Manufacture of biopharmaceuticals using mammalian cells inherently incurs a risk of viral contamination during cell cultivation. If introduced, viruses can infect and replicate in cells used to produce a therapeutic protein or vaccine. The consequences of such contaminations can be dramatic. Not only can a company lose contaminated batches, but it also faces potentially extensive root-cause investigations, facility cleanup efforts, and introduction of preventive measures. Until contamination issues are resolved adequately, production should not be resumed, and facility downtime brings…
Thursday, September 30, 2021 Daily Archives
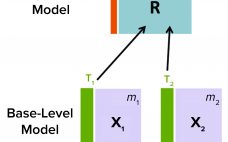
Advanced Data-Driven Modeling for Biopharmaceutical Purification Processes
Purification is an essential process in biopharmaceutical manufacturing that separates a therapeutic protein in its active form from impurities. A typical purification process consists of several chromatography unit operations, and each unit operation comprises multiple phases. During the operation of each step, continuous (time-series data per parameter for each batch) and batch data (one data point per parameter for each batch) are generated by in-line sensors installed in chromatography skids on the production floor and with at-line/off-line in-process samples, respectively.…
Simplifying the Bioprocessing 4.0 Journey
Bioprocessing 4.0, the biopharmaceutical version of Industry 4.0, is on course to become a reality in the next decade (1). This is because its “cyber-physical systems” that comprise cloud computing, connected systems, and digital process control offer many benefits. They include better process monitoring and management of a biologic’s critical quality attributes (CQAs) and the chance to control intensified processes for faster, less-expensive production of protein-based biologics and vaccines. Automation also can reduce the number of skilled operators needed while…
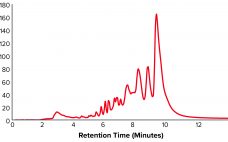
Development of a Universal Preparative Anion-Exchange Method to Purify Oligonucleotides
Oligonucleotide-based therapeutics have been studied over recent decades, and their promise as a new drug modality is now being realized. The growing interest in oligonucleotides is driven by their high potential for treating different medical conditions, the growing number of oligonucleotide drugs approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an increased focus on personalized medicines, the development of therapies for rare diseases, and the wide adoption of nucleotide-based COVID-19 vaccines. Oligonucleotides are short, linear sequences of DNA or…
eBook: CAR-T Cell Therapy — Mitigating Clinical and Bioprocess Limitations
Developers of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies are working in a state of tempered optimism. As of September 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration has approved only five such products, two coming this year. Now that those approved products have demonstrated the viability of CAR-based immunotherapies, drug developers are trying to address significant limitations that have come to light with increases in available clinical data and bioprocess knowledge. One shortcoming concerns therapeutic efficacy. Blood cancer patients who have…
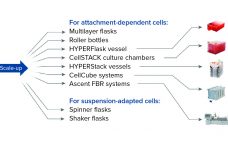
Strategizing Scale-Up and Scale-Out for Cell Therapy Production
When considering strategies for expanding the number of cells being grown to support cell therapy development, companies often focus on decisions regarding scale-up and scale-out: increasing capacity either by using larger vessels to increase production volume or by implementing more units of the same vessel, respectively. Complete workflows often involve both. Figure 1 shows an example of scaling out from one to multiple cell culture flasks of the same dimension before transitioning to a larger format. Scale-out can be straightforward…
The Effect of Benzonase Endonuclease Addition to Purification of Sabin Poliovirus Type 3
During production of vaccines and viral vectors, the size and quantity of extracellular nucleic acids must be reduced using endonuclease enzymes. Merck/MilliporeSigma’s proprietary Benzonase endonuclease is a genetically engineered nuclease derived from the Gram-negative bacteria Serratia marcescens. It attacks and degrades all forms of DNA and RNA. It is manufactured under good manufacturing practice (GMP) conditions and has a drug master file (MDF) in place with the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which can be cited in regulatory filings.…
Single-Use Technology for Formulation and Filling: A Case Study from Swissfillon AG and Pall Corporation
Swissfillon AG is a contract manufacturing organization (CMO) based in Switzerland. Fully compliant with current good manufacturing practice (CGMP) regulations, it provides state-of-the-art aseptic filling for pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, from clinical-phase materials to commercial quantities. This CMO specializes in high-value, difficult-to-fill products. Swissfillon recognized that adoption of single-use systems (SUS) on a commercial scale required major improvements in consistency and reliability compared to manual operations at pilot and clinical-trial scale. The single-use formulation and filling process, which includes an…
Neurophth gene therapy plant a nod to China’s preference for inhouse
Neurophth Biotechnology has opened a gene therapy manufacturing plant at Suzhou Biomedical industrial park (BioBay) in China, eliminating dependence on CDMOs. Neurophth claims to be China’s first gene therapy firm for ophthalmic diseases headquartered in Wuhan with subsidiaries located in Shanghai and Suzhou, China, and San Diego, California. The recently opened 8,000 square meter gene therapy-focused manufacturing facility includes two drug substance production suites, a cell banking suite, two filling lines, a technology transfer laboratory, and a quality control laboratory.…
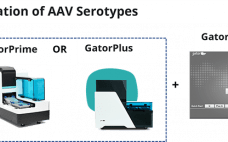
GatorTM AAVX Probes for Rapid and Label-free Quantitation of AAV Serotypes
Adeno associated virus (AAV) capsids are a leading modality for in vivo gene delivery. Complete and precise characterization of capsid particles, including capsid and vector genome concentration is necessary to safely and efficaciously dose patients. In virus development and production, it is important to determine the virus concentration at different stages of the process, optimize the clone used and obtain best production yields. Easy, rapid and cost effective quantitation methods are critical to achieve above goals. The Gator AAVX probes…