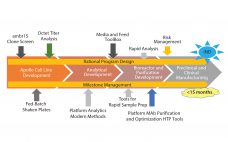
Rapid Development of High-Quality, Robust Mammalian Cell Culture Manufacturing Processes
With increasing industry emphasis on providing both rapid and robust processes, companies are reaping the benefits of new tools for risk management and process analytical controls. As a current example of these approaches, Fujifilm Diosynth scientists have accelerated the development process from gene to finish by shortening the timeline, incorporating quality by design (QbD) principles, and designing the process to be as robust as possible. When the Apollo mammalian expression cell line was introduced three years ago, the time from…
Quality By Design for Monoclonal Antibodies, Part 1: Establishing the Foundations for Process Development
The quality by design (QbD) modernized approach to pharmaceutical development is intended to provide regulatory flexibility, increased development and manufacturing efficiency, and greater room to innovate as well as improve manufacturing processes within defined ranges without obtaining regulatory approval first. QbD is a systematic developmental approach that starts with a clear goal in mind and emphasizes understanding of how variability in both process and materials affects a final product (1). Historically, product quality has been assured either with end-product testing…
Special Report on Continuous Bioprocessing: Upstream, Downstream, Ready for Prime Time?
Once an engineering curiosity and smallscale laboratory technique, continuous bioprocessing has evolved in just a few short years to a topic of intense and increasing interest to most bioprocessors. Critics point to a steep learning/adoption curve, but that is nothing new in biomanufacturing.Andrew Zydney is a distinguished professor of chemical engineering at Pennsylvania State University. He has noted these challenges facing continuous processing: commercially unproven unit operations (especially downstream), a lack of equipment robustness, sterility concerns, and uncertain development timelines…
Orbital Shaking and Acoustic-Resonance Mixing: Comparing Culture Characteristics
Production of recombinant proteins usually happens in suspension cultures, with oxygen limitation playing a major role. Oxygen and nutrition feeds are of great significance to aerobic suspension cultures. Oxygen is often the controlling factor in orbital shaken systems because oxygen transfer occurs only through diffusion, which is limited by gas-exchange surface and mixing characteristics. Here, we compare growth characteristics of microbial cultures in a standard shaken incubator with those of cultures in a RAMbio fermentation system, paying particular attention to…
Evaluating New Film for Single-Use Bags: Growth Performance Studies with Animal and Human Cells
In biopharmaceutical development and manufacturing processes, single-use technology has become widely accepted (1). Storage and cultivation bags are particularly common. They are fabricated from plastics consisting of multilayer films and are typically provided gamma-sterilized by suppliers (2). The bags offer several advantages such as savings in time and cost. Lowered contamination risk results from reduced cleaning and sterilization demands. However, some adverse effects of polymer films on cell growth and metabolism have been reported, both for storage and cultivation bags…