In biopharmaceutical manufacturing, cell culture media supply critical nutrients and maintain pH and osmolality to optimize protein product yield. Because media composition and condition have a strong effect on final biologic product quality and production, biopharmaceutical companies monitor media for lot-to-lot variability. Stability testing for degradation due to light exposure, temperature changes, or shelf-life/time is possible with rapid spectroscopic methods. In an 8 October 2019 “Ask the Expert” webinar, O. Dean Stuart (product manager at Thermo Fisher Scientific) explained how…
Laboratory Equipment
Analytical Testing Strategies for CAR T-Cell Products
Assay lifecycle development for traditional biopharmaceuticals such as vaccines and monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) has a clearly defined pathway, from preclinical method selection, development, and optimization through the milestones in preclinical phase trials, and finally to postlicensure method evaluations, comparability, and improvements. The analytical development roadmap for nontraditional biologics such as chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies and gene therapies are not as clearly defined and can present many challenges along the way. Understanding the “what, how, and when” of analytical…
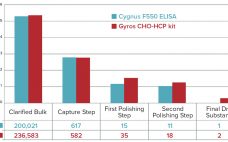
Host-Cell Protein Analysis to Support Downstream Process Development: A High-Throughput Platform with Automated Sample Preparation
In the past few years, increasing numbers of biotherapeutics have been approved for market (1). Among all the regulatory concerns for commercial biotherapeutics, host-cell proteins (HCPs) are a major class of process-related impurities that remains a critical quality attribute (CQA) for bioprocess development because of associated risks to product quality, safety, and efficacy. HCP identification, clearance, assay setup, and process control are critical points for health authorities, and many guidelines aim for better control of HCP content in final biologic…
Technology Highlights from the 2019 BioProcess International Conference
This year’s BioProcess International Conference and Exhibition, held 9–12 September 2019, hosted nearly 200 exhibitors showcasing technical innovations for the biopharmaceutical industry. This year’s conference sessions also included daily technical workshops detailing supplier solutions and technologies. Below are some notable technologies featured that demonstrate the industry’s dedication to finding new ways to help manufacturers shorten time to market. Most systems offer the benefits of single use, integration, process control, economies of scale, automation, and closed-system processing. Upstream Production The exhibit…
Emerging Tools for Exosome Purification and In-Process Monitoring
This eBook introduces new analytical approaches that enable in-line chromatographic detection of exosomes. One approach can discriminate extracellular vesicles from nonvesicle contaminants, and one potentially can discriminate exosomes from other vesicles. Examples illustrate how they enable development of more effective and better documented purification methods. The special qualifications of monolithic chromatography media for exosome purification are discussed. New process tools designed to accommodate some of the special challenges of exosome purification are introduced. Exosomes represent one of several species of…
Qualitative and Quantitative Host Cell Protein Analysis Using Mass Spectrometry
Host cell proteins (HCPs) originate from host organisms that are used to produce biopharmaceutical products. They are in-process contaminants that must be minimized during downstream process operations. According to regulatory agencies, the maximum permitted level of total HCP in a biopharmaceutical product is 100 ng per mg (100 ppm) (1). HCPs can decrease drug efficacy and pose a risk to patient safety because they can bring on undesirable immune responses. Thus, HCPs are a critical quality attribute that should be…
Using Slope Spectroscopy Methods: Risk Assessment and Cost Savings
The biopharmaceutical industry’s need for rapid, accurate concentration measurements of protein-containing products is critical. The protein-concentration assay measures ultraviolet absorption at 280 nm (A280) and usually is performed both as an in-process test and for product-release testing. The SoloVPE system can analyze samples across a wide range of target concentrations without the need for labor-intensive and error-prone dilutions. Slope Spectroscopy methods provide companies with a universal platform for determining protein concentration for all in-process, clinical, and commercial methods. During in-process UV…
Building a Bridge Across the “Valley of Death”: Strategies to Help Support Technology Development
On Thursday 6 September 2018 at the annual BioProcess International Conference in Boston, the first “Technology Round Robin Featuring Six Innovative Bioprocess Technologies” was presented in an interactive session with attendees as active participants, asking questions and engaging in conversation with the six featured entrepreneurs. Detailed below, this session was a culmination of several steps in an overall strategy for some of the companies participating. To fully appreciate the launch of new technologies into the bioprocess arena, you first must…
Speeding Characterization of Biologics: Replace Traditional Assay Technologies with Label-Free Quantification and Kinetics
FortĂ©Bio’s Octet instruments are an ideal replacement for ELISA, HPLC, and SPR techniques in quantification of antibodies and recombinant proteins and in testing product potency for lot release. Bio-Layer Interferometry (BLI) technology monitors biomolecular interactions in real time to determine affinity, kinetics, and concentration. The plate-based, microfluidics-free format offers users several distinct advantages over other technologies. BLI-based systems can achieve higher throughput, with the flexibility to measure two to 96 samples simultaneously. Lower maintenance requirements and increased ease-of-use further shorten…
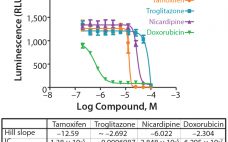
A Novel 3D Culture System for High-Throughput Hepatoxicity Screening
Cells grown as three-dimensional (3D) spheroids are thought to more closely mimic in vivo physiology in terms of morphology, structural complexity, and phenotype. Being more physiologically relevant, 3D cultures can be highly predictive for compound profiling and evaluating cytotoxicity, a critical step in evaluating chemotherapeutic drug candidates. Unfortunately, evaluation of drug cytotoxicity traditionally has relied on the use of two-dimensional (2D) cell culture monolayers. When grown in monolayers, cells are not exposed to soluble gradients, are forced into an apical-basal…