Flow-through anion-exchange (AEX) chromatography is used frequently in biopharmaceutical purification processes for reduction of net–negatively charged host-cell proteins (HCPs) and viruses as part of a validated viral clearance strategy (1, 2). AEX column chromatography is the technology most often used for electrostatic viral clearance, particularly in commercial-scale biopharmaceutical manufacturing, for which columns have a long-established history of reliable and well-understood performance (3). Still, validation of HCP and viral clearance by AEX columns in biopharmaceutical processes involves complexities that contribute significantly…
Thursday, October 29, 2020 Daily Archives
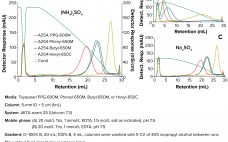
Simple and Effective Method for Purification of DMT-On Oligonucleotides Using HIC Resins
Within the biopharmaceutical industry, oligonucleotide drug pipelines have increased significantly because of the effectiveness of such drug products in treating devastating diseases. Downstream specialists need improved purification techniques for such highly valuable materials. Dimethoxytrityl (DMT) is used to synthesize oligonucleotides and temporarily mask the characteristic chemistry of the 5ʹ-hydroxy functional group. DMT can be left on an oligonucleotide following synthesis to provide stability to a molecule during subsequent processing. Herein, we describe a novel, effective, and high-recovery method for purifying…
Advantage of Antibody-Based Selectivity in the Purification of Next-Generation Biologics
The webcast features: Laurens Sierkstra, Senior Director, Business Leader Purification, Thermo Fisher Scientific Advances in biotherapeutics are generating an increasing range of complex molecules that present unique and often complex purification challenges. Affinity chromatography can serve as a platform solution for the purification of these challenging molecule modalities. An effective affinity resin can help to simplify biomolecule purification, reduce the number of purification steps, and reduce the overall cost of goods in biotherapeutic manufacturing. By taking advantage of antibody-based selectivity, camelid…
eBook: Mixed-Mode Chromatography for Purification of Biopharmaceuticals
Mixed-mode chromatography offers several advantages in downstream processing of biotherapeutics. Mixed-mode chromatography resins use ligands that are capable of at least two modes of interaction with solutes such as hydrophobic, ion exchange, and metal affinity. The interactions between stationary and mobile phases that result from those combinations enhance chromatographic selectivity, facilitating separation efficiencies that are not possible using other chromatography media. As this eBook illustrates, the multimodal approach can save developers time and money by enabling robust purification of biopharmaceuticals…
Endotoxin Questions and Answers
Endotoxin — also known as lipopolysaccharide (LPS) — is a large molecule made up of a lipid and a polysaccharide portion found in the outer membrane of each Gram-negative bacterial cell. Examination of endotoxins is necessary for microbial and animal cell-culture operations that produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and vaccines. If a cell culture is contaminated with endotoxins, it could affect cell growth and function (thus potentially affecting product quality). Biopharmaceutical companies need to understand the endotoxin levels within their…
Catalent bones up on CGTs with Skeletal Cell Therapy buy
Catalent has agreed to buy Bone Therapeutics’ manufacturing unit – Skeletal Cell Therapy Support SA – and make trial supplies of the candidate bone disease cell therapy, ALLOB. The contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) will pay €12 million ($14 million) for Skeletal Cell Therapy Support SA (SCTS), which operates a 3,800 square meter manufacturing facility, development lab and warehouse at the Brussels South Charleroi Biopark, in Belgium. The site produces Bone’s allogenic cell therapy candidate ALLOB, which has been…
Amyris and IDRI agree RNA vaccine platform deal
The two partners will collaborate to develop an RNA vaccine against COVID-19, as well as vaccines for three additional indications. Amyris will license the Infectious Disease Research Institute (IDRI)’s novel ribonucleic acid (RNA) vaccine platform. Alongside the vaccine platform, Amyris will gain access to IDRI’s nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) platform, which will be combined with its own semi-synthetic squalene technology to develop RNA vaccines against various infectious disease targets, potentially including influenza and certain cancer treatments. The first project will…