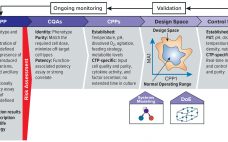
As advanced therapies, including regenerative medicines, progress toward commercialization and market approval, early warnings from key opinion leaders (1, 2) regarding the importance of better understanding quality target product profiles (QTPPs) and critical quality attributes (CQAs) of such products have resounded ever louder (see the “Terminology” box for definitions). Costly late-stage delays, redirections, and even abandonment of clinical programs can be linked to quality issues associated with inadequate understanding of process and product. Therefore, a review of the benefits of…
Author Archives: Kim Bure
Scalable Purification of Viral Vectors for Gene Therapy: An Appraisal of Downstream Processing Approaches
Gene therapy is the transfer of genetic material to a patient’s cells to achieve a therapeutic effect. Therapeutic DNA is largely delivered using viral vector systems based on adenoviruses (Ad), adenoassociated viruses (AAV), and lentiviruses (LV). With the application of such viral vectors as clinical therapeutics growing, scalable commercial processes (particularly for purification) are being investigated and optimized to best ensure that critical quality attributes (CQAs) are retained. Herein we review viral vector purification techniques and the effect of different…
Therapeutic Gene Editing: Tools to Facilitate Basic Science or Stimuli for a Paradigm Shift in Biomanufacturing?
Historically, fundamental science and process engineering were separated by distinct vernaculars and a decade or more in the translation pathway of candidate therapeutics from laboratory to bedside (1). This crude metric holds true for the origins of the modern pharmaceutical industry, namely fine chemicals that supported the high-margin small molecules that constitute the majority of the pharmacopoeia even today. But as illustrated by deeply interwoven careers, companies, and technologies — including those related to monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) — that classic…
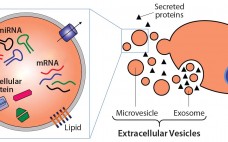
Extracellular Vesicles Commercial Potential As Byproducts of Cell Manufacturing for Research and Therapeutic Use
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are emerging as a potential alternative to some stem-cell–derived therapeutics (1, 2). Sometimes called exosomes, they are small, secreted vesicles that can possess similar therapeutic mechanisms to whole cells, possibly representing the active pharmaceutical ingredient. In the past 15 years, academic and industry interest in EVs has exponentially increased as mounting evidence demonstrates their role in physiology and pathology as well as their therapeutic potential. In light of growing efforts in using EVs for research and therapy,…
The Potential Application of Real‑Time Release Testing for the Biomanufacture of Autologous Cell‑Based Immunotherapies
Cell-based immunotherapies (iTx) are emerging as a truly transformative therapeutic modality that is both complementary and convergent with existing regenerative medicine approaches, including gene therapy, cell therapy, and tissue engineering (Figure 1). Critically, iTx offer step-change improvements in efficacy compared with current standards of care (1) for a range of clinical indications and unmet therapeutic needs — particularly oncology. The clear efficacy of iTx is in contrast with some previous regenerative medicine approaches, including early mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapies…
Cell Therapy Bioprocessing Technologies and Indicators of Technological Convergence
The cell therapy industry is undergoing a natural evolution from scientific curiosity into a commercially and clinically attractive opportunity (1). This evolution is by no means complete, and growing evidence suggests that its progression is driving significant developments in cell therapy bioprocessing — notably, convergence. Table 1: 194; () Progressively, bioprocessing technologies primarily used in production of noncell-based products are being evaluated for cell therapy bioprocessing applications (2). Consequently, this process of convergence is leading to an increasing proportion of…