Single-use components and systems have been incorporated into many bioprocesses as an alternative to cleanable, reusable systems. A wide range of publications have detailed the reasons for this trend toward a single-use approach. Justification in many cases comes from process-specific benefits such as increased manufacturing flexibility — especially for contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) — enhanced sterility assurance, elimination of cleaning, reduced capital investment, faster processing times with increased productivity, faster start-up, and other benefits (1). One critical factor in the…
2016
Special Report on Process- and Product-Related Impurities (A CMC Strategy Forum Special Focus Series): Extractables, Leachables, Particles, and Aggregates
The CMC Strategy Forums focus on relevant chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) issues throughout the life cycle of a therapeutic and thereby foster collaborative technical and regulatory interaction. Forum chairs share information with regulatory agencies to help them merge good scientific and regulatory practices. Outcomes of forum meetings are published in BioProcess International and on the CASSS website (www.casss.org). This process is meant to help ensure that biopharmaceutical products manufactured with advancing technologies in a regulated environment will continue to…
Continuous Cell Culture Operation at 2,000-L Scale
In the biopharmaceutical industry, continuous manufacturing is often cited as a method for increasing the productivity of bioprocesses (1). Compared with batch processing, it has the potential to enable production of more product within a smaller facility footprint — while improving product quality, particularly for sensitive and unstable molecules. Investigation into continuous methods is taking place for both upstream and downstream operations. For the full benefit of continuous processing to be realized, an argument has been made that cell culture,…
Membrane-Based Clarification of Polysaccharide Vaccines
Polysaccharide vaccines are essential for protection against infectious diseases, which remain an alarming cause of mortality. The first glycoconjugate vaccine for use in humans — a Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) conjugate — was licensed in the United States in 1987. This vaccine successfully reduced the incidence of invasive Hib disease in childhood and led to the further development of conjugate vaccines designed to prevent infection by other encapsulated bacteria (1). Polysaccharides are relatively complex carbohydrates made up of many…
November: From the Editor
In 2012, to mark BPI’s 10th year of publication, we launched our biennial BioProcess International Awards program. Our publication has from the start aimed to help drive advancements in this industry, not simply to report on them. We have to date (in 2012, 2014, and now 2016) recognized more than 50 people and companies that represent excellence in leadership, corporate citizenship, collaborations and partnerships, and innovative technologies and applications. This year, our 16-member judging panel evaluated each nomination within assigned…
Spotlight for November
EU Workshop Report on Authorization of Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products The European Medicines Agency (EMA) published a report from a multi-stakeholder expert meeting held in May exploring ways to foster the development of ATMPs in Europe and expand patients’ access to these new treatments. ATMPs comprise gene therapies, tissue-engineered products, and somatic cell therapies. These medicines have the potential to reshape treatments of a wide range of conditions, particularly in diseases for which conventional approaches are inadequate. However, eight years…
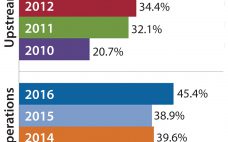
Outsourcing of Buffer Preparation Activity Is Increasing
The major fluid products used in bioprocessing — culture media and buffers — are classically prepared in-house by rehydrating (dissolving and mixing) powders purchased from suppliers. Most bioprocessing facilities consider in-house preparation of these fluids to be a core bioprocessing task. However, some companies are outsourcing the work either by purchasing preprepared materials from vendors or hiring contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) to prepare them. Buffer fluid preparation is one area of downstream production operations that are seeing an increase in…
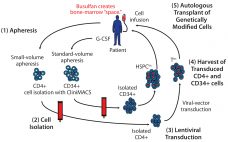
Cell-Delivered Gene Therapy: This Viral Vector Manufacturing Method Could Widen Its Applicability
Cell-delivered gene therapy is making an impact on a range of diseases (1–17). To date, successful treatments have generally been in conditions involving genetic deficiencies/abnormalities, for which introduction of a normal gene allele has been corrective (1–12, 18). Such an approach requires a vector containing the normal allele to overcome the mutant or lacking gene. The vector of choice for cell-delivered gene therapy is often a lentivirus that integrates and expresses introduced therapeutic genes in host target cells and their…
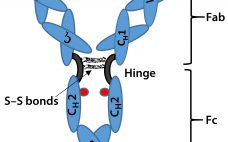
Biosimilar Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies: Gaps in Science Limit Development of an Industry Standard for Their Regulatory Approval, Part 2
Last month, Part 1 of this discussion briefly described the regulatory landscape for developing biosimilar therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (TMAbs). We identified certain specific structural components of TMAb drug substances that warrant particular attention because alterations to them are likely to affect therapeutic safety and effectiveness. Now we conclude by considering whether studies of reference materials can further the development of analytical industry standards to ensure comparability of putative biosimilar TMAbs with innovator TMAbs. We suggest that the time is right…
Special Report on Antibody-Drug Conjugates: Technical Challenges and Opportunities
Among the emerging targeted therapies in biotechnology, antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) hold a unique position. An ADC consists of a monoclonal antibody (MAb) with affinity to tumor cells, a cytotoxic small-molecule payload, and a linker connecting the two. Together the MAb, conjugation chemistry, and cytotoxin increase the complexity of ADCs several-fold relative to unmodified MAbs — and exponentially relative to chemotherapies. Viewing ADCs as hybrids of antibody- and chemotherapy-based cancer therapies is tempting. That description applies chemically and structurally, but ADCs’…