Manufacture of synthetic peptides ranges from milligram to multikilogram amounts. When a peptide is a biopharmaceutical (API) candidate, the amount required will increase as it moves through clinical trials to marketed product. When developing purification methods, the required “product” API quantity and purity should be considered.
Bradykinin is a physiologically and pharmacologically active peptide of the kinin family used in development of antagonists and therapies for hereditary angioedema. Here we describe two different methods of purifying a crude sample of synthetic bradykinin on a preparative scale.
ExperimentalFollowing analytical method development on a 250 mm × 4.6 mm PLRP-S 10-µm 100Å column, isocratic separation conditions of 0.1% TFA in 21:79 ACN/water were chosen at a flow rate of 360 cm/hr. For a 50-mg purification of crude bradykinin, a 1-in. dynamic axial compression (DAC) column was used because it scales to full production. Therefore, a 250 mm × 1-in. Load&Lock™ (L&L) column was packed with PLRP-S 10-µm 100Å and used for the purification.
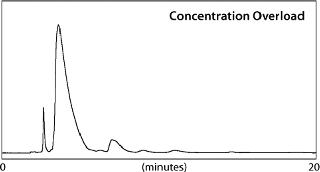
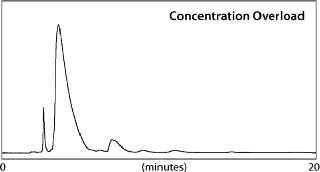
For comparison, two 50-mg loadings were made on the 1-in. L&L column. Because bradykinin is readily soluble in the eluent, a single 50-mg/mL injection could be made (concentration overload, Figure 1). For comparison, a very dilute solution (480 mL) of bradykinin containing 50 mg of the peptide in a low-strength solvent was loaded onto the column. Elution was achieved through a step gradient from the binding conditions to the elution conditions of 0.1% TFA in 21% ACN (volume overload, Figure 2).
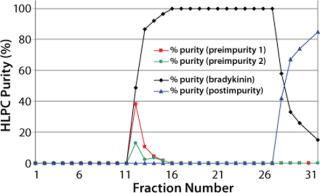
Following each purification run, fractions were collected and screened to determine the purity and yield of bradykinin in each. Figure 3 plots percent-purity for all fractions collected during the volume-overload purification. Combining fractions for purity and yield showed that with volume overload, 100% purity can be obtained at a 77% recovery. However, for concentration overload, 100% purity was achieved at a 97% recovery (purity of the crude was 84.6%).
Peptides can be purified on a preparative scale using both concentration and volume overload regimes with isocratic/step-gradient elution. Using volume overload, however, some peak broadening occurs, so resulting fractions are more dilute.