The product development team at a gene therapy contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) was working on a high-priority drug-substance project for a key client. The material was crucial to that client’s early stage clinical trial, with an immediate value over US$500,000 to both the client and the CDMO. Unfortunately, the bioreactor used in the upstream process — a transfection unit operation for an adenoassociated virus (AAV) vector — had developed an intermittent problem that could force it to shut…
Analytical
eBook: Potency Bioassays — Development, Trending,
Transfer, and Automation
Bioassay development is a complex process that must be undertaken with great rigor and attention to detail. Potency testing experts use a range of methods including cell-based and binding assays. Consistency and reliability of results over time are paramount. Well-developed and -characterized methods are the end result of much phase-appropriate development work that goes on in parallel with bioprocess and biotherapeutic product development. This eBook begins with BPI senior technical editor Cheryl Scott’s report from the Biopharmaceutical Emerging Best Practices…
Navigating New Options for Commercial-Scale Biopharmaceutical Production
Scalability remains a critically important topic for biopharmaceutical companies. For conventional protein products, the strategy once was straightforward: Drug makers would scale up, beginning with cultures in flasks and roller bottles to grow enough cells to inoculate laboratory-scale (often glass) bioreactors, then again to pilot- and commercial-scale, stainless-steel, stirred-tank bioreactors. At their highest volumes, such reactors can handle tens of thousands of liters of cells and growth media. If a drug developer did not have the requisite equipment to scale…
Reducing Downstream Scale-Up Needs: Advances Toward Continuous Downstream Processing
The biopharmaceutical industry generally acknowledges that upstream and downstream aspects of drug-substance manufacturing are experiencing a capacity mismatch. Today, many recombinant proteins can be produced at expression titers of 3 g/L, with some yields exceeding 10 g/L. Such titers represent 100-fold increases in production capability compared with values from twenty years ago (1, 2). Increases in cell-culture density and improvements to perfusion-mode bioreactor systems hold promise for increasing yields further still. Such developments, combined with the broad availability of concentrated…
Scaling AAV Production: Easing the Transition from Laboratory Scales to Commercial Manufacturing
Adenoassociated virus (AAV) has emerged as the leading vector for gene therapy delivery. Compared with options such as lentivirus and adenovirus, AAV exhibits a strong safety profile because it has low pathogenicity and requires a helper virus to replicate. AAV is also capable of long-term gene expression, and it can infect both dividing and nondividing cells (1–5). Developers of advanced therapies have found such advantages to be quite attractive. As of January 2021, two gene therapy products have gained US…
Smart, Real-Time Quality Insights Boost Life Sciences Manufacturing
The COVID-19 pandemic has shone a light on restrictive business processes, information silos, and poor supply-chain visibility in many sectors. In biopharmaceutical manufacturing, for example, difficulties associated with product-quality management have been exposed and starkly felt. However, public healthcare measures over the past 18 months have put physical distance between team members, thereby hampering the usual form-filling, manual sign-offs and spreadsheet-based recordkeeping associated with monitoring traditional manufacturing processes. In some cases, a lack of formal face-to-face discussions in the workplace…
Mycotoxin Risk Determination: Measuring the Potential for Patient Exposure with Antithrombin Alfa Sourced from Transgenic Goat Milk
Antithrombin alfa is a recombinant human antithrombin developed as an anticoagulant treatment for people with hereditary antithrombin deficiency who are undergoing surgical or childbirth procedures (1). Marketed under the ATryn brand name by LFB SA (Les Ulis, France), antithrombin alfa was approved for use in adults by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in February 2009 (2). Antithrombin alfa is expressed in the milk of transgenic goats and purified through a multistep downstream process encompassing both filtration and chromatography.…
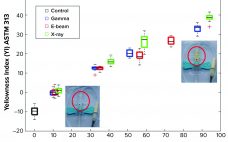
Supplementing Gamma Sterilization with X-Ray and E-Beam Technologies: An International Industry and Academia Collaboration
Ionizing-technology–based industries are growing rapidly around the world. The expansion is driven mostly by the technology’s myriad applications, including polymer crosslinking, medical device sterilization, food pasteurization, and phytosanitary treatment. Ionization also is used in the manufacture of some healthcare products such as medical devices and biopharmaceuticals. Industrial sterilization methods render single-use products and manufacturing components safe and ready for their intended use. ISO11137-1 describes the validation and routine control of a sterilization process for medical devices and mentions the three…
Mind the Gap: Managing Relationships Between Upstream and Downstream Intensification
Process intensification (PI) describes an integrated framework of strategies to maximize the output of a unit operation, a process, or an entire facility. By implementing PI strategies, biomanufacturers can accomplish their productivity goals by increasing production speeds and titers, reducing facility footprints, and cutting costs. Overall, such changes improve production efficiency and flexibility. Collectively, the biotherapeutic industry has made multiple advancements in intensifying upstream processing. PI strategies include using high-density cell banks, implementing seed-train intensification (n – 1 perfusion), and…
eBook: Sensors — Process Analytics for Modern Biopharmaceutical Workflows
To achieve quality by design in biopharmaceutical production, manufacturers need tools that can ensure the stability of critical process parameters (CPPs) and other performance indicators related to product critical quality attributes (CQAs). Over the past couple of decades, sophisticated process analytical technologies (PATs) have emerged to address such needs. Offerings are now abounding for single-purpose sensors that measure temperature, pressure, pH, glucose, protein concentration, or dissolved oxygen. New in-line formats are enabling such instruments to provide data in real time,…