Regardless of the industry and product being manufactured, continuous processing has demonstrated numerous benefits. In addition to smaller manufacturing footprints, reduced material consumption and waste generation, increased efficiencies, and lower capital and operating costs continuous manufacturing typically leads to more consistent processes and product quality. In the pharmaceutical industry, the latter two attributes align perfectly with FDA’s Quality by Design (QbD) and process analytical technology (PAT) initiatives. The challenge is determining how to apply these concepts in practice. Applying the…
QA/QC
Using Technology to Overcome Bioprocessing Complexity: Advanced Concentration and Analytical Technologies Accelerate Development and Manufacture of mAbs, Vaccines, and Biosimilars
Unlike chemically synthesized drugs, whose structure is known and reproducible, biological drugs are derived from living cells and are sensitive, complex mixtures requiring cutting-edge biological technologies for their production. The growing importance of biosimilars in recent years is reflected in a corresponding rise in market value. The value of the global biologic therapeutic drug market reached approximately US$230 billion in 2014 and, according to BCC Research, will increase to nearly $390 billion by the end of 2019. This corresponds to…
Critical Factors for Fill–Finish Manufacturing of Biologics
Over recent decades, protein-based therapeutics have emerged as key drivers of growth in the pharmaceutical industry. Drug development pipelines have filled with biologics, and a handful of monoclonal antibody (MAb) products have become some of the best-selling drugs around the world. Production of biotherapeutics is often challenging because of the inherent instability of these large, complex molecules. Their fragile nature has forced manufacturers to change how bulk drug substances (BDSs) are handled and final drug product is formulated, sterile filtered,…
Clearance of Persistent Small-Molecule Impurities: Alternative Strategies
Small-molecule impurities that bind to and copurify with protein biopharmaceuticals traditionally have been removed using bind-and-elute (BE) chromatography. However, that approach may be undesirable for a number of reasons. For instance, it may present a facility-fit challenge or provide a lower process yield than what is acceptable. A common scenario in which BE chromatography may be undesirable is in removal of unreacted conjugation reagents. Bioconjugates represent an important and growing class of pharmaceuticals that include PEGylated proteins, vaccines, and antibody–drug…
Best Practices for Critical Sterile Filter Operation: A Case Study
A number of regulatory guidelines recommend preuse integrity testing of critical sterilizing liquid filters for aseptic processing (1–3). Before sterilization, a preuse test will confirm that a filter is installed properly and was not damaged during shipment or handling. Performing a preuse test after sterilization detects damage that may have occurred during the sterilization cycle. Testing after sterilization limits risk, so it is a practice applied based on risk assessment. Because it is perceived to reduce business loss risk, preuse…
Fucosylation of a Therapeutic Antibody: Effects on Antibody-Dependent, Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) Potency and Efficacy
Product quality attributes are critical for the functionality and manufacturability of therapeutic antibodies. They can be significantly influenced by a number of production process parameters, such as cell culture media. The composition of growth and feed media can influence antibody glycosylation, including the concentration of ammonia, glutamine, glucose, and metal ions (1, 2). Thus, it is critical during media development and optimization to monitor and consider a culture medium’s impact on glycosylation. For therapeutic antibodies whose mechanism of action includes…
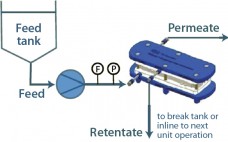
Prepacked Chromatography Columns: Evaluation for Use in Pilot and Large-Scale Bioprocessing
Time to market, resource requirements, cost, and flexibility are key considerations in designing purification processes suitable for manufacturing biopharmaceutical products. Over the past decade, many advances have been achieved in disposable processing systems that have allowed for increased processing at a lower cost. That is in part attributable to reductions in necessary resources, changeover costs, and cleaning-validation requirements. Large-scale, prepacked chromatography columns have recently become available for clinical and commercial manufacturing, and they represent a growing trend in the industry.…
Benefits of Using Tetradetector SEC to Characterize Membrane Proteins
About 60% of all drug targets are membrane proteins. So understanding their structure and function as well as their interactions with drug candidates is critical to discovery and development of new therapeutic agents. Solubilization of these proteins is an essential precursor to in vitro studies of receptor function, structure, and activity. Purification and crystallization are important aspects. However, solubilization is complicated by the hydrophobic nature of a protein’s membrane-spanning part. Surfactant micelles and other stabilizing systems thus are used to…
Virus-Filtration Process Development Optimization: The Key to a More Efficient and Cost-Effective Step
Size-exclusion–based parvovirus filtration is an important step toward drug product safety in biopharmaceutical production. However, once a virus filter is in place, and the required virus safety is ensured, less attention typically is paid to its optimization within the process. That might seem odd given that virus filtration can be one of the more expensive downstream processing steps ($/g protein processed). Most likely, the lack of attention can be attributed to aggressive timelines, limited process development resources, and the virus…
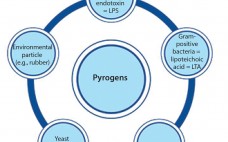
Detecting the Broad Spectrum of Pyrogens with the Human Whole-Blood Monocyte Activation Test
In the early 20th century, some patients injected with the drug Salvarsan experienced febrile reactions due to contamination of the drug’s distilled water. That incident (involving the first effective treatment for syphilis) prompted not only the widespread use of injectable drugs, but also the need for pyrogen control. Pyrogens constitute a heterogeneous group of microbial and nonmicrobial substances that include those derived from Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and lipoteichoic acid (LTA), respectively, as well as particles…