Manufacture of biopharmaceuticals using mammalian cells inherently incurs a risk of viral contamination during cell cultivation. If introduced, viruses can infect and replicate in cells used to produce a therapeutic protein or vaccine. The consequences of such contaminations can be dramatic. Not only can a company lose contaminated batches, but it also faces potentially extensive root-cause investigations, facility cleanup efforts, and introduction of preventive measures. Until contamination issues are resolved adequately, production should not be resumed, and facility downtime brings…
Author Archives: Søren Kamstrup
Virus Assay Variation Is the Main Source of Variation in Viral Clearance Studies: Retrospective Analysis of a Large Data Set
Biopharmaceuticals produced from mammalian cell cultures are susceptible to viral contamination. That risk is mitigated by applying complementary approaches. Those include extensive testing of cell banks, selecting low-risk raw materials, testing cultivations for viruses, and documenting the capacity of a purification process to inactivate and remove viral contaminants. The latter commonly is referred to as viral clearance and usually expressed as a log reduction value (LRV). Novo Nordisk has performed several viral clearance studies for different processes and process steps.…
How Much Harm Can a Single Droplet Do? Considerations for a Viral Inactivation Step
Viral clearance is a fundamental aspect of viral safety for biopharmaceutical products. Regulatory agencies around the world require biomanufacturers to segregate their operations appropriately to mitigate the risks of carryover contamination from previous process steps or product batches and of crossover contamination between product(s) made in the same facility. Guidelines are vague in defining “appropriate,” leaving biomanufacturers to interpret regulatory expectations and define their own virus reduction and segregation strategies. Given the differences among manufacturing processes and facilities housing such…
A Challenge in Viral Clearance Determination: Estimation of Fifty-Percent Tissue Culture Infective Dose (TCID50) for Low Virus Concentrations
Performing viral clearance studies is an important safety element of manufacturing all biopharmaceuticals expressed from mammalian cells (1). Typically, viral clearance is described as a log reduction value (LRV) and calculated as the log10 of the ratio of input to output virus load. Amounts of virus load are calculated from the volume and concentration of input and output fractions. Virus concentration is often calculated as 50% of tissue-culture infective dose (TCID50) using the Spearman–Kärber (SK) equation (2, 3). In this…
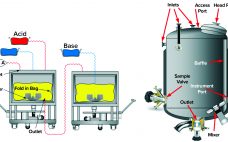
Shared Clean-in-Place Systems: To Share or Not to Share?
Risk of viral contamination is a an accepted part of developing biopharmaceutical products derived from mammalian-cell culture. Viral safety is achieved through a combination of complementary approaches such as selecting non–animal-derived raw materials, testing cell banks, testing for adventitious virus contamination during cultivation, and demonstrating viral reduction capacity of a purification process (1). The latter commonly is referred to as viral clearance by orthogonal purification. Clearly, viral clearance and appropriate viral segregation are important considerations in biopharmaceutical manufacturing process and…
Virus Segregation During Purification Processes: Calculation of Critical Potential Carryover of Viruses
Before a pharmaceutical product is introduced into humans, either in a clinical trial or as a marketed product, virus safety must be evaluated carefully. Virus safety normally is ensured using a three step complementary approach: selecting and testing cell lines and/or raw materials for the absence of viruses, testing the product at appropriate steps of production, and assessing the capacity of a production process to clear infectious viruses (1). The latter (also referred to as viral clearance) is the subject herein. Spiking studies are conducted to evaluate the capacity of a purification…