In commercial-scale biopharmaceutical manufacturing, downstream chromatography steps are still a bottleneck and contribute to significant operational costs (1, 2). Some of those costs are inherent (e.g., resins, large buffer quantities, and cleaning) whereas others are avoidable (e.g., product loss due to rejected lots or deviations that result in production downtime). Maintaining efficient and robust chromatography process performance is therefore critical for minimizing operating costs. To do so, we introduce a simple and one-point multiparameter technique (SOP-MPT) for monitoring chromatographic process…
Downstream Validation
eBook: Development of a Representative Scale-Down UF/DF Model: Overcoming Equipment Limitations and Associated Process Challenges
Scale-down models (SDM) are physical, small-scale models of commercial-scale unit operations or processes that are used throughout the biopharmaceutical industry for validation studies, commercial deviation investigations, and postapproval process improvements. To support these studies, regulatory guidelines state that SDMs should be representative of the commercial process. For some downstream unit operations such as column chromatography, developing a representative SDM is straightforward because a linear scale-down approach can be used. However, developing a representative SDM for other downstream unit operations such…
Development of a Host-Cell Protein Platform Assay for a Chinese Hamster Ovary Cell Line
The Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line is the most prevalent biopharmaceutical expression system and has been proven safe for commercial production of protein therapeutics (1). However, even after multiple purification steps, biopharmaceuticals contain residual host-cell protein (HCP) impurities that pose a potential safety risk to patients (2). Health authorities demand close monitoring of HCP impurities and require sensitive analytical methods with high coverage: the ability to detect a broad range of HCP impurities (3, 4). Polyclonal sandwich immunoassays are…
Aggregation from Shear Stress and Surface Interaction: Molecule-Specific or Universal Phenomenon?
Exposure to solid–liquid and air–water interfaces during production, freezing and thawing, shipment and storage of protein therapeutics may be a contributing factor in their degradation (e.g., aggregation, fragmentation) (1, 2). Surface exposure, particularly during manufacturing processes, often is accompanied by various degrees and durations of shear stresses originating from fluid flow and acting on proteins at interfaces. The magnitude and duration of shear rates depends on velocity gradients within each solution and varies significantly among manufacturing steps. On the low…
Conditional/Inducible Gene-Expression Mouse Models Using Advanced Gene Editing
Transgenic mouse models have been an essential part of biomedical research for many decades. They have provided valuable insights in developmental biology, gene regulation, and our understanding of the genetic basis of human disease. And they play a critical role in drug discovery and development. Traditional methods to generate these mouse models entailed a milieu of disadvantages: e.g., low efficiency, high incidence of undesirable recombination outcomes, randomly and multiply inserted genes of interest, ectopic expression, gene silencing, and insertional mutations…
Residual Host-Cell DNA in Biopharmaceutical Products: 96-Well Plate-Based Extraction and Real-Time PCR Assay for Quantitative Measurement
Regulatory guidelines that cover the development of biopharmaceutical products require testing of host-cell deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) impurities. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has become a popular technology for DNA quantitation and monitoring of process impurities associated with biomanufacturing. One critical challenge associated with host-cell DNA impurity testing is that recombinant proteins (e.g., monoclonal antibodies, MAbs) and their corresponding buffer components often interfere with DNA quantitation in real-time PCR reactions (1, 2). Some sample types do not require a full extraction…
A Statistical Approach to Assess and Justify Potential Product Specifications
As stated in ICH Q6B, specifications are critical quality standards that are both proposed and justified by drug product manufacturers. Xiaoyu et al. provide information on several statistically based strategies to establish specification acceptance criteria (SAC) (1). Here we address an alternative approach to relate proposed SAC for quantitative data to relevant lot history. In particular, proposed SAC can be derived in part by using calculated limits for which the lower bound of an approximate 95% confidence interval for the…
Examining Single-Use Harvest Clarification Options: A Case Study Comparing Depth-Filter Turbidities and Recoveries
Steadily increasing demand for biopharmaceutical drugs has led the industry to examine its manufacturing scales while pressuring research and development groups to produce high-yielding clones and processes. Improved media, feed supplements, bioreactor designs, and control of process parameters have helped biomanufacturers achieve multifold increases in volumetric productivity from production bioreactors. However, cell culture processes are significantly affected by their bioreactor’s ability to support cells at higher densities and sustain cultures at lower viabilities. With the implementation of a number of…
CMC Forum: Evolution of Biopharmaceutical Control Strategy Through Continued Process Verification
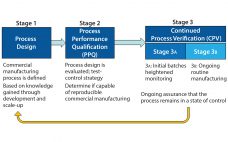
As defined in the ICH Q10 guideline, a control strategy is “a planned set of controls, derived from current product and process understanding, that assures process performance and product quality” (1). Every biopharmaceutical manufacturing process has an associated control strategy. FDA’s 2011 guidance for process validation (2) describes process validation activities in three stages (Figure 1). A primary goal of stage 1 is to establish a strategy for process control that ensures a commercial process consistently produces acceptable quality products.…
Response to the Publication of USP ‹1207›
The BioPhorum Operation Group’s (BPOG’s) Container Closure Integrity Testing (CCIT) workstream would like to congratulate the United States Pharmacopeia’s committee for its latest revision to USP chapter <1207> Package Integrity Evaluation: Sterile Products. Generally, we believe it provides a comprehensive overview of the available methods for container–closure testing and outlines many important elements for consideration in establishing a successful CCIT strategy. We first responded to the USP <1207> draft when it was released for comment in 2014. And from our…