At the recent World Vaccine Conference, Victor Ayala, PhD, an early stage investigator with Advanced BioScience Laboratories, Inc. (ABL), discussed how to accelerate vaccine production using a nonviral enabling technology for cell engineering. ABL is a contract research/manufacturing organization (CRO/CMO) providing manufacturing and laboratory research services to advance leading vaccines and therapies from clinical development to the commercial market. The company has been conducting R&D research for over 55 years and performing CMO manufacturing for over 25 years. With more…
Analytical
eBook: Quality By Design for Monoclonal Antibodies — Establishing the Foundations for Process Development, Design Space, and Process Control Strategies
The quality by design (QbD) modernized approach to pharmaceutical development is intended to provide regulatory flexibility, increased development and manufacturing efficiency, and greater room to innovate as well as improve manufacturing processes within defined ranges without obtaining regulatory approval first. QbD is a systematic developmental approach that starts with a clear goal in mind and emphasizes understanding of how variability in both process and materials affects a final product (1). Historically, product quality has been assured either with end-product testing…
Methods on the Move: Addressing Method Transfer Challenges for the Biopharmaceutical Industry
Analytical method transfers are essential components of the current global biotechnology environment. Analytical method transfer can be defined as “a documented process that qualifies a laboratory (the receiving laboratory) to use a validated analytical test procedure that originated in another laboratory (sending laboratory), thus ensuring that the receiving laboratory has the procedural knowledge and ability to perform the transferred analytical procedure as intended” (1). The goal is to ensure that a method continues to perform in the validated state regardless…
Host-Cell Protein Risk Management and Control During Bioprocess Development: A Consolidated Biotech Industry Review, Part 2
Even with increased understanding of host cell proteins (HCPs) and their potential risks, no practical approach has been made available for HCP risk management during bioprocess development. A BioPhorum Development Group (BPDG) team has identified common HCP-related risk factors and built a template for semiquantitative risk assessment during process development based on publicly available information. To this end, the BPDG HCP working team’s assay and knowledge-sharing experts have established a common HCP risk assessment tool and mitigation strategy to guide…
Dual Sourcing of Protein A Resin to Mitigate Supply Chain Risk: A Comparative Study to Determine Equivalence
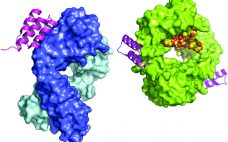
Protein A affinity chromatography is a well-established technology that is used extensively for large-scale purification of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs). With this mode of chromatography, very high product purity can be achieved in a single, relatively simple unit operation. A solution containing the target protein of interest is applied to a liquid-chromatography column at near-neutral pH, and one or more wash steps follow to lower product- and process-related impurities (1). Product is eluted through application of a low-pH buffer. Finally, the…
A Product–Packaging Interaction Study to Support Drug Product Development
Drug packaging is subject to a number of regulatory requirements, including those for product containers and packaging. For example, according to the federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C) section 501(a)(3), a drug is considered adulterated “if its container is composed, in whole or in part, of any poisonous or deleterious substance which may render the contents injurious to health.” And 21 CFR states that drug packaging “shall not be reactive, additive, or absorptive so as to alter the safety,…
Host-Cell Protein Risk Management and Control During Bioprocess Development: A Consolidated Biotech Industry Review, Part 1
Host-cell proteins (HCPs) constitute a significant class of process-related impurities during biologics manufacturing. Due to their potential impact on product quality and efficacy as well as patient safety, the total amount of residual HCP in a biological drug substance generally is considered a critical quality attribute (CQA) that usually needs to be tested for during batch release (1, 2). It is both an “industrywide” common understanding and a regulatory requirement to remove HCPs from biologics to acceptably low levels that…
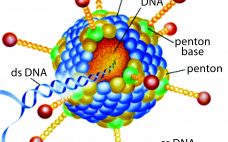
Development of a Freeze-Dried Ebola-Expressing Adenoviral Vector: Unexpected Findings and Problems Solved
In December 2013, a two-year-old child in Guinea became the first person to be killed by Ebola in the most recent outbreak. In March of the following year, that outbreak was declared in West Africa. By mid-2014, the World Health Organization (WHO) had declared it to be a public health emergency of international concern and urged pharmaceutical companies to accelerate their development of candidate vaccines. At the peak of the outbreak in 2014, more than 1,200 new cases of Ebola…
Rational Design of Liquid Protein Formulations: Application of Biophysical Stability Predictors and Descriptors to Reformulate Biotherapeutics
Successful development of liquid biopharmaceutical formulations requires careful assessment of the biophysical properties of the protein in solution, primarily focused on achieving optimal conformational and colloidal stability of the drug-substance molecule (1–11). It also involves extensive stability studies under stressed conditions. Using state-of-the-art biophysical tools for characterization of developed products, those studies are based on key biophysical descriptors and extended particulate characterization methods (subvisible particles in micro- and nano-size range) to deliver a stable product for market with a shelf…
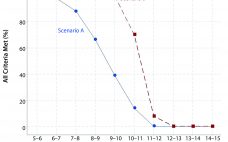
Statistical Assessments of Bioassay Validation Acceptance Criteria
Analytical linearity as well as assessments of precision and accuracy determine the range for a bioassay (1). USP <1033> recommends comparing confidence intervals (CIs) against target validation acceptance criteria in a bioassay validation exercise, but there are no clear guidelines for determining the criteria (2). Here I address several aspects of a bioassay validation, namely • Linearity (coefficient of determination (R2), slope, and intercept parameters) • Accuracy (%relative bias, %RB) • Precision (percent coefficient of variation, %CV) CIs for the…