Temperature control during sourcing, manufacturing, and delivery of cell therapies is crucial, as fluctuations can affect viability and function of the cells, and potentially, the overall efficacy and safety of the therapeutic product. In many cell therapy workflows, source cells arrive cryopreserved at LN2 temperatures (-150 to -196 °C) and post-manufacturing, cells are again cryopreserved and stored in vapor- or liquid phase LN2 prior to their use in the clinic. In either case, containers filled with dry ice (-50 to…
Tuesday, November 17, 2015 Daily Archives
Efficient Optimization of CHO Cell Culture Medium and Feed for Increased Antibody Production
Traditional medium optimization strategies are labor intensive, costly, and time consuming. In this project, high-throughput screening technology was adopted along with statistical design to reduce costs and decrease time for optimizing culture conditions for maximized antibody production from a custom Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell clone. The presented work includes two phases: phase 1 for basal medium optimization and phase 2 for feed optimization. Phase 1 and phase 2 each have two rounds. A DoE screening methodology was used to…
An Intensified Perfusion One-Step Process with High-Density Cell Banks
Seed culture expansion is commonly performed in several consecutive batch cultures. Starting from a cryopreserved cell stock, the initial culture expansion is typically performed in shake flasks, while the final steps are performed, at greater scales, in bioreactor vessels. Such a procedure is time-consuming and labor intensive with multiple steps that introduce risk for mishandling and contamination. This work describes how the use of perfusion in the seed culture expansion process, in combination with the use of high-density cell banks,…
CIMac™ Analytical Columns for In-Process Control of Adenoviruses
Determining the concentration of viruses is a crucial step in any production process. The most commonly used methods for virus quantification are either based on the infectivity of the virus (plaque assay, TCID50) determination of their genomic material (qPCR), or protein content (SRID, ELISA) and are very cumbersome and time consuming. HPLC analytical methods represent a fast alternative to these assays since they provide information on the virus content and purity in a matter of minutes. In this work the…
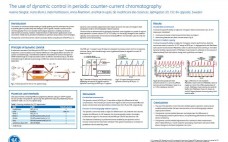
The Use of Dynamic Control in Periodic Counter-Current Chromatography
The interest in continuous bioprocessing to introduce productivity gains and cost savings is rapidly growing. Periodic counter-current chromatography (PCC) is one suitable technological approach, enabling continuous downstream processing. However, implementation in downstream applications is still uncommon mainly due to perceived complexity in operation and process control strategies. This work demonstrates the dynamic control function of ÄKTA™ pcc 75 chromatography system when applied to a protein A capture step operated in a three-column PCC (3C PCC) setup. Dynamic control enables sample…
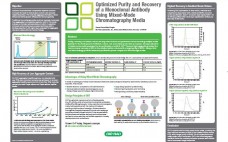
Optimized Purity and Recovery of a Monoclonal Antibody Using Mixed-Mode Chromatography Media
Purity, recovery, and elution volume are important factors and parameters when screening multiple media (resins) for the development of efficient, robust, and economical production processes. Among a selection of mixed-mode media evaluated for the purification of MAb S, CHT™ Ceramic Hydroxyapatite provided the best monomer recovery at 83% in the smallest elution volume with a target purity of 99.5%. Using a bind and elute strategy provided enhanced purification power compared to flow-through modes.
From the Editor
Along with products and processing operations moving upstream and downstream, they also move toward the mainstream. The ramifications can become so interconnected that it is hard to discern cause and effect. One example from the past 10 years is single-use materials moving into larger scale processing. That in turn has driven much exploration into flexible operations and variations of continuous processing — neither particularly new concepts, but both now taken into more (potentially) economical directions. Related discussions are bringing heightened…
Spotlight
Niche Disease: Epidermolysis Bullosa by Cheryl Scott Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of rare diseases that cause skin to blister easily. In severe cases, blisters may even be internal (e.g., in mucosal tissues or organs). More than 300 mutations have been identified in this condition. Most of the many types of EB are inherited, and the condition usually manifests in infants and young children; some patients don’t develop symptoms until adolescence or early adulthood. Exceptionally mild cases may remain…
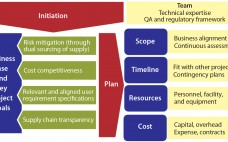
A Risk-Based Approach to Supplier and Raw Materials Management
Ensuring a continuous supply of safe medicines is a key objective for the pharmaceutical industry and health authorities alike. A critical component to that end is maintaining a reliable supply of qualified raw materials (RMs) used in drug production. However, changes in suppliers, their processes, their providers, and consequently the materials they supply can occur (for a number of reasons) at any time during the life cycle of drug production. A product-supply organization therefore must be prepared to address such…
Outsourcing Stability Testing: Discussions with Contract Laboratories
Stability testing is required for all biopharmaceutical drug products to detect all changes in identity, purity, and potency as a result of a number of environmental and processing factors. Whether testing is conducted in-house or through contact laboratories, it involves the development and performance of comprehensive and specific stability protocols for all stages of a product’s life cycle (1). Testing product stability in-house requires signficant time and resources, and carries challenges associated with commercialization market, time, and capacity. Market: The…