For protein therapeutics and other biologics, the importance of the molecule’s structure to its efficacy and safety is well established (1–5). In particular, their tertiary and quaternary structures play very important roles in product quality and have been monitored extensively in comparability studies (6–12). However, because of both the large molecular size and rotational property of amino acid α carbons, a protein can assume an enormous number of different conformations (13). For antibody-based biologics such as monoclonal antibodies (MAbs), fusion…
Author Archives: Xing Wang
Higher-Order Structure Comparability: Case Studies of Biosimilar Monoclonal Antibodies
Great successes for monoclonal antibody (MAb)–based biologics over the past decade have provided many valuable options for patients combating some of the most serious diseases in the world, including cancer and autoimmune diseases. MAbs and antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) are among the fastest growing biologic segments in development, with hundreds of candidates currently under clinical study. Meanwhile, society is facing the challenge of increasingly higher costs in healthcare including the cost of pharmaceuticals. With an aging population in many parts of…
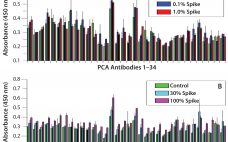
Improved HCP Quantitation By Minimizing Antibody Cross-Reactivity to Target Proteins
Host cell proteins (HCPs) are process-related impurities derived from a host cell expression system that may be present in trace amounts in a final drug substance. During biologics development, it is important to demonstrate that a bioprocess is efficient in removing HCPs and that it provides consistent control of HCP levels. Several techniques are typically used for detection, quantitation, and risk evaluation of HCPs in biologics. The most common are enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), Western blotting, sodium-dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide…