Conjugated protein biotherapeutics such as PEGylated proteins (with polyethylene glycol), antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs), and protein–haptens often present unique analytical challenges related to characterizing the conjugation aspect of their manufacturing processes. Analytical characterization of this class of proteins requires knowledge of the sites of conjugation, the degree of conjugation, and the drug-to-protein ratio. Here we present case studies in development of reliable methods based on mass spectrometry (MS) to characterize a protein–hapten drug substance during late-phase process validation. This protein is…
Product Characterization
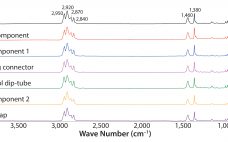
Investigation of Foreign-Particle Contamination: Practical Application of FT-IR, Raman, and SEM-EDS Technologies
The presence of visible foreign particulate matter is considered a critical defect in parenteral products and one of the main reasons they can be recalled (1). Foreign particles present during any stage of manufacturing are considered to be contaminants and can impose a risk to the control of the manufacturing processes (2). For those reasons, particle contamination arising in any manufacturing step initiates a nonconformance or out-of-specification observation. That requires an investigation to identify root cause so as to mitigate…
Science, Risks, and Regulations: Current Perspectives on Host Cell Protein Analysis and Control
State-of-the-art analytics guide process development by providing companies with thorough understanding, effective removal, suitable control, and comparability assessment after process changes of host cell proteins (HCPs) in recombinant biotechnology products. An array of analytical techniques and approaches can be used to establish control strategies for host cell proteins. Techniques used for HCP characterization and comparability include two-dimensional (2D) gel electrophoresis with a range of stains, 2D immunoblotting, 2D high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), 2D difference gel electrophoresis (DIGE), and increasingly mass…
Osmolality Measurements for High-Concentration Protein–Polymer Solutions: Variation Based on Working Principles of Osmometers
Osmolality is a critical attribute for injectable formulations. It is desirable to have products match physiological osmotic conditions. Furthermore, osmolality provides confirmation of soluble content in solution. Preventing injection of hypo- or hyperosmotic solutions is a key element of parenteral formulation development. Additionally, some investigators have explored correlations between injection pain and formulation osmolality, although no significant correlation has yet been observed (1–4). Osmolality is a valuable in-process test also because it provides a reliable and repeatable value that reflects…
Enhanced Biosimilar Product Characterization: A Case Study Using Raman Spectroscopy Combined with Dynamic Light Scattering
Biophysical characterization has drawn great attention from the biopharmaceutical industry and regulatory agencies across the globe, especially for use in biosimilar drug product development. Currently available biophysical characterization tools can help in screening and optimizing better (more stable) formulations for such products. However, most tools cannot be used for head-to-head comparison of the biophysical properties of an optimized biosimilar formulation with those of an innovator product at higher concentrations. We developed and optimized a formulation for monoclonal antibody MAb B…
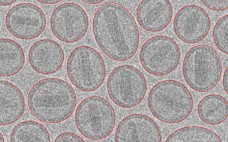
Ask the Expert Liposome and Viral Vector Characterization: Use of Electron Microscopy and Image Analysis
with Dr. Josefina Nilsson For this webcast, Josefina Nilsson (EM Services business unit head) discussed Vironova’s work, including case studies. She focused on characterization of drug and gene delivery platforms with electron microscopy and image analysis, specifically for systems that use viral vectors or liposomes. Along with two colleagues — Gustaf Kylberg (image analysis expert) and Mathieu Colomb-Delsuc (electron microscopist) — she then answered questions from the audience. Nilsson’s Presentation Structural characterization provides important insights into the quality of development and…
Fucosylation of a Therapeutic Antibody: Effects on Antibody-Dependent, Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) Potency and Efficacy
Product quality attributes are critical for the functionality and manufacturability of therapeutic antibodies. They can be significantly influenced by a number of production process parameters, such as cell culture media. The composition of growth and feed media can influence antibody glycosylation, including the concentration of ammonia, glutamine, glucose, and metal ions (1, 2). Thus, it is critical during media development and optimization to monitor and consider a culture medium’s impact on glycosylation. For therapeutic antibodies whose mechanism of action includes…
Benefits of Using Tetradetector SEC to Characterize Membrane Proteins
About 60% of all drug targets are membrane proteins. So understanding their structure and function as well as their interactions with drug candidates is critical to discovery and development of new therapeutic agents. Solubilization of these proteins is an essential precursor to in vitro studies of receptor function, structure, and activity. Purification and crystallization are important aspects. However, solubilization is complicated by the hydrophobic nature of a protein’s membrane-spanning part. Surfactant micelles and other stabilizing systems thus are used to…
Bridging Analytical Methods for Release and Stability Testing: Technical, Quality and Regulatory Considerations
To monitor the control and consistency of products derived from biological systems, a broad array of analytical methods are used for biopharmaceutical release and stability testing. These methods include both classical and state-of-the-art technologies as well as new technologies as they emerge over time.During the life cycle of a product, several reasons can arise for making changes in existing analytical methods: e.g., improved sensitivity, specificity, or accuracy; increased operational robustness; streamlined workflows; shortened testing times; and lowered cost of testing.…
Primary and Higher-Order Structural Characterization Strategy for Biosimilarity Assessment
The development pathway of a biosimilar is unlike that of a novel biotherapeutic. Many regulatory authorities reference a stepwise approach to establishing biosimilarity. Analytical requirements are greatly increased before a product enters clinical testing. Enhanced analytical efforts entail physical, chemical, and biological characterization of a biosimilar product compared with an originator reference product. Strategies at this early stage must include intensive characterization of multiple batches to determine variability of quality attributes. Here I address some issues involved in meeting regulatory…