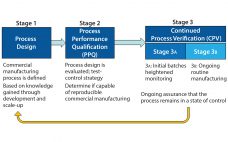
As defined in the ICH Q10 guideline, a control strategy is “a planned set of controls, derived from current product and process understanding, that assures process performance and product quality” (1). Every biopharmaceutical manufacturing process has an associated control strategy. FDA’s 2011 guidance for process validation (2) describes process validation activities in three stages (Figure 1). A primary goal of stage 1 is to establish a strategy for process control that ensures a commercial process consistently produces acceptable quality products.…
PAT
Mass Spectrometric Conjugate Characterization: Process Qualification of Recombinant Protein–Hapten Conjugation
Conjugated protein biotherapeutics such as PEGylated proteins (with polyethylene glycol), antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs), and protein–haptens often present unique analytical challenges related to characterizing the conjugation aspect of their manufacturing processes. Analytical characterization of this class of proteins requires knowledge of the sites of conjugation, the degree of conjugation, and the drug-to-protein ratio. Here we present case studies in development of reliable methods based on mass spectrometry (MS) to characterize a protein–hapten drug substance during late-phase process validation. This protein is…
Essentials in Quality By Design
Quality by design (QbD) is a systematic approach to drug development. It begins with predefined objectives and emphasizes product and process understanding and process control, all based on sound science, data-based decision making, and quality risk management (QRM). As introduced by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), QbD brings modern drug development methodologies to chemistry, manufacturing, and control (CMC) teams working on biologics, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines. The innovations associated with QbD are not so much the development concepts (which…
Analytics for Modern Bioprocess Development
Twelve years ago, about the same time the US Food and Drug Administration was putting the finishing touches on its quality by design (QbD) and process analytical technology (PAT) guidelines, I wrote an article about breakthrough pharmaceutical educational programs. That article included the perspectives from a few members in academia of the future essential skills for pharmaceutical students. At the time, bioinformatics and computerized industrial process modeling were relatively new disciplines, but their importance in future manufacturing was clear. Several…
Design of Experiments for Fed-Batch Process Development in Shaken Cultures
When designing a recombinant protein production process, a high number of parallel cultivations must be carried out. That task is typically performed using batch cultures in shake flasks or microwell plates, in which fermentation conditions are not monitored. To overcome that limitation, we combined the SensorDish Reader and Shake Flask Reader systems (from PreSens) with an enzymatic glucose delivery system (EnBase technology from BioSilta Oy) for Escherichia coli cultivations. Our objective was to determine whether SensorDish reader cultures would yield…
Responding to Life Sciences Manufacturing Industry Guidance
Increasingly, life science manufacturing companies are applying technology to meet quality by design (QbD) goals. Organizations collect overflowing volumes of process data as part of programs designed to improve manufacturing variability and outcomes. Collecting valuable data is now an everyday task thanks to available software and process analytical technology (PAT) tools. The industry today, in fact, has focused so much on gathering data that it often has lost sight of an important fact: Data collection systems are valuable only if…
New Paradigms for Process Validation
Both the United States and the European Union have recently evolved guidance on how to execute process validation (1, 2) with the prospect of a more appropriate life-cycle approach. It goes beyond the traditional three to five lots run at the center point of proposed ranges for operating parameters. New approaches leverage product design and process development information. They facilitate adapting the quality by design (QbD) paradigm to allow for a science- and risk-based selection of critical process…
NIR Spectroscopy for Process Monitoring and Control in Mammalian Cell Cultivation
The quality by design (QbD) and process analytical technology (PAT) approaches have shown significant benefit in the classical pharmaceutical industry and are now strongly influencing bioprocessing. Monitoring critical process parameters (CPPs) during biotechnological cell cultivations is essential to maintaining high efficiencies and quality. Commercial sensor systems for real-time inline monitoring are available for some parameters, such as pH or the concentration of dissolved oxygen (DO). For others such as glucose concentration, total cell count (TCC), and viability no robust online…
A Powerful Pairing
Biological product and process characterization are not new to this quality by design (QbD) and process analytical technology (PAT) era. In the 1990s we saw the FDA introduce the concept of well-characterized biologics: an acknowledgment that analytical technology had advanced to the point where the bioprocess did not necessarily (or not fully, anyway) define a biopharmaceutical product. That ultimately led to the regulation of some types of products within the United States moving from the purview of FDA’s Center for…
Manufacturing Culture
Life sciences company leaders need to put the right people, processes, and technologies in place to create evolutionary cultures. Such cultures would embrace advanced manufacturing process intelligence and reap related business benefits. Since the late 1990s, my software company has helped biomanufacturers improve their process understanding. In that time, we’ve seen regulatory drivers such as quality by design (QbD) and process analytical technology (PAT) guidances call for improved manufacturing process performance through better process understanding and optimization. We define process…