Discover how Pall Corporation and Lonza collaborated to improve single-use technology training for operators using a blended approach to learning. This article presents: The importance of SUT training for operators. Why a blended approach ensures that operators get the training they need in the format that best suits their learning style. How collaboration between suppliers and biomanufacturers can shorten training program development timelines and increase the quality of training tools. How Pall and Lonza developed a digital training approach together.…
Author Archives: Hélène Pora
Integrity of Single-Use Systems: Practical Applications and Deployment
Single-use (SU) technology plays an important role in modern vaccine and biologics manufacturing. System integrity, managed by critical process controls, ensures sterility and is a prerequisite for successful leak-free processing. Nonintegral systems cause loss of product, quality, and time; increase costs through investigations; and lead to potential safety problems. The BioProcess Systems Alliance (BPSA) issued a white paper in 2017, Design, Control, and Monitoring of Single-Use Systems for Integrity Assurance (1), that describes in detail the strategies for design and…
Managing Risk in Single-Use Systems Design and Implementation: A Shared Responsibility
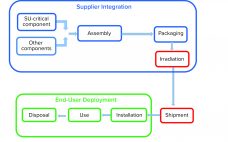
Managing risk in single-use systems design and implementation is a shared responsibility. The ultimate responsibility for drug processes and products will always remain with manufacturers. However, implementation of single-use systems can shift responsibilities to suppliers within key areas, including design and sterilization, which must be clearly controlled and validated. This Special Report discusses how suppliers and manufacturers when working together can mitigate the risk of applying single-use systems in biopharmaceutical production from design through validation to point-of-use testing and operator…
The First Quantitative Industry Assessment of Single-Use System (SUS) Reliability: Raising the Bar for BPSA’s Value to Industry
Over the past 24 months, the leadership of the Bio-Process Systems Alliance (BPSA) has initiated a pilot program to demonstrate the joint feasibility of collecting and sharing pertinent industry business data. We began with “quality-complaint data” centered on the premise that product complaints are tightly associated with product-quality defects in single-use systems (SUSs). This approach can be viewed as “risk assessment 101.” BPSA’s Representation of the Single-Use Industry BPSA is an industry organization primarily comprising drug manufacturers, single-use system suppliers,…
A Prescriptive Approach to Management of Solid Waste from Single-Use Systems
In biopharmaceutical manufacturing, the disposal of solid waste from single-use systems is becoming an increasingly important issue. The new focus is driven by several major factors including a broadening range of disposable technologies enabling, in some cases, the installation of completely disposable multistage systems; improved scalability of single-use components offering production capacities to thousands of liters; and the environmental impact of waste disposal. The latter concern includes not only regulatory and cost constraints, but also the need for…
Environmental Impact of Single-Use and Reusable Bioprocess Systems
Bioprocess manufacturing systems have incorporated single-use/disposable components for more than 50 years and have demonstrated well-defined process benefits from their use (1,2,3,4,5,6). The environmental impact of single-use technologies, however, has been a major focus of attention only in recent years. This evolving interest has been driven by many factors including concerns over environmental change, emissions, and energy supplies; rapidly increasing costs and restrictions on waste disposal; greater recognition of the role of disposables in bioprocessing; and availability of…
Managing Solid Waste from Single-Use Systems in Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing
The increasing implementation of single-use systems (SUS) in biopharmaceutical manufacturing has been driven by multiple factors including cost reduction, increased flexibility, improved process development time, and reduced capital investment. But questions are being raised over the disposal of solid waste materials from this alternative technology. Disposal concerns may not be justified on financial considerations because solid-waste disposal costs represent only a small proportion of the total manufacturing costs when using disposable systems (1, 2). Furthermore, comparative studies have…