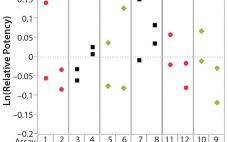
During lifecycle development of a biological assay (bioassay), identifying and reducing sources of variability might be required to improve method performance. Here I recommend some statistical and graphical approaches (consistent with USP <1033>) for practitioners to identify variation from experimental results (1). Sources of Variation in a Bioassay To correctly identify sources of variation in a bioassay, analysts must consider how that bioassay is to be executed. In particular, the experience and technical expertise of each analyst expected to execute…
2018
Biological Stealth Bombers: Potency, Regulatory, and Bioprocessing Concerns of Antibody–Drug Conjugates
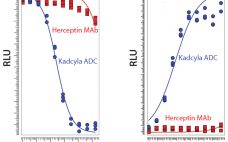
Seven years ago, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the first product in a new class of biologics: antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs). The idea for these products already had been hatched a decade earlier when the promising field of antibody research — touting such molecules as “magic bullets” — had faltered, specifically against oncology-related indications. The early crop of anticancer monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) proved to have only limited efficacy, and interest in developing antibodies as therapeutic agents against cancer…
BioProcess Insider for October
Launched in June 2018, the BioProcess Insider digital information portal delivers the latest financial and business news and expert insider views influencing the commercialization of biopharmaceuticals. Here are just a few recent stories edited for our space limitations in print. For more discussion and in-depth analysis, check out the website at www.bioprocessinsider.com. Every edition provides expert and insider perspectives on current financial movements and deal-making; the newest technology purchases and capacity investments; regulations affecting the bioprocessing sector; global market actions…
Bridging Polymer Science to Biotechnology Applications: A Single-Use Technology Conference Report
Single-use (SU) technology is used more every year throughout the biotechnology industry. As applications now span from cell banking to drug product, that in turn is raising interest in the interaction of extractables with proteins and cells. The second “Single-Use Technologies” conference organized through Engineering Conference International (ECI) was subtitled “Bridging Polymer Science to Biotechnology Applications” and delved into the science of plastics in bioprocessing applications. On 7–10 May 2017 at the Hotel dos Templários in Tomar, Portugal, people from…
Proposing a Systematic QbD Approach Toward Validated Guidelines for CMO RFI and RFP Processes: Biopharmaceutical Vendor Evaluation and Selection Minimum Standards (BioVesel)
Three major concerns predominate biotechnology executive management in organizations of all sizes and above all other risks: finance (or its absence at critical moments), technological performance, and failures in coordination. Some business functions, such as human resources (HR), are effectively siloed horizontally and therein are more likely to be susceptible to only one of those risks (1). Few functions are subject to this trinity of risks simultaneously; all functions may be exposed to failures in internal coordination, and a smaller…
Using Data and Advanced Analytics to Improve Chromatography and Batch Comparisons
With all the hype surrounding the industrial Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and digital transformations, the most important information technology factors still are data and the connections of sensors, systems, and applications that generate, store, find, and use those data to obtain operational intelligence. Data volumes are increasing rapidly, and they will continue to do so. The ability to find and make sense of data to obtain intelligence that improves process outcomes is more important than ever. For clinical-…
Intensification of Influenza Virus Purification: From Clarified Harvest to Formulated Product in a Single Shift
Influenza is a global respiratory disease with an estimated mortality of up to a half million people per year (1). The majority of traditional influenza vaccines are still produced in eggs. Downstream processing typically consists of clarification by centrifugation, concentration by ultrafiltration, and purification by ultracentrifugation (2). Recombinant vaccines are most often purified by chromatography. Chromatographic purification of viruses already has achieved major improvements in recovery and scalability (3), but it also is important because it enables virus purification to…
Rational Selection of Sugars for Biotherapeutic Stabilization: A Practitioner’s Perspective
Biotherapeutics from recombinant DNA technology include diverse modalities such as peptides; enzymes, antibodies, and other proteins; nucleic acids; and cellular therapies. Such products present physical, chemical, and biophysical challenges. Excipients used in stabilization of these biotherapeutics can be broadly classified into the following classes (subgroups) that have been reviewed carefully elsewhere (1–4) : Buffers (e.g., phosphate, acetate, and histidine) Tonicity agents/stabilizers (sugars such as sucrose, polyols such as sorbitol) Bulking agents (lyoprotectants such as mannitol) Surfactants (e.g., polysorbates) Antioxidants (e.g.,…
Sticking In or Standing Out? Dichotomy in Vaccine Purification By Chromatography
A general vaccine purification strategy can be divided into three stages, with one or more steps for each stage. The first stage is to concentrate and isolate the target molecule quickly to remove it from conditions that could lead to its inactivation or loss. Intermediate purification seeks to remove remaining contaminants, typically using an orthogonal approach. That is followed by a polishing step in which trace impurities are removed through high-efficiency steps because those impurities usually are similar to the…
Process Analytics and Intermediate Purification of Bispecific Antibodies with a Non-Affinity Platform
The therapeutic benefits of monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) have been demonstrated in recent decades with uncontestable success as treatments for human disease. Despite MAbs’ key features such as specificity, selectivity, and safety, the format has limitations (1, 2). Bispecific antibodies may overcome number of difficulties (3). Multiple formats of bispecific antibodies have been developed, although only the κλ-body is fully human and devoid of linkers or mutations. It requires no genetic modifications of heavy and light chains and results in bispecific antibodies…