On 20 September 2018, Jiali Liao (principal scientist in process chromatography R&D at Bio-Rad Laboratories) led a BPI “Ask the Expert” webinar introducing the high-performance, high-capacity Nuvia HP-Q Anion Exchange Resin, which can be used for purifying large biomolecules. Liao’s Presentation Purifying large biomolecules — e.g., plasma proteins, immunoglobulins, viruses, virus-like particles (VLPs), and PEGylated proteins — can be difficult. Their size makes for slow diffusion through the pores of traditional chromatography resins and poor mass-transfer kinetics, which decreases binding…
2018
The Complete e-Book of Biosafety Testing
Expect the expected. But plan for the unexpected. If your Biosafety Development takes a nose dive, Eurofins Lancaster Laboratories’ team of regulatory experts and experienced scientists will help you land safely on two feet. Download The Complete e-Book of Biosafety Testing to learn more about our expertise in biologics raw materials, cell bank preparation, adventitious virus testing, viral clearance studies, next-generation sequencing, genetic stability testing, and more. This e-Book contains the following chapters: Mitigating Risk and Reducing Regulatory Scrutiny of…
Manufactured by Jetting: The Future in Protein A Affinity Matrix Design
Protein A affinity chromatography continues to be the preferred method for commercial purification of antibodies because of its high selectivity and robust resin performance over repeated purification cycles. Reports estimate that US$125 billion of yearly sales will be generated from monoclonal antibody (MAb) products by 2020 (1). Most of those will be purified by largescale protein A affinity chromatography. With the continued growth and commercial importance of MAb production, availability of high-quality resin material and options for secondary sourcing are…
Cell Culture Scale-Up in Stirred-Tank Single-Use Bioreactors
Bioprocess development usually is carried out in systems with small working volumes. This helps save time and resources because, at small scale, several experiments can be conducted in parallel. Costs for media are kept low, and relatively little laboratory space is required to operate small-scale bioreactors. But over the course of development, biopharmaceutical companies need more material for characterization, trial runs, and finally for commercialization. They transition to bench scale and then up to pilot or production scale with the…
eBook: Using Modern In Situ Analytics and PAT for Automated Feedback Control of Critical Process Parameters
Simply put, the best way to control a critical process parameter (CPP) is to measure that specific parameter, integrate the live signal into your control system, and apply a smart feedback algorithm for an automated control loop. The challenge in doing this for bioprocesses has been due, in part, to the complex, highly dynamic, and variable nature of the process along with the lack of robust, scalable, and multiformat (single-use or multiuse) technologies that can monitor in real time such…
October From the Editor
As we send this issue to the printer, the BPI editors are enjoying the start of the western Oregon fall season. Early rains are beginning finally to extinguish the remaining wildfires that have kept our valley (along with much of the west coast) choked with smoke much of the summer. With the fires on this side of the country and the recent storms to the east, we hope that all our colleagues and readers remain safe. For BPI, changes begun…
Viral Risk Mitigation: A Global Regulatory Perspective
The production of biologics will always have the risk of viral contamination. Manufacturers have developed a multitiered approach — tailored to individual processes — to prevent adventitious viruses from entering production processes, detect contamination in raw materials and process intermediates, and remove viruses in downstream purification. This article provides an overview of the global regulatory framework to ensure the viral safety of biologics. Past Contamination Events Past contamination events have resulted in corrective and preventative actions to reduce the risk…
Development of a Standardized Extractables Approach for Single-Use Components: General Considerations and Practical Aspects — A Manufacturer’s Perspective
The subject of extractables for single-use bioprocess contact materials has been a subject of heated debate since roughly the summer of 2012, when the first ISPE paper was published issuing a call to action to develop a standardized extractables protocol for the industry (1). As a supplier that pioneered the science of extractables (2‒11) and has published extractables data for our products for over 20 years, Sartorius Stedim Biotech (SSB) took the opportunity to look back, take stock, rationalize, and…
BioProcess International Conference and Exhibition 2018 Postevent Report: Key Insights, Highlights, and Take-Away Messages
From the global shift in demographics to increased efficiencies in chromatography media, change is constant within the bioprocessing industry and a major reason delegates flock to the annual BPI Conference and Exhibition. As a place to get an overview of the hot topics affecting this industry, the meeting brings together key aspects of bioprocessing — therapeutic modalities, cells, expression systems, upstream production, downstream processing, development, and manufacturing — with digital integration and the increasing importance of analytics. Add in macrobusiness…
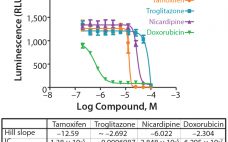
A Novel 3D Culture System for High-Throughput Hepatoxicity Screening
Cells grown as three-dimensional (3D) spheroids are thought to more closely mimic in vivo physiology in terms of morphology, structural complexity, and phenotype. Being more physiologically relevant, 3D cultures can be highly predictive for compound profiling and evaluating cytotoxicity, a critical step in evaluating chemotherapeutic drug candidates. Unfortunately, evaluation of drug cytotoxicity traditionally has relied on the use of two-dimensional (2D) cell culture monolayers. When grown in monolayers, cells are not exposed to soluble gradients, are forced into an apical-basal…