with Francesc Gòdia (chemical engineering professor at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona) Chemically defined media free of animal-derived components are required for bioprocess operations based on mammalian cells. Supplementation of commercial media with specific compounds was studied using a design of experiments (DoE) approach to screen the most efficient compounds for two cell lines and then determine their optimal conditions. DoE allowed simultaneous testing of several compounds to determine potential interactions among them in addition to their individual effects. Gòdia’s…
Upstream Development
Immunoglobulin Fc-Fusion Proteins Part 2: Therapeutic Uses and Clinical Development
The potential therapeutic value of many proteins — including enzymes, receptors, cytokines, blood factors and peptides — can be realized by fusing them to the Fc region of human immunoglobulin G. Of the 46 monoclonal antibody (MAb) and MAb-derivative products approved by the FDA to date as human therapeutics, 10 are Fc-fusion proteins (Table 2). Among approved products, several structural variations are represented (Figure 4). In BPI’s October 2014 issue, Part 1 of this review examined the structure and manufacturing…
Reducing Timelines in Early Process Development – Using a Multiparametric Clone-Selection and Feed-Optimization Strategy
The market for biopharmaceutical products remains highly attractive to small biotechnology companies and big pharmaceutical corporations alike (1). Most leading market products are made using recombinant technology (2). Pressures are continually increasing on process development groups to reduce development costs and timelines for taking new clinical products forward from product research bench scale into initial clinical evaluation studies. For many years a recognized critical bottleneck in development of products from mammalian cell lines was selection and isolation of stable, high-producing…
Immunoglobulin Fc-Fusion Proteins Part 1: Their Design and Manufacture
Over the past three decades, 45 monoclonal antibody (MAbs) and MAb-derivative products have been approved for therapeutic use in the United States (Table 1). One class of antibody derivatives is growing in importance: Fc-fusion proteins. Many biologically active proteins, including receptor ECDs (see “Abbreviations” box), cytokines, enzymes, and bioactive peptides have very short serum half lives because rapid renal clearance limits their exposure in target tissue (and, consequently, their pharmacological effect). The primary reason for fusing a biologically active protein…
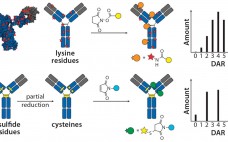
The Next Step in Homogenous Bioconjugate Development: Optimizing Payload Placement and Conjugate Composition
[Audio Recording] Bringing a new biologic drug to market is a long and expensive process, with research and development (R&D) cycles that can span up to 15 years and may cost over a billion dollars. Biologic drug development also involves significantly more complex manufacturing and CMC components than does development of small molecules. Nonetheless, the pharmaceutical industry is increasingly shifting its R&D efforts to focus on biologic drugs. According to a recent report from Tufts Center for Study of Drug…
Bioconjugation Reaction Engineering and Kinetics Simulation
Bioconjugates represent an important and growing class of pharmaceuticals that include PEGylated proteins, vaccines, and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) (1–8). Numerous protein conjugation techniques exist (9). Among the more important conjugation chemistries used for protein therapeutics are N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS), aldehyde, and maleimide (10–13). To date, process development of industrial biopharmaceutical conjugation reactions has largely been empirical in nature. Typically, many experiments testing different reaction parameters are required to identify optimal process conditions. In some instances, nonmechanistic statistical models can be used,…
Fine-Tuning ADCs for Best-in-Class Therapeutics
Antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) use the targeting ability of a monoclonal antibody (MAb) to deliver a highly biologically active drug to diseased cells while sparing healthy cells, creating potent and effective therapies. This emerging class of novel drugs currently focuses almost exclusively on cancer treatment. Two blockbuster ADCs — brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris from Seattle Genetics) for treatment of rare lymphomas and ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla from Genentech/ Roche, manufactured by Lonza) for treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer — have improved treatment…
Automated Mini Bioreactor Technology for Microbial and Mammalian Cell Culture: Flexible Strategy to Optimize Early Process Development of Biologics and Vaccines
The use of mammalian and microbial cells in the production of biologics and vaccines is well established, and the majority of the top 10 drugs are now manufactured in this way. There is a significant and growing pipeline of new biologics (1), which in combination with increased pressure on cost reduction and generic competition from biosimilars (2), means that many biopharmaceutical companies are looking for ways to improve productivity in their development laboratories to ensure that upstream processes are efficient…
Design of Experiments with Small-Scale Bioreactor Systems: Efficient Bioprocess Development and Optimization
Design of experiments (DoE) is one of the most valuable techniques for organized and efficient planning, execution, and statistical evaluation of experiments. Although a DoE investigation can be completed using several runs in one bioreactor, small-scale bioreactor systems designed for parallel operation (such as the ambr15 or ambr250 systems) provide the optimal basis to economically realize a series of experiments. Because of the multitude of interdependent parameters involved in applications such as cell line development, culture media screening, and the…
Consistently Superior Cell Growth: Achieved with New Polyethylene Film Formulation
During the past decade, single-use bioprocessing bags and bioreactors have gained a significant foothold in the biopharmaceutical industry because they offer a number of advantages over traditional stainless steel equipment, especially for clinical production, multiproduct facilities, and emerging economies. At the same time, some companies are concerned that plastic materials might release potentially toxic substances that could affect cell growth and product titers (1). In a worst-case scenario, they could even compromise drug safety when a company uses disposable bags…