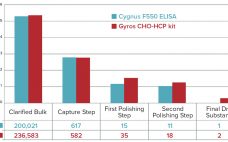
Hydrophobic Interaction chromatography (HIC) is a powerful polishing tool for the downstream purification and manufacture of biotherapeutics. HIC offers orthogonal selectivity for the clearance of difficult process and product-related impurities such as aggregates, host cell proteins and endogenous and adventitious viruses. In this study, a family of POROS HIC resins with novel ethyl and benzyl chemistries was used to successfully polish two clinical stage monoclonal antibodies harboring very high levels of product aggregation (>10%). In addition to aggregate removal, viral…
2019
Risk and Lifecycle Management for Biopharma Operations
By working with the best biopharmaceutical companies for over a decade, 4Tune Engineering (4TE) has built a portfolio of services that enables companies to address current-century challenges. The biotechnology industry needs to address advanced therapies and personalized medicines and deliver explicit patient outcomes. Biologics today fall into four categories: monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), biosimilars, advanced therapeutic medicinal products (ATMPs), and cell and gene therapies (CGTs). Consequently, we can ask whether our manufacturing science and technology (MSAT) approaches are up to the…
AAV Vector Manufacturing Platform Selection and Product Development
Adenoassociated virus (AAV) vectors have emerged as the prominent delivery mechanisms of corrective gene therapies. Three such products — Glybera (alipogene tiparvovec, uniQure), Luxturna (voretigene neparvovec-rzyl, Spark Therapeutics), and Zolgensma (onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi, AveXis) — have been licensed, and a growing number of candidates are entering late-stage development. In mapping out an AAV gene therapy product development strategy, biomanufacturers should address fundamental considerations for their manufacturing strategies for both phase 1–2 clinical evaluation and translation for commercial market supply. A manufacturing…
eBook: Speed to IND — Balancing Risk and Reward
With so many biopharmaceuticals obtaining breakthrough or fast-track designations, companies that use accelerated strategies to be first in human studies can be left with significant quality and manufacturing challenges that must be solved later on. Despite regulatory encouragement to create solid design spaces and define parameters according to quality by design (QbD), those may go by the wayside given the pressures of speed. The reward is the investigational new drug (IND) application itself — but if companies lock in subpar…
The Road to Commercialization: A Commercial CDMO’s Perspective
Richard Richieri, chief operation officer (COO) of Avid Bioservices, recently presented an Avid case study and strategy to design, prepare, and execute process validation in preparation for successful product approval inspections. The goals of the presentation were to share lessons about some of the strengths learned from Avid’s experience and to offer advice on industry best practices. Finding a CMO that meets your quality expectations and scale is a key driver for your eventual commercial success. Particularly, working with CMO…
Matrix: The Highly Automated Multibioreactor Solution That Fits to Your Bench Space, Bioprocessing Needs, and Budget
To improve their bioprocess performance, life-science specialists need flexibility in their R&D laboratories because of constantly changing bioprocessing demands. In addition, more experiments need to be performed with more accuracy and reproducibility on less bench space than ever before — and with limited budgets. Therefore, having flexibility in the number of bioreactors that fit available bench space and budget is crucial — along with the flexibility to connect and integrate the right software, sampling tools, and analytical devices. Running multiple…
Host-Cell Protein Analysis to Support Downstream Process Development: A High-Throughput Platform with Automated Sample Preparation
In the past few years, increasing numbers of biotherapeutics have been approved for market (1). Among all the regulatory concerns for commercial biotherapeutics, host-cell proteins (HCPs) are a major class of process-related impurities that remains a critical quality attribute (CQA) for bioprocess development because of associated risks to product quality, safety, and efficacy. HCP identification, clearance, assay setup, and process control are critical points for health authorities, and many guidelines aim for better control of HCP content in final biologic…
Cell Viability in Bioprocesses: Making a Case for Reevaluation
Trypan blue dye exclusion first was proposed as a means of measuring mammalian cell damages over a century ago in 1917 (1). Despite extensive documentation of its limitations (2), it remains the “gold standard” method of measuring cell viability in common use today. But can this method truly measure viability? And how do we define cell viability, for that matter? Those fundamental questions are linked to whether we refer to cells as “alive” or “dead” in the context of bioprocessing…
Making Media a Priority: An Interview with Susan Riley of Advanced Bioprocessing
Susan Riley is vice president and general manager of Advanced Bioprocessing. It’s been a year since Thermo Fisher Scientific’s acquisition of the Advanced Bioprocessing business from Becton Dickinson (BD). Why did Thermo Fisher see the Advanced Bioprocessing (AB) business as a good fit with its life-science offerings? AB has a significant portfolio in premium supplements for cell culture and microbial fermentation. The AB business was seen as a good fit for several reasons: It goes hand-in-glove with Gibco media, for…
Demonstrating Intactness of Biopharmaceutical Products: Intact Molecular-Weight Analysis and Terminal Sequencing of Proteins
Regulations require that biomanufacturers assess the intactness of protein and glycoprotein products as well as confirm the terminal sequences to look for existing variations. ICH Q6B guideline section 6.1.1 c states: Terminal amino acid analysis is performed to identify the nature and homogeneity of the amino- and carboxy-terminal amino acids. If the desired product is found to be heterogeneous with respect to the terminal amino acids, the relative amounts of the variant forms should be determined using an appropriate analytical…