Viral vectors are synonymous with gene therapies, so their development, production, and processing are of upmost importance to all gene therapy researchers and manufacturers. Every year, I look forward to attending the Cell and Gene Bioprocessing and Commercialization conference in Boston and talking to leaders in industry and academia about their current approaches to advancing gene therapies. Like most other meetings this year, the conference was entirely online and had to provide a shortened agenda. Nonetheless, there was no shortage…
November-December 2020 Featured Report
Manufacture and Regulation of Cell, Gene, and Tissue Therapies, Part 1: Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Control Challenges
Cell, gene, and tissue (CGT) therapies and other advanced-therapy medicinal products (ATMPs) have made tremendous progress over the past decade. They are different from other biologics and small molecules because of their inherent complexity and variability. Although many unknowns remain about the development of these products, their clinical success has enabled the CGT therapy and ATMP fields to advance rapidly. We are seeing an increase in the number of marketing authorization applications (MAAs) filed in the European Union and new…
Streamlining Industrial Purification of Adeno-Associated Virus
With its first licensed therapeutic now marketed worldwide (1), adeno-associated virus (AAV) has become a preferred vector for gene therapy. However, unlocking its full potential still poses challenges, many of which are associated with purification. The first involves the transition from upstream to downstream processes. AAV-bearing lysates are laden with debris that foul filtration media and limit or prevent concentration. Another challenge involves reduction of soluble host-cell DNA, which is complicated by its strong association with nucleoproteins. A third involves…
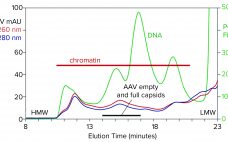
Ultracentrifugation for Recombinant Adenoassociated Virus Therapies
Quantitation of different capsid species in viral-vector gene-delivery drugs, including recombinant adenoassociated virus (AAV) therapies, is essential for proper assessment of critical quality attributes before regulatory approval and during commercial production. If rAAV full-capsid percentages are maximized, and variants such as empty or partially-filled capsids are reduced as much as possible, then potency is increased for improved dosing and tolerance outcomes. Traditionally, characterization of AAV purity with respect to empty, full, and other variants has been performed by techniques such…