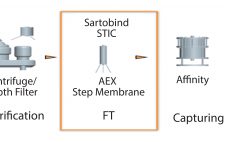
Protein A has made monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) highly manufacturable and easier to develop in laboratories. Its use has enabled purification platform approaches, which have been key elements in growth of the MAb market. But in general, protein A columns are too large, which means they either limit the use of prepacked technology, or create a mismatch between a protein A column and downstream operations. Protein A columns also are more prone to bioburden contamination than any other step in a…
2018
An Approach to Generating Better Biosimilars: Considerations in Controlling Glycosylation Variability in Protein Therapeutics
The global market for biotherapeutics has expanded extensively over the past decade and is projected to account for more than a quarter of the pharmaceutical market by 2020, with sales exceeding US$290 billion (1). Continued expansion of the biosimilar marketplace has led to many commercial opportunities and technical challenges. The biological systems used to manufacture such drug products are inherently variable — a feature that has important consequences for the reproducibility, safety, and efficacy of the resulting products. Therefore, a…
New Dimensions in Single-Use Filtration
Whether viral vectors are clarified or the bioburden after cell harvest needs to be reduced to recover antibodies, such applications in biopharmaceutical production require large filtration areas. Single-use technologies are indispensable in many such bioprocesses. Although some single-use filter assemblies have reached their limits, Sartorius Stedim Biotech has made developments to revolutionize these production steps. Scale-Up Limitations in Single-Use technology Conventional stainless steel process systems have been established for decades in the pharmaceutical industry. They are the basis of safe…
Establishing Effective High-Throughput Contaminant Removal with Membrane Chromatography
Bharat Serums and Vaccines Limited (BSV) in India conducted a study based on effective removal of host cell proteins (HCPs) from a recombinant hormone with a wide isoform profile in the acidic range imparting drug-product activity. Because the hormone and HCPs have a similar range of active species, the purification process with conventional chromatography resins had difficultly removing those HCPs from the active isoforms of the hormone. To solve that issue, a membrane chromatography technique was implemented. Our initial choice…
Extend the Life of Your Facility: Flexibility Allows for Biopharmaceutical Process Innovation
For an industry built on constant change, there’s a surprising disconnect between the continuous drive for innovation and the inflexible facilities that house biopharmaceutical operations. Some of today’s facilities are built for today’s use with little thought about tomorrow’s. The typical approach for a new process or drug coming to market is to start with a brand-new building and permanently embedded equipment designed around that specific process. That approach is expensive and unsustainable. New bioproduction facilities can cost US$500 million…
Conference Report: The Drug Product Track at 2017’s BioProcess International Conference and Exhibition in Boston, MA
At the Hynes Convention Center in Boston, MA, during Knect365’s “Biotech Week Boston” in late September of 2017, one track of the BioProcess International Conference focused on drug products, fill–finish, and formulations. Presenters represented a number of major biopharmaceutical companies — AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Genentech (Roche), GlaxoSmithKline, Johnson & Johnson, Lonza, Pfizer, and Sanofi — as well as suppliers Bosch, Merck (MilliporeSigma), ReForm, and Single-Use Support. They focused on predictive modeling, quality by design (QbD) and process analytics,…
A Vaccine Case Study: Qualifying Redundant Disconnection Technologies As Container-Closure Systems for Long-Term Storage and Shipping
The expanding complexity of biopharmaceutical manufacturing puts increasing pressure on single-use systems to meet the demands of the modern industry’s global footprint. Individual sites within a given organization often are specialized to a fixed number of “modular” process steps (1). Such product segregation increases plant efficiency and output while making the best of staff competencies. But it also can create an additional need for transportation of intermediate or bulk drug substance (BDS) over long distances. Freezing generally is used to…
Beyond Compliance: Serialization Has More to Offer
As the global pharmaceutical industry implements serialization (track and trace from manufacturing to dispensing) to meet governmental regulatory requirements, other opportunities arise for drug companies. The main driver here is to improve the integrity of the overall drug supply chain, but other meaningful business benefits can come from serialization. Generally accomplished through automated, electronic means, it involves such practices as recording, authenticating, maintaining, and sharing accurate records of products. Outside-the-Box Benefits In addition to tightening up the supply chain and…
eBook: Of Microbrews and Medicines — Understanding Their Similarities and Differences in Bioprocessing Can Help Improve Yields and Quality While Reducing Cost
Meeting a biopharmaceutical scientist or engineer who proclaims a love for brewing is not surprising. Perhaps it’s because of the challenge of mixing raw ingredients together and waiting patiently for the final product, maybe it’s the hands-on nature of the equipment or the data analytics entertainment, or it just might be the simple joy of creating something. Whatever attracts a scientist or engineer to making medicines and/or craft brews, a surprising number of principles hold true for both bioprocesses despite…
eBook: Bioinks for Bioprinting — Three-Dimensional Printing in Research and Medicine
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is one method of digital biomanufacturing for both basic biological research and translational, clinical applications. The medical field has used it to create such constructions as 3D surgical models for preoperative planning, to assist surgeons in their procedure preparations, which improves postsurgical outcomes. Examples here include generation of cleft-palate models (1), orthopedic applications (2), and cardiovascular surgical planning (3). Other forms of 3D printing for biological applications — such as 3D bioprinting — go beyond such surgical…